Usercube-Anonymize
This tool anonymizes data based on a certain knowledge of the database and the data structure.
Overview
Anonymizing data helps unlock situations where it is necessary to send data to varied teams while guaranteeing the privacy of the data owners.
For example, it can be necessary to transmit data to an integration team that needs to set up tests or a development environment to work on the applicative configuration. For example, users sometimes need to send data to Usercube's support team to reproduce a bug and get it corrected.
Technical Principles
Anonymizing can be performed on data:
-
from a CSV file, with the output written to a new CSV file;
-
directly inside a SQL database, overwriting existing data with the anonymized data.
In this case, the plain data is lost. So make sure to work on a copy of the original database.
Several types of data can be anonymized, according to distinct substitution methods that are deterministic and non-reversible:
-
strings have each alphabetical character substituted for another alphabetical character;
For example,
John DoebecomesXert Okl.Diacritical characters are replaced by a non-diacritical equivalent.
-
numbers have each digit substituted for another digit;
For example,
54689becomes32016. -
emails have the username anonymized, while leaving the domain name as is;
For example,
johndoe@contoso.combecomesxertoekl@contoso.com. -
Active Directory's RDN properties (Relative Distinguished Names), in the attribute=value format, are anonymized via the string method on the value, leaving the attribute as is.
For example,
CN=John DoebecomesCN=Xert Okl.
Examples
Anonymizing a CSV file
The following example anonymizes the first_name, last_name, email and phone column of the
following CSV file:
id,first_name,last_name,email,gender,phone
1,Darrin,Crumpe,dcrumpe0@nifty.com,Male,2666420820
2,Lyon,Boddam,lboddam1@eepurl.com,Male,5927617041
3,Roxana,Prose,rprose2@statcounter.com,Female,5134883113
4,Vladimir,Grisedale,vgrisedale3@blogtalkradio.com,Male,1338476916
5,Jaquith,Pendrich,jpendrich4@merriam-webster.com,Female,1894520819
6,Art,Sweatland,asweatland5@boston.com,Male,5066492715
7,Lynelle,Klammt,lklammt6@stumbleupon.com,Female,5653774981
8,Chicky,Blatherwick,cblatherwick7@walmart.com,Male,4095068397
9,Delilah,Kauscher,dkauscher8@de.vu,Female,9324858513
10,Estelle,Melmeth,emelmeth9@dot.gov,Female,2176715812
The following command outputs the anonymized data in STDOUT.
./identitymanager-Anonymize.exe -n C:/Projects/identitymanager/Documentation/exampleSources/Anonymizer/users.csv -s "," --columns first_name,last_name,mail:email,number:phone
The output is:
id,first_name,last_name,email,gender,phone
1,Afccrp,Icqesl,aicqesl0@nifty.com,Male,6111065265
2,Mdhp,Qhaafe,mqhaafe1@eepurl.com,Male,4665125502
3,Chlfpf,Schnl,cschnl2@statcounter.com,Female,4230223223
4,Imfarerc,Ocrnlafml,iocrnlafml3@blogtalkradio.com,Male,2332051621
5,Jfkqrfg,Slpacrig,jslpacrig4@merriam-webster.com,Female,2260465226
6,Fcf,Nalffmfpa,fnalffmfpa5@boston.com,Male,4511066524
7,Mdplmml,Bmfeef,mbmfeef6@stumbleupon.com,Female,4143550622
8,Igribd,Qmffglcarib,iqmffglcarib7@walmart.com,Male,0564512365
9,Almrmfg,Bfqniglc,abfqniglc8@de.vu,Female,6360242423
10,Lnflmml,Elmelfg,lelmelfg9@dot.gov,Female,6251524226
Anonymizing a SQL Server table
The following example overwrites the UR_Resources table of Usercube's database with anonymized
data for the C3, C8, CA, CB, CC and CD columns for all resources whose Type is 17.
.\Usercube-Anonymize.exe --connection-string "data source=.;Database=Usercube;Integrated Security=SSPI;Min Pool Size=10;encrypt=false" --table UR_Resources --columns "number:C3,C8,number:CA,mail:CB,number:CC,number:CD" --select-query "select * FROM UR_Resources WHERE Type = 17"
Arguments
| Argument Name | Details |
|---|---|
| --columns required | Type Strings Description Columns from the CSV or SQL database that need anonymizing. Usage The value is a string sequence in the form type:columname, separated by a coma ,, where type is used to choose the anonymize algorithm from among the following formats: string (default value); mail; number; rdn, and where columnname is the actual name, not case-sensitive, of the column to anonymize. See more details on formats in the previous section. |
| --connection-string optional | Type String Description Connection string to the SQL Server database to be anonymized. Note: required when anonymizing a database. |
| --csv-separator (-s) default value: ; | Type String Description Separator of the input CSV file, provided between simple quotes. Note: used only when anonymizing a CSV file. |
| --entry-file (-n) optional | Type String Description Path to the input CSV file to anonymize. Note: required when anonymizing a CSV file. |
| --no-transaction optional | Type No Value Description Disables the SQL transaction for the request made by the anonymizing tool to the target SQL Server database. Warning: NETWRIX recommends using this option only when using transactions leads to a failure (exceeded RAM usage, exceeded CPU usage), because it could corrupt the data from the database. Make sure to prepare a backup of the database before using this option. Note: used only when anonymizing a database. |
| --output (-o) default value: STDOUT | Type String Description Path of the output CSV file to write the anonymized data. Note: used only when anonymizing a CSV file. |
| --select-query (-q) optional | Type String Description SQL query to filter the rows to be anonymized. Note: used only when anonymizing a database, and useful only when the query includes a "WHERE" condition, otherwise the --table and --columns arguments are enough. Usage The table targeted by the query must be on the table specified in --table. Examples SELECT Id, name, firstName FROM Resources WHERE resourceType = 'Person' is a query with a simple condition. SELECT * FROM Persons WHERE resourceType = 'Person' AND specialFlag = 'TopSecret' selects all columns, and adds a specific condition. |
| --table (-t) optional | Type String Description Name of the table from the SQL Server database to be anonymized. Note: required when anonymizing a database. |
Usercube-Compute-CorrelationKeys
This tool is used to compute the values of all correlation keys.
Examples
The following example computes the correlation keys of the database defined by the connection string, for all entity types.
./identitymanager-Compute-CorrelationKeys.exe --database-connection-string "data source=.;Database=Usercube;Integrated Security=SSPI;Min Pool Size=10;encrypt=false" -a
Arguments
| Argument Name | Details |
|---|---|
| --batch-size (-q) default value: 5000 | Type Int32 Description Batch size for queries. See more details. |
| --- | --- |
| --database-connection-string required | Type String Description Connection string of the database. |
| --- | --- |
| --all-entityType (-a) optional | Type No Value Description Applies the tool to all entity types. |
| --batch-size (-q) default value: 5000 | Type Int32 Description Batch size for queries. See more details. |
| --dirty optional | Type No Value Description Applies the tool incrementally by applying it only to resources marked as dirty, i.e. recently modified. |
| --entitytype-list optional | Type String List Description List of entity types that the tool is to be applied to. Note: required when --all-entityType is not specified. |
| --resource-identity-property optional | Type String Description Property used to override the resource identity property set in SelectUserByIdentityQueryHandler. |
| --- | --- |
| --log-level optional | Type LogLevel Description Level of log information among: Verbose; Debug; Information; Warning; Error; Fatal. |
Usercube-EasyVistaTicket-UpdateFulfillmentState
The use of this executable supposes a previous use of the Usercube-Fulfill-ToEasyVistaTicket
executable.
Usercube-Fulfill-ToEasyVistaTicket creates tickets in an EasyVista instance:
Usercube-EasyVistaTicket-UpdateFulfillmentState sets the fulfillment state of the corresponding
assigned resource types in Usercube for tickets that are closed (Executed) or canceled (Error).
Examples
Connector specified
When specifying --connector, there is no need to specify --resource-types:
--connector "3" --api-url "http://localhost:5000/" --api-client-id "Job" --api-secret "secret" --url "https://easyvista.contoso.com" --account "12345" --login "Contoso" --password "cOntoSo6789"
But the identifier can be also given instead of the id:
--connector "EasyVista" --api-url "http://localhost:5000/" --api-client-id "Job" --api-secret "secret" --url "https://easyvista.contoso.com" --account "12345" --login "Contoso" --password "cOntoSo6789"
In this example, for all resource types that have a target entity type of the connector EasyVista,
we set the fulfillment state of the corresponding assigned resource types.
Resource types specified
When specifying --resource-types, there is no need to specify --connector:
--resource-types "40" "41" --api-url "http://localhost:5000/" --api-client-id "Job" --api-secret "secret" --url "https://easyvista.contoso.com" --account "12345" --login "Contoso" --password "cOntoSo6789"
But the identifiers can be also given instead of the id:
--resource-types "EasyVista_NominativeUser" "EasyVista_Administrator" --api-url "http://localhost:5000/" --api-client-id "Job" --api-secret "secret"--url "https://easyvista.contoso.com" --account "12345" --login "Contoso" --password "cOntoSo6789"
In this example, for the resource types EasyVista_NominativeUser and EasyVista_Administrator, we
set the fulfillment state of the corresponding assigned resource types.
Arguments
| Argument Name | Details |
|---|---|
| --- | --- |
| --api-client-id required | Type String Description Login used to authenticate to the server. Every request from agent to server needs to be authenticated with an OpenID Connect ClientId/Secret pair, linked to a profile with the relevant permissions. |
| --api-secret required | Type String Description Password used to authenticate to the server. Every request from agent to server needs to be authenticated with an OpenID Connect ClientId/Secret pair, linked to a profile with the relevant permissions. |
| --api-url required | Type String Description URL of Usercube server. |
| --- | --- |
| --url required | Type String Description EasyVista API Endpoint URL. |
| --account required | Type String Description EasyVista account. |
| --login required | Type String Description Path of the file used for complete synchronization. |
| --password required | Type String Description EasyVista server password. |
| --- | --- |
| --connector required if --resource-typesis not given | Type String Description Id or Identifier of the resource types' connector we want to update the fulfillment state. |
| --resource-types required if --connectoris not given | Type String List Description Id or Identifier of the resource types we want to update the fulfillment state. |
| --certificate-identifier optional | Type String Description Unique key used to retrieve the certificate in Azure Key Vault. |
| --vault optional | Type String Description Vault uri. |
| --vault-connection-string optional | Type String Description Connection string to connect to Azure Key Vault. |
| --batch-size default value: 1000 | Type Int32 Description Number of provisioning orders to wait between each progress report. |
| --task-instance-id optional | Type String Description Id of the task instance which have launch the exe in a job context (for log purposes). |
Usercube-Fulfill-EasyVista
This executable creates, updates and archives employees in an EasyVista instance.
Examples
Connector specified
When specifying --connector, there is no need to specify --resource-types:
--connector "3" --api-url "http://localhost:5000/" --api-client-id "Job" --api-secret "secret" --url "https://easyvista.contoso.com" --account "12345" --login "Contoso" --password "cOntoSo6789"
But the identifier can be also given instead of the id:
--connector "EasyVista" --api-url "http://localhost:5000/" --api-client-id "Job" --api-secret "secret" --url "https://easyvista.contoso.com" --account "12345" --login "Contoso" --password "cOntoSo6789"
Resource types specified
When specifying --resource-types, there is no need to specify --connector:
--resource-types "40" "41" --api-url "http://localhost:5000/" --api-client-id "Job" --api-secret "secret" --url "https://easyvista.contoso.com" --account "12345" --login "Contoso" --password "cOntoSo6789"
But the identifiers can be also given instead of the id:
--resource-types "EasyVista_NominativeUser" "EasyVista_Administrator" --api-url "http://localhost:5000/" --api-client-id "Job" --api-secret "secret"--url "https://easyvista.contoso.com" --account "12345" --login "Contoso" --password "cOntoSo6789"
Arguments
| Argument Name | Details |
|---|---|
| --- | --- |
| --api-client-id required | Type String Description Login used to authenticate to the server. Every request from agent to server needs to be authenticated with an OpenID Connect ClientId/Secret pair, linked to a profile with the relevant permissions. |
| --api-secret required | Type String Description Password used to authenticate to the server. Every request from agent to server needs to be authenticated with an OpenID Connect ClientId/Secret pair, linked to a profile with the relevant permissions. |
| --api-url required | Type String Description URL of Usercube server. |
| --- | --- |
| --url required | Type String Description EasyVista API Endpoint URL. |
| --account required | Type String Description EasyVista account. |
| --login required | Type String Description Path of the file used for complete synchronization. |
| --password required | Type String Description EasyVista server password. |
| --- | --- |
| --connector required if --resource-typesis not given | Type String Description Id or Identifier of the resource types' connector we want to update the fulfillment state. |
| --resource-types required if --connectoris not given | Type String List Description Id or Identifier of the resource types we want to update the fulfillment state. |
| --certificate-identifier optional | Type String Description Unique key used to retrieve the certificate in Azure Key Vault. |
| --vault optional | Type String Description Vault uri. |
| --vault-connection-string optional | Type String Description Connection string to connect to Azure Key Vault. |
| --batch-size default value: 1000 | Type Int32 Description Number of provisioning orders to wait between each progress report. |
| --task-instance-id optional | Type String Description Id of the task instance which have launch the exe in a job context (for log purposes). |
Usercube-Fulfill-Scim
This executable creates, updates and deleles entries in an application using the SCIM API.
Examples
Connector specified
When specifying --connector, there is no need to specify --resource-types:
--connector "3" --api-url "http://localhost:5000/" --api-client-id "Job" --api-secret "secret" --url "https://scim.contoso.com" --account "12345" --login "Contoso" --password "cOntoSo6789"
But the identifier can be also given instead of the id:
--connector "SCIM" --api-url "http://localhost:5000/" --api-client-id "Job" --api-secret "secret" --url "https://scim.contoso.com" --account "12345" --login "Contoso" --password "cOntoSo6789"
Resource types specified
When specifying --resource-types, there is no need to specify --connector:
--resource-types "40" "41" --api-url "http://localhost:5000/" --api-client-id "Job" --api-secret "secret" --url "https://scim.contoso.com" --account "12345" --login "Contoso" --password "cOntoSo6789"
But the identifiers can be also given instead of the id:
--resource-types "SCIM_NominativeUser" "SCIM_Administrator" --api-url "http://localhost:5000/" --api-client-id "Job" --api-secret "secret"--url "https://scim.contoso.com" --account "12345" --login "Contoso" --password "cOntoSo6789"
Arguments
| Argument Name | Details |
|---|---|
| --- | --- |
| --api-client-id required | Type String Description Login used to authenticate to the server. Every request from agent to server needs to be authenticated with an OpenID Connect ClientId/Secret pair, linked to a profile with the relevant permissions. |
| --api-secret required | Type String Description Password used to authenticate to the server. Every request from agent to server needs to be authenticated with an OpenID Connect ClientId/Secret pair, linked to a profile with the relevant permissions. |
| --api-url required | Type String Description URL of Usercube server. |
| --- | --- |
| --server required | Type String Description URL of the SCIM endpoints of your application, not including the v2. |
| --login optional | Type String Description Specifies the login of the account you may need. |
| --password optional | Type String Description Specifies the password of the account you may need. |
| --application-id optional | Type String Description Specifies the application connection login or the login of your application's id provider. |
| --application-key optional | Type String Description Specifies the application connection password or the password of your application's id provider. |
| --oauth-url optional | Type String Description The server's url when using OAuth2 authentication. |
| --oauth-token optional | Type String Description Specifies the OAuth token to connect to the application. |
| --scim-syntax optional | Type Enum Description Specifies the syntax used for requests body. Has to be one of those values: Salesforce (default value) or CyberArk |
Usercube-Fulfill-ToEasyVistaTicket
This executable creates tickets in an EasyVista instance.
Examples
Connector specified
When specifying --connector, there is no need to specify --resource-types:
--connector "3" --api-url "http://localhost:5000/" --api-client-id "Job" --api-secret "secret" --url "https://easyvista.contoso.com" --account "12345" --login "Contoso" --password "cOntoSo6789"
But the identifier can be also given instead of the id:
--connector "EasyVista" --api-url "http://localhost:5000/" --api-client-id "Job" --api-secret "secret" --url "https://easyvista.contoso.com" --account "12345" --login "Contoso" --password "cOntoSo6789"
Resource types specified
When specifying --resource-types, there is no need to specify --connector:
--resource-types "40" "41" --api-url "http://localhost:5000/" --api-client-id "Job" --api-secret "secret" --url "https://easyvista.contoso.com" --account "12345" --login "Contoso" --password "cOntoSo6789"
But the identifiers can be also given instead of the id:
--resource-types "EasyVista_NominativeUser" "EasyVista_Administrator" --api-url "http://localhost:5000/" --api-client-id "Job" --api-secret "secret"--url "https://easyvista.contoso.com" --account "12345" --login "Contoso" --password "cOntoSo6789"
Arguments
| Argument Name | Details |
|---|---|
| --- | --- |
| --api-client-id required | Type String Description Login used to authenticate to the server. Every request from agent to server needs to be authenticated with an OpenID Connect ClientId/Secret pair, linked to a profile with the relevant permissions. |
| --api-secret required | Type String Description Password used to authenticate to the server. Every request from agent to server needs to be authenticated with an OpenID Connect ClientId/Secret pair, linked to a profile with the relevant permissions. |
| --api-url required | Type String Description URL of Usercube server. |
| --- | --- |
| --url required | Type String Description EasyVista API Endpoint URL. |
| --account required | Type String Description EasyVista account. |
| --login required | Type String Description Path of the file used for complete synchronization. |
| --password required | Type String Description EasyVista server password. |
| --- | --- |
| --connector required if --resource-typesis not given | Type String Description Id or Identifier of the resource types' connector we want to update the fulfillment state. |
| --resource-types required if --connectoris not given | Type String List Description Id or Identifier of the resource types we want to update the fulfillment state. |
| --certificate-identifier optional | Type String Description Unique key used to retrieve the certificate in Azure Key Vault. |
| --vault optional | Type String Description Vault uri. |
| --vault-connection-string optional | Type String Description Connection string to connect to Azure Key Vault. |
| --batch-size default value: 1000 | Type Int32 Description Number of provisioning orders to wait between each progress report. |
| --task-instance-id optional | Type String Description Id of the task instance which have launch the exe in a job context (for log purposes). |
Usercube-Get-JobSteps
This agent-side tool returns the list of all tasks present in a given job.
Examples
.\Usercube-Get-JobSteps.exe --api-url "http://localhost:5000" --api-client-id "Job" --api-secret "secret" --job-identifier "InitializationJob"
Task : InitializationJob_0_CreateDatabaseViews, Order : 0
Task : InitializationJob_1_AD_ExportActiveDirectory_Initial_ADExport, Order : 1
Task : InitializationJob_2_LDAP_ExportLDAP_Initial_LDAPExport0, Order : 2
Task : InitializationJob_3_LDAP_ExportLDAP_Initial_LDAPExport1, Order : 3
Task : InitializationJob_4_AD_PrepareSynchronizationActiveDirectory_Initial, Order : 4
Task : InitializationJob_5_HR_PrepareSynchronization_Initial, Order : 5
Task : InitializationJob_6_LDAP_PrepareSynchronization_Initial, Order : 6
Task : InitializationJob_7_SAB_PrepareSynchronization_Initial, Order : 7
Task : InitializationJob_8_AD_SynchronizeActiveDirectory_ForceSynchronization, Order : 8
Task : InitializationJob_9_HR_Synchronize_ForceSynchronization, Order : 9
Task : InitializationJob_10_LDAP_Synchronize_ForceSynchronization, Order : 10
Task : InitializationJob_11_SAB_Synchronize_ForceSynchronization, Order : 11
Task : Init_SetAdminProfile, Order : 12
Task : Init_DatabaseIndex, Order : 13
Task : InitializationJob_14_AllEntities_UpdateEntityPropertyExpressions, Order : 14
Task : InitializationJob_15_AllEntities_ComputeCorrelationKeys, Order : 15
Task : InitializationJob_16_ComputeRoleModel, Order : 16
Task : InitializationJob_17_Directory_GenerateProvisioningOrders_ForceProvisioning, Order : 17
Task : InitializationJob_18_Directory_FulfillInternalResources_IgnoreHistorization, Order : 18
Task : InitializationJob_19_AllEntities_ComputeCorrelationKeys, Order : 19
Task : InitializationJob_20_ComputeRoleModel, Order : 20
Task : Init_SetManualAssignments, Order : 21
Task : Init_ApproveFutureuserAccountContol, Order : 22
Task : InitializationJob_23_AllEntities_ComputeCorrelationKeys, Order : 23
Task : InitializationJob_24_ComputeRoleModel, Order : 24
Task : InitializationJob_25_Directory_GenerateProvisioningOrders_ForceProvisioning, Order : 25
Task : InitializationJob_26_Directory_FulfillInternalResources_IgnoreHistorization, Order : 26
Task : InitializationJob_27_AllEntities_ComputeCorrelationKeys, Order : 27
Task : InitializationJob_28_ComputeRoleModel, Order : 28
Task : InitializationJob_29_Directory_GenerateProvisioningOrders_ForceProvisioning, Order : 29
Task : InitializationJob_30_Directory_FulfillInternalResources_IgnoreHistorization, Order : 30
Task : Directory_Collect_Initial, Order : 31
Task : Directory_Synchronization_Init, Order : 32
Task : InitializationJob_33_AllEntities_UpdateEntityPropertyExpressions, Order : 33
Task : InitializationJob_34_DeployConfiguration, Order : 34
Task : InitializationJob_36_AllEntities_ComputeCorrelationKeys, Order : 35
Task : InitializationJob_37_ComputeRoleModel, Order : 36
Task : InitializationJob_38_ComputeRiskScores, Order : 37
Task : Init_LoadApplications, Order : 38
Task : Init_LoadPhotos, Order : 39
Task : InitializationJob_41_UpdateClassification, Order : 40
Task : InitializationJob_42_SetInternalUserProfiles, Order : 41
Task : InitializationJob_43_ResetValidFrom, Order : 42
Task : InitializationJob_44_UpdateParametersContextDisplayNames, Order : 43
Task : Init_Translate, Order : 44
Task : Init_SetLastLogon, Order : 45
Task : Init_SuggestedRoles, Order : 46
Task : InitializationJob_49_AllEntities_ComputeCorrelationKeys, Order : 47
Task : InitializationJob_50_ComputeRoleModel, Order : 48
Task : InitializationJob_51_SavePreExistingAccessRights, Order : 49
Arguments
| Argument Name | Details |
|---|---|
| --api-client-id optional | Type String Description Login to Usercube server. |
| --api-secret optional | Type String Description Password to Usercube server. |
| --api-url optional | Type String Description URL of Usercube server. |
| --job-identifier required | Type String Description Identifier of the job whose tasks/steps are to be listed. |
| --- | --- |
| --log-level optional | Type LogLevel Description Level of log information among: Verbose; Debug; Information; Warning; Error; Fatal. |
References: Executables
-
Usercube-Agent
Runs the Agent.- #### Usercube-Anonymize Transforms strings to anonymize given data.- #### Usercube-Compute-CorrelationKeys Computes the values of all correlation keys.- #### Usercube-Configuration-Transform Applies a series of transformation.- #### Usercube-Create-DatabaseViews Generates entity model SQL views in the Usercube database.- #### Usercube-CSV-Transform Modifies a CSV file by performing operations on its headers and/or columns.- #### Usercube-Decrypt-File Decrypts an input file to save it into an output file or an OutPutConsole that can be used in Powershell scripts or programs.- #### Usercube-Deploy-Configuration Retrieves all XML configuration files from a given folder, in order to calculate the configuration items to insert, update or delete in the application.- #### Usercube-EasyVistaTicket-UpdateFulfillmentState Updates the assigned resource types according to EasyVista tickets state.- #### Usercube-Encrypt-File Encrypts an input file or the InputConsole of a Powershell program or file to save it as an encrypted output file.- #### Usercube-Export-Bacpac Exports the database to a bacpac file.- #### Usercube-Export-Configuration Generates in a folder the files of the configuration found in the database.- #### Usercube-Export-Csv Exports CSV files.- #### Usercube-Export-EasyVista Exports EasyVista entities to CSV files.- #### Usercube-Export-Excel Exports Excel files.- #### Usercube-Export-Scim Exports SCIM entries to a CSV file.- #### Usercube-FillBankingDatabase Fills theBankingSystemdatabase for the Banking demo application.- #### Usercube-Fulfill-EasyVista Creates, updates and archives employees in an EasyVista instance.- #### Usercube-Fulfill-Scim Creates, updates and deleles entries in an application using the SCIM API.- #### Usercube-Fulfill-ToEasyVistaTicket Creates ticket in an EasyVista instance.- #### Usercube-Generate-Configuration Generates from a CSV file the configuration of a connector with these entities.- #### Usercube-Get-JobSteps Returns the list of all tasks present in a given job.- #### Usercube-Invoke-Job Launches a job on the agent side.- #### Usercube-Invoke-ServerJob Launches jobs on the server side.- #### Usercube-Login Provides an authentication token needed for SaaS configuration deployment/export.- #### Usercube-Manage-ConfigurationDependantIndexes Creates the necessary indexes based on the latest deployed configuration to optimize performances- #### Usercube-Manage-History Manages the data history stored in the database. It can purge old data or consolidate the history.- #### Usercube-New-OpenIDSecret Allows to generate the hashed password of the secret to connect to the given client for agent side job Usercube.- #### Usercube-PasswordGenerator Generates a password.- #### Usercube-Prepare-Synchronization Cleanses exported CSV files.- #### Usercube-Protect-CertificatePassword Encrypts a .pfx archive password using a Usercube provided RSA key.- #### Usercube-Protect-X509JsonFile Encrypts sensitive data from a given JSON file.- #### Usercube-Protect-X509JsonValue Encrypts the values of sensitive data.- #### Usercube-RefreshSchema Refreshes the schema of a given connection. Takes as input a connection, and refreshes its schema. The result of the update is stored into the database.- #### Usercube-Send-PasswordNotification Sends a mail notification for a password initialization or change.- #### Usercube-Server Runs the Server.- #### Usercube-Update-EntityPropertyExpressions Recomputes the values of all properties defined via expressions.- #### Usercube-Upgrade-ConfigurationVersion Upgrades your configuration from your current version entered in settings to the latest version.- #### Usercube-Upgrade-DatabaseVersion Runs all the migration scripts to upgrade the database.
Usercube-Invoke-Job
This tool launches a job on the agent side.
Behavior Details
The Usercube-Invoke-Job.exe tool is a state machine.
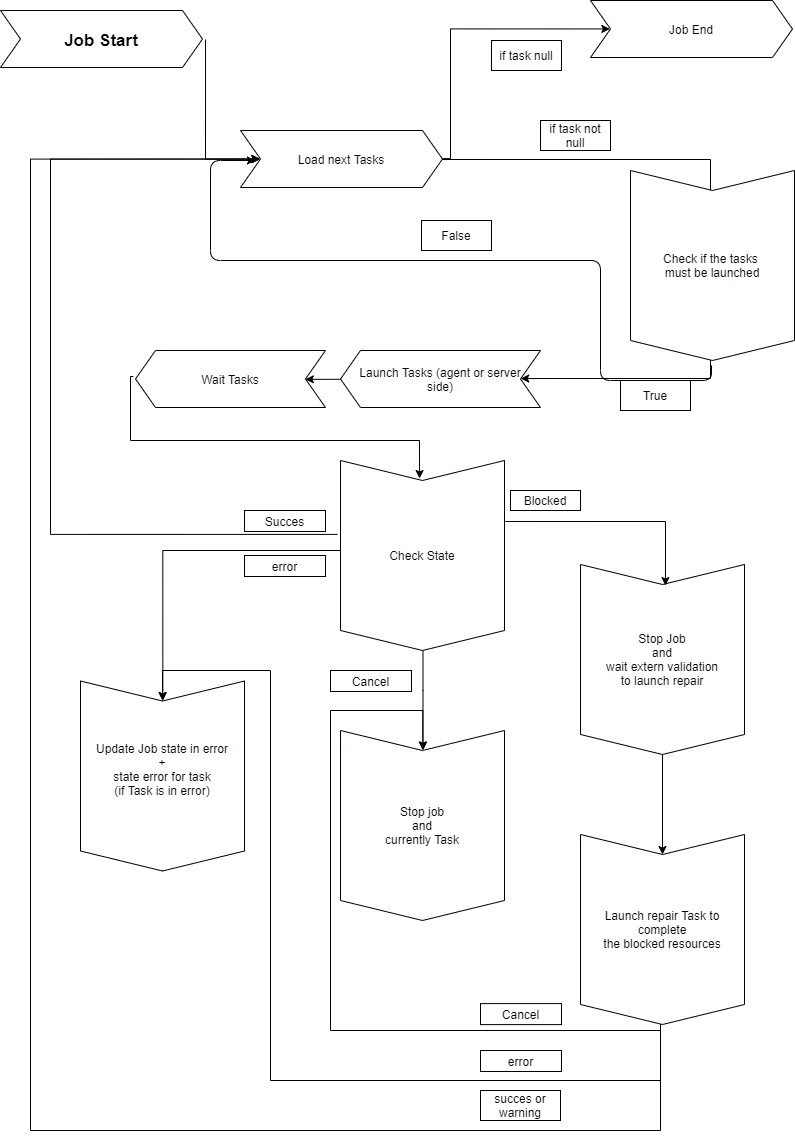
When a job is launched, the state machine starts by computing all the tasks that must be launched in the job.
Each task is assigned a launch order which can be configured in job steps. All the job's tasks are grouped together according to their launch order, and they are launched by group. Such task grouping allows the job to be faster executed.
The launch orders of all the tasks of a job can be listed by using the
Usercube-Get-JobSteps
executable.
Before any task is launched, the state machine checks the task's parent tasks in order to verify whether the task must be launched or not.
If the task must be launched, then the state machine checks whether the task should be started server- or agent-side.
Then the task is launched, and then:
-
if the task completes successfully, then the next task is loaded and started, or if this was the last task then the job ends successfully;
-
if the task exits in error, then the whole job exits in error and stops;
-
if the job is requested to stop from the UI, then the job's state switches to
cancelledand is transmitted to the current task in order to not launch the next task;A canceled job is not stopped straight away, as the current task first needs to be finished.
-
if the task exits in error while the warning mode is active, then the next job is loaded.
Only export tasks can have this warning mode.
-
if the task exits blocked, then the whole job stops and can be restarted manually at its breakpoint;
Only synchronization and provisioning tasks can exit blocked.
In the case where the job is blocked and restarted:
-
if the blocked task is a
SynchronizeTask, then the state machine runs a synchronization validation on the related connector, and uses the id of the blocked task instance to synchronize the related tables; -
if the blocked task is a
GenerateProvisioningOrdersTask, then the state machine forces the same provisioning on the related connector.Both the synchronization validation and the forced provisioning are virtual jobs that do not exist in the database. However, they will be visible in the UI which keeps track of any launched task.
In both cases, the state machine resumes the job with the tasks that were not started due to the blockage.
Any task launched by the state machine is linked to a job instance in order to keep track of the launch group.
Example
./identitymanager-Invoke-Job.exe -j "AccessCertificationEnd" --api-secret secret --api-client-id Job --api-url "http://localhost:5000"
Arguments
| Argument Name | Details |
|---|---|
| --- | --- |
| --job-identifier (-j) required | Type String Description Job's identifier to be launched. |
| --repair-job (-r) optional | Type No Value Description Bool to Decide launch Synchronization Validation or Provisioning with force. |
| --begin-job-step (-b) optional | Type String Description The step from which the job starts. |
| --end-job-step (-e) optional | Type String Description The step at which the job stops. |
| --task-identifier (-t) optional | Type String Description Specify the identification of the task to be started in the job (only this task will be started). |
| --force-synchronization-provisioning (-f) optional | Type Int64 Description Forces execution when the threshold is reached or exceeded. |
| --task-type (-c) optional | Type String Description The first task found with this type is launched. |
| --task-string-contains (-s) optional | Type String Description Launches all tasks with an identifier containing the given value. |
| --- | --- |
| --api-client-id required | Type String Description Login used to authenticate to the server. Every request from agent to server needs to be authenticated with an OpenID Connect ClientId/Secret pair, linked to a profile with the relevant permissions. |
| --api-secret required | Type String Description Password used to authenticate to the server. Every request from agent to server needs to be authenticated with an OpenID Connect ClientId/Secret pair, linked to a profile with the relevant permissions. |
| --api-url required | Type String Description URL of Usercube server. |
Usercube-Invoke-ServerJob
Invoke a Job (Server Side)
To launch the job in the Server side only you need to run the executable Usercube-Invoke-ServerJob.exe.
To know the task launch orders in job use the following exe: Usercube-Get-JobSteps.exe
Examples
.\Usercube-Invoke-ServerJob.exe -g "CleanDatabase" -s secret
Arguments
| Argument Name | Details |
|---|---|
| --- | --- |
| --job-identifier (-j) required | Type String Description Job's identifier to be launched. |
| --repair-job (-r) optional | Type No Value Description Bool to Decide launch Synchronization Validation or Provisioning with force. |
| --begin-job-step (-b) optional | Type String Description The step from which the job starts. |
| --end-job-step (-e) optional | Type String Description The step at which the job stops. |
| --task-identifier (-t) optional | Type String Description Specify the identification of the task to be started in the job (only this task will be started). |
| --force-synchronization-provisioning (-f) optional | Type Int64 Description Forces execution when the threshold is reached or exceeded. |
| --task-type (-c) optional | Type String Description The first task found with this type is launched. |
| --task-string-contains (-s) optional | Type String Description Launches all tasks with an identifier containing the given value. |
Usercube-Login
Delegates the authentication process to a third-party Identity Provider which will provide an authentication token required to allow the remote deployment/export of Usercube configuration.
The provided authentication token is meant to be sent to the Usercube administrator.
Examples
The following example launches the authentication to Usercube's in-house Identity Provider (IDP). It
will open your default browser to http://localhost:5005 where you will be redirected to Usercube's
IDP that will provide you with the authentication token.
./identitymanager-Login.exe
The following example launches the authentication to a specific Identity Provider whose
authentication URL and Client Id are respectively https://my_oidc_authentication_server.com and
34b3c-fb45da-3ed32. It will open your default browser to http://localhost:5005 where you will be
redirected to the IDP that will provide you with the authentication token.
./identitymanager-Login.exe --authority https://my_oidc_authentication_server.com --client-id 34b3c-fb45da-3ed32
The following example launches the authentication to Usercube's Identity Provider, but using a
specific port 5050. It will open your default browser to http://localhost:5050 where you will be
redirected to Usercube's IDP. that will provide you with the authentication token.
./identitymanager-Login.exe --port 5050
Arguments
| Argument Name | Details |
|---|---|
| --authority optional | Type String Description Base URL of the Identity Provider used for authentication. When not specified, Usercube provides an in-house Identity Provider. |
| --client-id optional | Type String Description Client Id of the application authorized to delegate the authentication to the specified Identity Provider. When not specified, Usercube provides the Client Id for the in-house Identity Provider. Note: ask for this id to your internal administrator. |
| --port default value: 5005 | Type Int64 Description Port used to run the local web page. |
Usercube-Manage-History
This tool optimizes the data history stored in the database, reducing its size and enhancing database performance.
The inner workings of this executable are based on the ValidFrom and ValidTo attributes that
specify the validity period of a given assignment. These attributes are inside the following tables
which are the tables actually purged: ur_resources; ur_resourcelinks;
up_assignedcompositeroles; up_assignedsingleroles; up_assignedresourcenavigations;
up_assignedresourcetypes.
Examples
Purge before a period
To clean the database periodically, it can be purged of all the history older than a given period of time.
The following example deletes all the history from the database that is more than 12-month old:
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
./identitymanager-Manage-History.exe --purge-before-months 12 --database-connection-string "data source=.;Database=Usercube;Integrated Security=SSPI;Min Pool Size=10;encrypt=false;"
Purge before a date
The database can be purged of all history older than a given date.
The following example deletes all the history from the database older than May 26th 1993:
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
./identitymanager-Manage-History.exe --purge-before-date 19930526 --database-connection-string "data source=.;Database=Usercube;Integrated Security=SSPI;Min Pool Size=10;encrypt=false;"
Optimize
The database's history can be optimized by removing intermediate versions based on their age, for example keeping only one version the last week, one per month the last 6 months and then one per year for 3 years.
The following example reduces the history from the database, keeping at most one history version per interval. Here we keep one version per day (1440 minutes) in the last 7 days, then one version per month (43920 minutes) in the last 6 months before the previously defined period, then one version per year (525960 minutes) in the last 2 years before the previously defined periods.
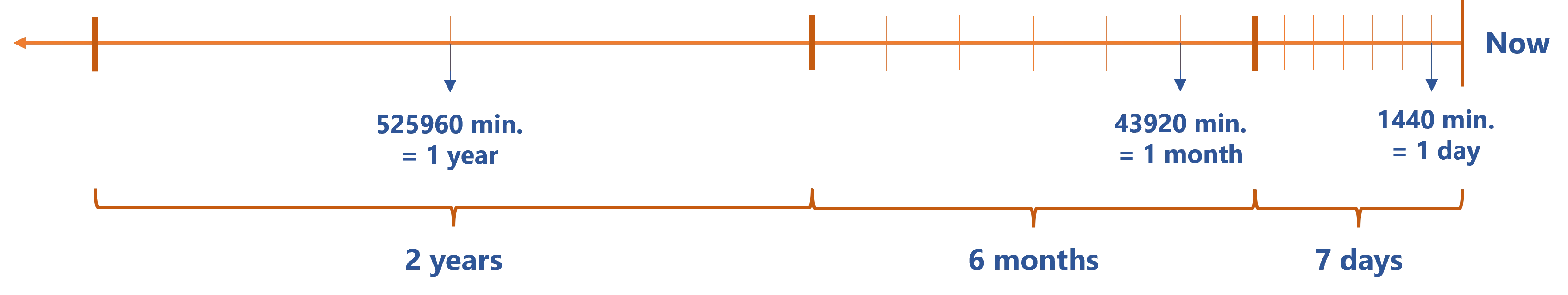
For each period, if there is more than one version (i.e. ValidFrom is inside the interval), the
versions are merged in the following way:
- The latest version is kept
- The oldest date is kept (that is, in the database, the
ValidForis equal to the one of the oldest version in the considered period).
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
./identitymanager-Manage-History.exe --optimize "1440:7 43920:6 525960:2" --database-connection-string "data source=.;Database=Usercube;Integrated Security=SSPI;Min Pool Size=10;encrypt=false;"
If you want to configure a time period when there is no purge and all history is kept as is, then
you can specify a short duration that allows a single change, for example only one minute. The
following example copies the previous one, in addition we want to keep all changes of the last 6
hours (360 minutes): --optimize 1:360 1440:7 43920:6 525960:2.
Clean duplicates
As given data can have several versions in the database, redundant rows can be deleted and replaced with one row that covers the consolidated time range.
The following example remove all duplicates in the database.
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
./identitymanager-Manage-History.exe --clean-duplicates --database-connection-string "data source=.;Database=Usercube;Integrated Security=SSPI;Min Pool Size=10;encrypt=false;"
The following example remove all duplicates induced by the pwdLastSet property.
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
./identitymanager-Manage-History.exe --clean-duplicates --excluded-resource-columns "pwdLastSet" --database-connection-string "data source=.;Database=Usercube;Integrated Security=SSPI;Min Pool Size=10;encrypt=false;"
Solicit memory rather than the database
To reduce the database load, the tool's optimizations can be made via the local device's memory.
The following example deletes all the history from the database that is more than 12-month old, the optimizations being computed in memory instead of in the database:
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
./identitymanager-Manage-History.exe --purge-before-months 12 --in-memory --database-connection-string "data source=.;Database=Usercube;Integrated Security=SSPI;Min Pool Size=10;encrypt=false;"
Arguments
| Argument Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| --clean-duplicates optional | No Value | Removes duplicate historical data. |
| --entity-type required if --excluded-resource-columns is set | String | When using --clean-duplicates option, defines the entity type (Id or Identifier) that should have its duplicates removed from the UR_Resources table. |
| --excluded-resource-columns required if --entity-type is set | String list | When using --clean-duplicates option, defines the list of column names (the name of the columns in the UR_Resources table, or the Identifier of the corresponding um_entityproperty) to exclude when comparing rows of UR_Resources table. |
| --in-memory default value: False | No value | Performs optimizations in memory instead of the database. It implies heavy memory consumption but light SQL load. |
| --optimize optional | String list | Reduces the history and optimizes the versions that are kept based on the precision given through ranges in the argument. A range is specified by a duration in minutes followed by the number of occurrences. For example 60:10 defines a range of 60 minutes repeated 10 times, or 10 snapshots repeated at 60 minute intervals. For each interval, at most one version is kept in the history. The intervals are evaluated in the given order from now, backwards. In the previous example, it means the more recent versions are kept with a high precision (one per day initially), then with lesser and lesser precision (one per month and then one per year). If the data has not changed over an interval, no optimization can be done. |
| --purge-before-date optional | String | Deletes all the history older than the given date in the yyyyMMdd format. |
| --purge-before-months optional | String | Deletes all the history older than the given number of months. |
| --database-connection-string required | String | Connection string of the database. |
The available actions (clean duplicates; purge; optimize) are all optional, but at least one must be used in the executable command.
Usercube-New-OpenIDSecret
This tools generates an hash. In practice, we hash a client secret but the tool can generate randomly a hash without an input string. The name of the executable is: �Usercube-New-OpenIDSecret.exe'.
Examples
./identitymanager-New-OpenIDSecret.exe --client-secret
Shared secret for 'secret' is 'K7gNU3sdo+OL0wNhqoVWhr3g6s1xYv72ol/pe/Unols='
The output shows the client secret and its hashed version. It must be entered in the OpenIdClient configuration.
Arguments
| Argument Name | Details |
|---|---|
| --client-secret optional | Type String Description Open id client secret that will be hashed by the program. |
| --- | --- |
| --log-level optional | Type LogLevel Description Level of log information among: Verbose; Debug; Information; Warning; Error; Fatal. |
Usercube-PasswordGenerator
Example
Manually generate a password
Consider an external system that is fulfilled manually and requires a new password.
To avoid writing the password in any file while still choosing a cryptographically secure password, we generate it just before using it.
--auto-generate true --digit-chars 2 --lower-case-chars 6 --symbol-chars 2 --upper-case-chars 2
Arguments
| Argument Name | Details |
|---|---|
| --default-password required if �auto-generate is false | Type String Description Specifies the default password used when --auto-generate is false. Example Set default password to password: --default-password password. |
| --auto-generate default value: false | Type No Value Description Specifies if the password should be the default password or generated automatically. Example Use default password: --auto-generate false. |
| --digit-chars default value: 0 | Type Integer Description Specifies the number of digits in the generated password. If the value is strictly positive, additional digits may be generated if --generated-length is higher than the sum of --digit-chars, --lower-chase-chars, --symbol-chars, and --upper-case-chars. Example Generate a password with 2 digits: --digit-chars 2. |
| --generated-length default value: 0 | Type Integer Description Specifies the length of the generated password. If it is lower than the sum of --digit-chars, --lower-chase-chars, --symbol-chars, and --upper-case-chars, the length of the generated password is equal to the sum. If it is higher than the sum of --digit-chars, --lower-chase-chars, --symbol-chars, and --upper-case-chars, extra characters of any type will be generated. Example Set a password length of 12: --generated-length 12. |
| --lower-case-chars default value: 0 | Type Integer Description Specifies the number of lower case characters in the generated password. If the value is strictly positive, additional lower case characters may be generated if --generated-length is higher than the sum of --digit-chars, --lower-chase-chars, --symbol-chars, and --upper-case-chars. If the sum of --digit-chars, --lower-chase-chars, --symbol-chars, and --upper-case-chars is 0, only lower case characters will be generated. Example Generate a password with 6 lower case characters: --lower-case-chars 6. |
| --strength-check default value: "^.*" | Type String Description The regular expression to check the password strength. By default, any password passes the strength check. Example Accept any password: --strength-check ^.*. |
| --symbol-chars default value: 0 | Type Integer Description Specifies the number of symbols in the generated password. If the value is strictly positive, additional symbols may be generated if --generated-length is higher than the sum of --digit-chars, --lower-chase-chars, --symbol-chars, and --upper-case-chars. Example Generate a password with 2 symbols: --symbol-chars 2. |
| --upper-case-chars default value: 0 | Type Integer Description Specifies the number of upper case characters in the generated password. If the value is strictly positive, additional upper case characters may be generated if --generated-length is higher than the sum of --digit-chars, --lower-chase-chars, --symbol-chars, and --upper-case-chars. Example Generate a password with 2 upper case characters: --upper-case-chars 2. |
Usercube-Prepare-Synchronization
Usercube-Prepare-Synchronization is used as the second step of the
synchronization process.
It cleanses exported CSV files before sending them to the server for database loading. It is
performed on the Agent side.
Behavior Details
The task reads files from the source directory, usually the temp folder > ExportOutput folder.
Cleanse data
The following actions are performed on the CSV source files:
- Remove columns that are not used in
<EntityTypeMapping>or<EntityAssociationMapping>. - Remove entries that have a null primary key.
- Remove duplicates.
- Sort entries according to the primary key.
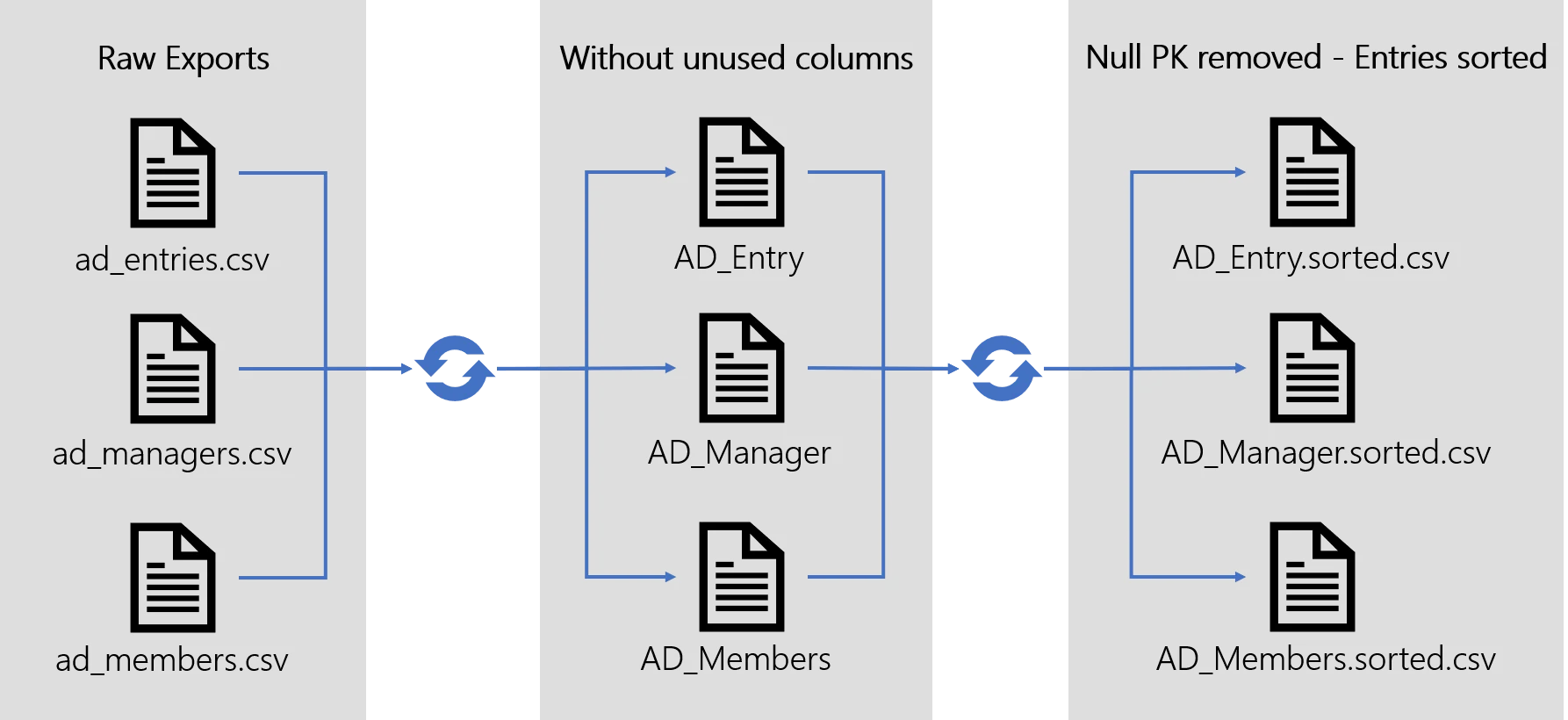
The result of the Prepare-Synchronization is stored in the export directory as three files:
- For every entity type of the relevant Connector involved in an
<EntityTypeMapping>or an<EntityAssociationMapping>, a.sorted.csvfile is generated, containing the final, cleansed and sorted result. - Duplicates are kept in a separate
.duplicates.csvfile. - Null primary key entries are kept in a separate
.nullpk.csvfile.
All files produced by the task are in the work folder > Collect directory.
Compute changes
In incremental mode, changes might need to be computed by the Agent:
- If the Export step has provided computed changes, no further process is required. The changes will be sent as-is to the server.
- If the Export step has provided a full extract of the managed systems, the
Prepare-Synchronization step computes changes. This computation is based on the result of the
last data cleansing, generated by the previous Prepare-Synchronization, and stored in the
previousfolder in the export directory.
For incremental mode, it is recommended, whenever possible, to use managed systems to compute changes. Dedicated workstations and knowledge of the inner data organization allow managed systems to compute changes with performance that Usercube can't match. Using managed systems for these operations avoids generating heavy files and alleviates Usercube's processing load.
The result is a set of clean lists of changes stored as a .sorted.delta file containing a
command column. The command column can take the following values:
- insert
- update
- delete
- merge
These values are instructions for the Synchronization step to apply the changes to the database.
The .sorted file (that is, the original clean export file, not the changes) is stored in
the previous folder inside the
export directory.
It will be used as a reference for the next incremental Prepare-Synchronization to compute the
changes, if needed.
Tampering with the previous folder content would result in false changes leading to false
computation. It would result in data corruption in the Usercube database. To restore the Usercube
database and reflect the managed system data updates, a complete__Sync Up would be required.
Prepare the server
At the beginning of every Prepare-Synchronization process, the Server is notified via HTTP.
Upon receiving the notification, the server creates a directory on its host environment, identified
by a unique GUID, to contain .sorted or .sorted.delta files that will be sent by the agent.
This is designed to prevent network errors that would cause an incremental database update to happen more than once.
This means that several Export and Prepare-Synchronization tasks can be executed simultaneously. These tasks will be processed by the server one at a time, in the right order.
Any notification of a complete Prepare-Synchronization would cancel the previous non-processed incremental Prepare-Synchronizations. As a complete Prepare-Synchronization reloads the whole database, it renders incremental changes computation moot.
Send clean exports
.sorted or .sorted.delta files are sent over HTTP to the Server for the last step.
Example
The figure models the complete Prepare-Synchronization steps applied to an Active Directory export. The matching Connector defines an Entity Type AD Entry and two associations (members and manager).
Examples
Usercube-Prepare-Synchronization can be used as an executable file as follows:
./identitymanager-Prepare-Synchronization --api-url myserver.usercube.com --api-client-id myclientid --api-secret myclient secret --connector --agent myagent --synchronization-mode complete
Arguments
| Name | Details |
|---|---|
| --agent required | Type Agent Description Identifier of the agent where the task runs. |
| --connector required | Type Connector Description Identifier of the linked connector. The task is linked to a connector whose entity types are synchronized. |
| --synchronization-mode required | Type SynchronizationMode Description Synchronization mode for this task can be one of the following: - Initial - Complete - Incremental This must be the same as the associated Export and Synchronize tasks. Use initial if this is the first time the target managed system is synchronized. Use complete to load the data from the managed system as a whole. Use incremental to consider only incremental changes from the last synchronization. In incremental mode, the Prepare-Synchronization task computes changes in the source managed system since the last Prepare-Synchronization. |
| --sources-directory default value: ExportOutput | Type String Description Directory path, relative to temp folder, from which export files to cleanse are read. |
| --working-directory default value: Collect | Type String Description The directory path, relative to work folder, to which intermediary and cleansed files are stored. |
| --- | --- |
| --api-client-id required | Type String Description Login used to authenticate to the server. Every request from agent to server needs to be authenticated with an OpenID Connect ClientId/Secret pair, linked to a profile with the relevant permissions. |
| --api-secret required | Type String Description Password used to authenticate to the server. Every request from agent to server needs to be authenticated with an OpenID Connect ClientId/Secret pair, linked to a profile with the relevant permissions. |
| --api-url required | Type String Description URL of Usercube server. |
| --- | --- |
| --log-level optional | Type LogLevel Description Level of log information among: Verbose; Debug; Information; Warning; Error; Fatal. |
Usercube-RefreshSchema
Examples
Usercube-RefreshSchema can be used as an executable file as follows:
dotnet Usercube-RefreshSchema.dll --api-url myserver.usercube.com --api-client-id myclientid --api-secret myclient secret --connection-id -2
The credentials used to connect to the connection come from the Agent Appsettings.
Arguments
| Name | Details |
|---|---|
| --connection-id *required | Type Integer Description Id of a connection whose schemas are updated. See Connection. |
| --- | --- |
| --api-client-id required | Type String Description Login used to authenticate to the server. Every request from agent to server needs to be authenticated with an OpenID Connect ClientId/Secret pair, linked to a profile with the relevant permissions. |
| --api-secret required | Type String Description Password used to authenticate to the server. Every request from agent to server needs to be authenticated with an OpenID Connect ClientId/Secret pair, linked to a profile with the relevant permissions. |
| --api-url required | Type String Description URL of Usercube server. |
| --- | --- |
| --log-level optional | Type LogLevel Description Level of log information among: Verbose; Debug; Information; Warning; Error; Fatal. |
Usercube-Send-PasswordNotification
Examples
Manually send a password initialisation mail notification
Consider a user who needs an account in an external system. Consider that this account requires a password.
As an example, we will consider that the id of the resource type mapping associated with the external system is 10, and the id of the assigned resource type associated with the user is 1000.
Once the password is set, we need to communicate this password to the user. We send a mail notification to inform the user.
--password true --assigned-resource-type 1000 --resource-type-mapping 10
For the notification to be sent, the server set at appsettings > ApplicationUri should be running. The resource type mapping should have an associated password reset setting. For the notification to be sent, the password reset settings should at least contain a notified email binding. For the notification to make sense, the password reset settings should at least contain a beneficary full name binding.
Arguments
| Argument Name | Details |
|---|---|
| --assigned-resource-type required | Type String Description Specifies the id of the assigned resource type corresponding to the user and the external system that is being fulfilled with a new password. This can be found in the provisioning order at ProvisioningOrdersList > AssignedResourceTypeId. Example Send a notification for the assigned resource type with id 1000: --assigned-resource-type 1000. |
| --password required | Type String Description Specifies the new password that will be sent by mail. Example Send a notification for the password NewPassword: --password NewPassword. |
| --resource-type-mapping required | Type String Description Specifies the id of the resource type mapping corresponding to the external system that is being fulfilled with a new password. This can be found in the provisioning order at ProvisioningOrdersList > ResourceType > Id, as the resource type and its corresponding resource type mapping share the same id. Example Send a notification for the resource type mapping with id 10: --resource-type-mapping 10. |
| --notification-cc optional | Type Integer Description Specifies an address that should also receive the notification. Example Add admin@acme.admin to the mail CC: --notification-cc admin@acme.admin. |
Usercube-Update-EntityPropertyExpressions
This tool is used to recompute the values of all properties defined via expressions (C#, etc.), usually to prepare for a connector's synchronization.
Examples
The following example updates the property expressions of the database defined by the connection string, for all entity types.
./identitymanager-Update-EntityPropertyExpressions.exe --database-connection-string "data source=.;Database=Usercube;Integrated Security=SSPI;Min Pool Size=10;encrypt=false" -a
Arguments
| Argument Name | Details |
|---|---|
| --batch-select-size (-q) default value: 10000 | Type Int32 Description Batch size for SELECT queries. See more details. |
| --batch-update-size (-c) default value: 20000 | Type Int32 Description Batch size for UPDATE queries. See more details. |
| --- | --- |
| --database-connection-string required | Type String Description Connection string of the database. |
| --- | --- |
| --all-entityType (-a) optional | Type No Value Description Applies the tool to all entity types. |
| --batch-size (-q) default value: 5000 | Type Int32 Description Batch size for queries. See more details. |
| --dirty optional | Type No Value Description Applies the tool incrementally by applying it only to resources marked as dirty, i.e. recently modified. |
| --entitytype-list optional | Type String List Description List of entity types that the tool is to be applied to. Note: required when --all-entityType is not specified. |
| --resource-identity-property optional | Type String Description Property used to override the resource identity property set in SelectUserByIdentityQueryHandler. |
| --- | --- |
| --log-level optional | Type LogLevel Description Level of log information among: Verbose; Debug; Information; Warning; Error; Fatal. |