SAP ERP 6.0 and SAP S4/HANA
This connector exports and fulfills users and roles from/to an SAP ERP 6.0 or SAP HANA instance.
This page is about ERP/SAP ERP 6.0.
Overview
The SAP Enterprise Resource Planning (SAP ERP) software incorporates the core business processes of an organization, such as finance, production, supply chain services, procurements, human resources (HR), etc. The SAP ERP connector exports and fulfills data from/to an SAP ERP 6.0 system.
Prerequisites
Implementing this connector requires:
- Reading first the appsettings documentation; See the appsettings.agent topic for additional information.
- An ASE or HANA database with a service account, as a database administrator
- A service account, as a SAP user with at least the roles for user management
- The prerequisites for reading should be set up
- The prerequisites for writing should be set up
ASE or HANA database with a service account, as a database administrator
To connect to the SAP database using SSH, use the following commands:
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
su sybaba
isql -S <database (ABA is the default value)> -U<administrator's login> -P<administrator's password> -X
For example:
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
isql -S ABA -Usapsso -PV1H#M$4JIgU$qd -X
Service account, as a SAP user with at least the roles for user management
Create a login for Identity Manager's service account with at least reading access on user management tables by using a command from the table below:
| Table | Usage |
|---|---|
| USR02 | Users table |
| AGR_USERS | Links between Users and Roles |
| AGR_TEXTS | Roles labels according to the language |
| USER_ADDR | |
| AGR_1016 AGR_PROF | Links between Profiles and Roles |
| USR10 | Profiles tables |
| USR11 | Profiles labels |
| AGR_DEFINE | Roles table |
| AGR_AGRS | Composition links |
| USGRP | Groups table |
| USGRPT | Groups labels |
| UST04 | Links between Users and Profiles |
| UST10C | Links between Profiles and Sub-profiles |
| AGR_TCODES | Links between Roles and Transactions |
| T002 | Languages codes |
For example:
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
execute sp_addlogin <login>, <password>, <database (ABA is the default value)>go use ABA go
execute sp_adduser <login>go grant select on ABA.SAPSR3.USR02 to usercube grant select on
ABA.SAPSR3.AGR_USERS to usercube grant select on ABA.SAPSR3.USER_ADDR to usercube grant select on
ABA.SAPSR3.AGR_1016 to usercube grant select on ABA.SAPSR3.USR10 to usercube grant select on
ABA.SAPSR3.USR11 to usercube grant select on ABA.SAPSR3.AGR_AGRS to usercube grant select on
ABA.SAPSR3.USGRP to usercube grant select on ABA.SAPSR3.UST04 to usercube grant select on
ABA.SAPSR3.AGR_TCODES to user grant select on ABA.SAPSR3.T002 to usercube Go
Set up the prerequisites for reading
To set up the prerequisites for reading follow the steps below.
Step 1 – Copy the DLL Sap.Data.Hana.Core.v2.1.dll into the Runtime of Identity Manager.
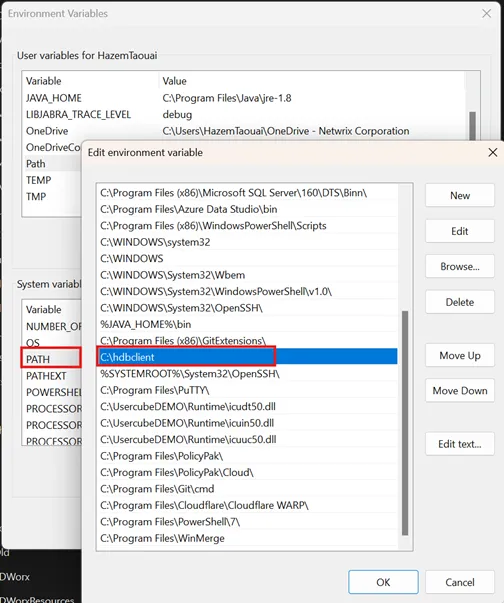
Step 2 – Unzip the “hdbclient.zip” archive to C: drive and add the path to the Path environment variables.
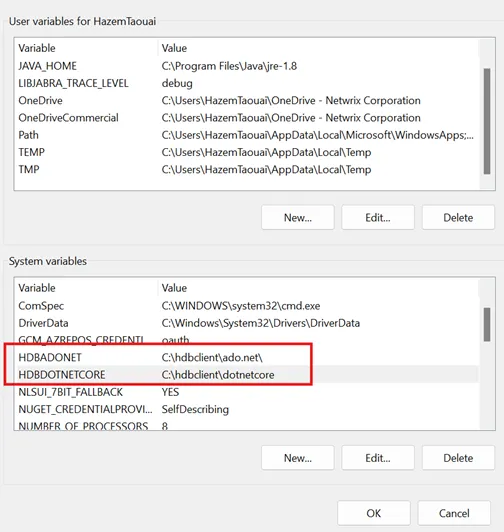
Step 3 – Create environment variables: HDBADOTNET=C:\hdbclient\ado.net and
HDBADOTNETCORE=C:\hdbclient\dotnetcore.
Set up the prerequisites for writing
NOTE: Make sure the Read prerequisites are configured first.
Step 1 – Copy the provided DLL sapnwrfc.dl into the Runtime of Identity Manager.
Step 2 – Unzip the dotnet86.zip archive to C:\dotnetx86.
Step 3 – Copy the DLLs icudt50.dll, icuin50.dll and icuuc50.dll into the Runtime of Identity
Manager.
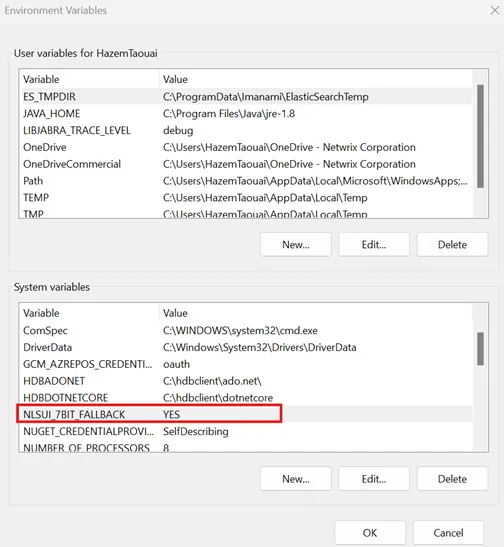
Step 4 – Disable DLLs search by adding the environment variable NLSUI_7BIT_FALLBACK=YES.
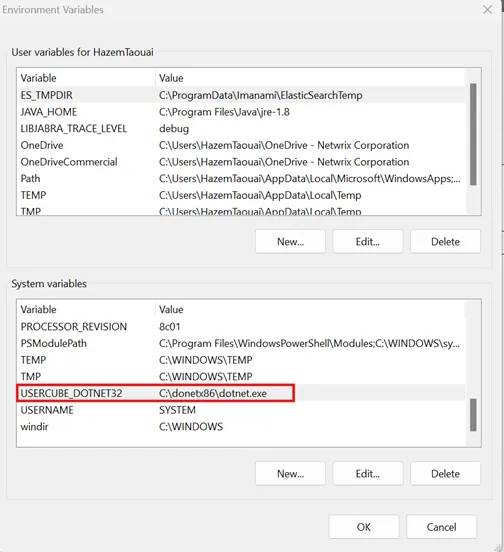
Step 5 – Add new environment variable USERCUBE_DOTNET32 containing the path to dotnetx86
(e.g.: C: \donetx86\dotnet.exe).
Export
This connector extracts users, roles, profiles, profile memberships, role memberships and groups from an SAP ERP instance, and writes the output to CSV files.
Configuration
This process is configured through a connection in the UI and/or the XML configuration, and in the appsettings.agent.json > Connections section. See the Connection topic for additional information.
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
appsettings.agent.json
{
...
"Connections": {
...
"<ConnectionIdentifier>": {
...
}
}
}
Remember, the identifier of the connection and thus the name of the subsection must:
- Be unique
- Not begin with a digit.
- Not contain
<,>,:,/,\,|,?,*, and_.
For example:
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
appsettings.agent.json
{
...
"Connections": {
...
"SAPExportFulfillment": {
"Server": "serverUrl",
"AseLogin": "login",
"AsePassword": "password",
"Instance": "sapInstance",
"Port": "4242",
"Client": "123",
"Language": "fr"
}
}
}
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| IsHana default value: false | Boolean | True to connect to an S/4 HANA instance instead of an ERP 6.0. |
| AseLogin required | String | Login to connect to SAP ASE. |
| AsePassword required | String | Password to connect to SAP ASE. |
| Client required | String | Client id of SAP. |
| Instance required | String | Instance of the SAP database. |
| Language required | String | SAP language. |
| Port required | String | Port of the SAP ERP server. |
| Server required | String | URL of the SAP ERP server. |
Output details
This connector is meant to generate to the ExportOutput folder the following files:
- SAPExportFulfillment_users.csv;
- SAPExportFulfillment_roles.csv;
- SAPExportFulfillment_usersroles.csv;
- SAPExportFulfillment_profiles.csv;
- SAPExportFulfillment_profilesprofiles.csv;
- SAPExportFulfillment_rolesprofiles.csv;
- SAPExportFulfillment_usersprofiles.csv;
- SAPExportFulfillment_rolesroles.csv;
- SAPExportFulfillment_groups.csv;
- SAPExportFulfillment_rolestransactions.csv.
See the Application Settings topic for additional information.
Fulfill
This connector can provision users, role memberships and group memberships to SAP ERP.
Configuration
Same as for export, fulfill is configured through connections. See the SAP ERP 6.0 and SAP S4/HANA topic for additional information.
For example:
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
appsettings.agent.json
{
...
"Connections": {
...
"SAPExportFulfillment": {
"Server": "<serverUrl>",
"BapiLogin": "<login>",
"BapiPassword": "<password>"
}
}
}
Setting attributes
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| IsHana default value: false | Boolean | True to connect to an S/4 HANA instance instead of an ERP 6.0. |
| Server required | String | URL of the SAP ERP server. |
| BapiLogin required | String | Login to connect to the specified server. |
| BapiPassword required | String | Password to connect to the specified server. |
Password reset
See the appsettings.agent topic for additional information on how to configure password reset settings.
When setting a password for an SAP ERP user, the password attribute is defined by the password specified in the corresponding RessourceTypeMapping. See the Sap Resource Type Mapping topic for additional information.
Credential protection
Data protection can be ensured through:
- RSA encryption, configured in the
appsettings.encrypted.agent.jsonfile - An Azure Key Vault safe
| Attribute | Naming Convention for the Key in Azure Key Vault |
|---|---|
| Server | Connections--<identifier>--Server |
| AseLogin | Connections--<identifier>--AseLogin |
| AsePassword | Connections--<identifier>--AsePassword |
| Instance | Connections--<identifier>--Instance |
| Port | Connections--<identifier>--Port |
| Client | Connections--<identifier>--Client |
| Language | Connections--<identifier>--Language |
| BapiLogin | Connections--<identifier>--BapiLogin |
| BapiPassword | Connections--<identifier>--BapiPassword |
| SystemNumber | Connections--<identifier>--SystemNumber |
- A CyberArk Vault able to store Active Directory's Login, Password, and Server.
See the RSA Encryption , Azure Key Vault, and CyberArk's AAM Credential Providers topics for additional information.
Protected attributes are stored inside a safe in CyberArk, into an account whose identifier can be
retrieved by Identity Manager from appsettings.cyberark.agent.json.
For example:
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
appsettings.cyberark.agent.json
{
...
"Connections": {
...
"SAPExportFulfillment": {
"Login": "SAPExportFulfillment_CyberArkKey",
"Password": "SAPExportFulfillment_CyberArkKey",
"Server": "SAPExportFulfillment_CyberArkKey"
}
}
}