Analyze Identity Manager's Data with Power BI
This topic explains how to prepare Identity Manager's data and use it in Power BI, with the final goal to generate user-friendly reports.
Overview
Power BI is used with Identity Manager to generate user-friendly reports in an interactive way, based on Identity Manager's database.
The SaaS edition Power BI Service contains an integrated Identity Manager connector, so we simply need to make Identity Manager's data usable by configuring a particular data model.
As this new model is to be organized into XML elements called universes, we will call the new data model the universe model.
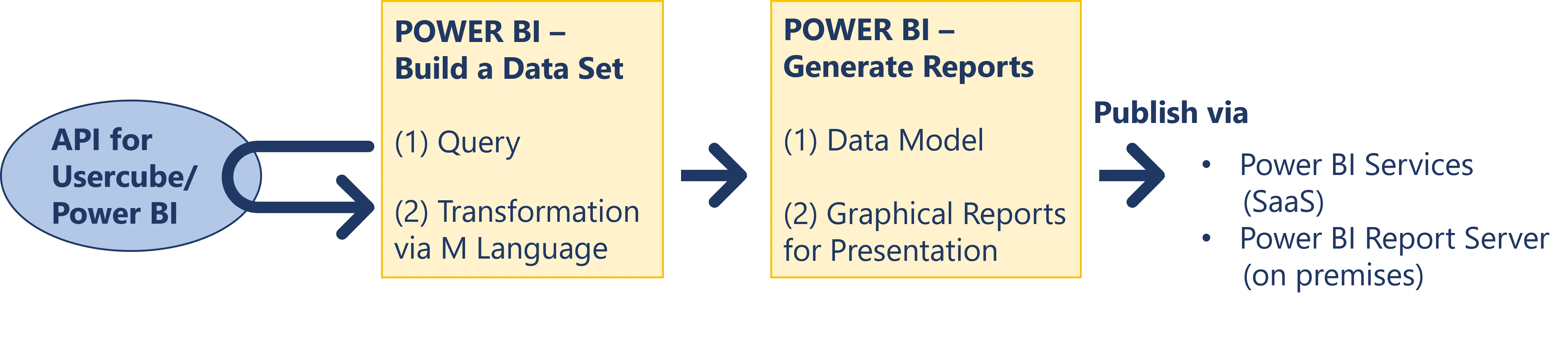
Based on this model, Power BI will be able to:
- query the database
- generate a model containing the data that we want to include in reports
- transform data if needed
- generate customized graphic reports
- publish the reports with Power BI Service (SaaS) or Power BI Report Server (on premises)
Prerequisites
Identity Manager's licenses for Power BI as well as Identity Manager Data are required to operate.
Integrators need to know:
- Identity Manager's data model, i.e. the entity names, the associations between the entities to display, etc. from both Identity Manager-hard-coded and customized parts
- what data needs to be displayed in the end
NOTE: Power BI is able to analyze all Identity Manager's data, hard-coded and customized, but only current data, i.e. nothing from the history.
Analyze Identity Manager's Data with Power BI
Build the universe model by proceeding as follows:
Step 1 – Define the appropriate universes using scaffoldings. See the Queries topic for additional information.
Remember, in order to understand business intelligence, with its universes, entity instances and
association instances. See the
Universe topic
for additional information.
Also note that XML objects that automatically generate XML snippets that would be complex and/or
tedious to write manually. See
theScaffoldings topic
for additional information.
Netwrix recommends creating no more than one universe to generate one report, to prevent issues about name uniqueness.
Step 2 – Connect Power BI to Identity Manager to visualize the output model. See the Connect Power BI to Identity Manager topic for additional information.
The Power BI applications Desktop, Service and Report Server all offer the Identity Manager plugin to access Identity Manager's database.
Step 3 – Remember to clear the cache in Power BI when modifying universes, to ensure that all changes are considered.
Step 4 – Customize the queries in Power BI, if needed, with the M language.
You can see in Power BI queries that Identity Manager must be specified as a source via the
expression Source = Usercube.Universes("<serverURL>").
Integrators may need to customize the model to make it more understandable and easily usable by end-users.
For example, the following M query removes the column Company Id from the table Directory_User_Records, considering that we do not need it for future reports.
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
let
Source = Usercube.Universes("<http://localhost:5000"),
Directory_User_SourcesAndTargets = Source{[Name="Directory_User_SourcesAndTargets"]}[Items],
Directory_User_Records = Directory_User_SourcesAndTargets{[Name="Directory_User_Records"]}[Data],
Directory_User_Records_WithoutCompany = Table.RemoveColumns(Directory_User_Records,{"Company Id>"})
in
Directory_User_Records_WithoutCompany
Another common use for manual queries is the denormalization of the model, when it simplifies the future queries and reports for end-users.
Step 5 – Generate reports and publish them for end-users by following the steps listed in the Power BI documentation.
This is how you analyze Identity Manager data through Power BI.
Maintain the Model
In order to maintain the model you must remember the ones listed below.
Refresh data
You must define, in Power BI Service or Report Server, a frequency for data refresh so that reports display up-to-date data. See the Power BI documentation for additional information.
Data is often refreshed once a day. Define the refresh frequency according to your needs.
Foresee the Impact of Model Modifications
A change inside an existing entity, for example adding a scalar field, does not require any particular actions on the universe model.
A change in an association requires making the corresponding change in the universe model, as association instances (in the universe model) are based on entity associations in Identity Manager's data model. See the Entity Association topic for additional information.