Configuration
XML Configuration Schema
Overview
The XML configuration schema shows some similarities with the database schema but they are not the same.
Family Entity Listing
-
Access Control
-
Connectors
-
Configuration
-
User Interface
-
Jobs
-
Metadata
-
Notifications
-
Provisioning
-
Reporting
-
Resources
-
Access Certification
-
Business Intelligence
-
Workflows
AccessControlEntityType
Child Element: Property
An AccessControlEntityProperty assigns an entity property to a visibility group. See the Access Control Property Group topic for additional information.
Properties
The list of properties for the Child Element: Property in listed below.
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VisibilityGroup optional | Int64 | The VisibilityGroup that controls access to the property. |
Binding
Usercube metadata provides a simple and consistent way to present and interact with metadata. A binding is a path of scalar/navigation properties used to configure a set of property keys.
Child Element: Property
Dimension
A dimension is an Entity Type used to define an organizational filter for the Usercube role model.
Examples
The following XML fragment defines the dimension Organization0. The dimension values are of
Directory_Organization type. The ColumnMapping attribute specifies the column (0 to 127) used to
store the dimension value in the assignment rule tables.
<Dimension Identifier="Organization0" DisplayName_L1="Department" EntityType="Directory_Organization" ColumnMapping="0" />
Some types of entities can be organized in a hierarchical tree structure. Thus, for example,
organizational units form a tree structure modeled by a Parent navigation property that links the
entity type to itself. It is possible to use the hierarchical aspect of a dimension in an assignment
rule criterion. For example, the assignment must be extended to the whole subunits of a department.
Such a dimension must be declared as a hierarchical dimension by specifying the attribute
IsHierarchical="true".
<Dimension Identifier="Organization0" DisplayName_L1="Department" EntityType="Directory_Organization" ColumnMapping="0" IsHierarchical="true" ParentProperty="Parent" /><EntityType Identifier="Directory_Organization" DisplayName_L1="Department">...
<Property Identifier="Path" DisplayName_L1="Path" Type="String" TargetColumnIndex="6" /> <Property Identifier="Parent" DisplayName_L1="Parent Department" Type="ForeignKey" TargetColumnIndex="128" />...
</EntityType>
The attribute ParentProperty specifies the navigational property defining the hierarchy (Parent
is the navigation property that links the Directory_Organization type to itself).
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| ColumnMapping required | Type Int32 Description Specifies the corresponding column in the role model rules. |
| DisplayName_L1 optional | Type String Description Display name of the dimension in language 1 (up to 16). |
| EntityType required | Type Int64 Description References the linked entity type. |
| Identifier required | Type String Description Unique identifier of the dimension. |
| IsExcludedFromRoleMining default value: false | Type Boolean Description true to exclude the dimension from role mining. It means that the dimension is not used as a criteria in the generated rules. |
| IsHierarchical default value: false | Type Boolean Description true to define a hierarchical dimension. Note: Cannot be used without ParentProperty. |
| ParentProperty optional | Type Int64 Description Specifies the navigational property defining the hierarchy. |
EntityAssociation
An entity association is used to model an association in Usercube's metadata. See the example of a whole connector with its entity properties and associations.
Examples
The following example associates one title (as a property from the entity type
Directory_UserRecord) with several user records (as a property from the entity type
Directory_Title).
<EntityAssociation Identifier="Directory_UserRecord_Title_User_Records" IsProperty2Collection="true"
Property1="Directory_UserRecord:Title" Property2="Directory_Title:UserRecords" />
Many-to-many association
The following example associates SAB users with groups, with the possibility to link one group to several users, and one user to several groups.
<EntityAssociation Identifier="SAB_Group_User" DisplayName_L1="User" IsProperty1Collection="true" IsProperty2Collection="true" Property1="SAB_Group:User" Property2="SAB_User:Group" />
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| DisplayName_L1 optional | Type String Description Display name of the association in language 1 (up to 16). |
| Identifier required | Type String Description Unique identifier of the association. It must be unique to the entity model scope. |
| IsProperty1Collection default value: false | Type Boolean Description true to define a many-to-one association. |
| IsProperty2Collection default value: false | Type Boolean Description true to define a one-to-many association. |
| Property1 required | Type Int64 Description Defines the first navigation property. A navigation property can be mono-valued or multi-valued (with its corresponding IsPropertyCollection set to true). Mono-valued navigation properties may be optimized (with a TargetColumnIndex) or not (without TargetColumnIndex). See more details under the TargetColumnIndex section of the entity type property's page. |
| Property2 required | Type Int64 Description Defines the second navigation property. |
EntityPropertyExpression
An entity property expression is a property computed from a binding and/or C# or literal expressions.
Examples
The following example computes the record display name.
<EntityPropertyExpression Identifier="Directory_UserRecord_InternalDisplayName" Expression="C#:person:return person.LastName + " " + person.FirstName;"
EntityType="Directory_UserRecord" Property="InternalDisplayName" />
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Binding optional | Type Int64 Description References the binding used to compute the result. |
| EntityType required | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the referenced entity type |
| Expression optional | Type String Description References the C# or literal expression used to compute the result. See more details on C# expressions. |
| Identifier required | Type String Description Unique identifier of the expression. |
| Priority default value: 0 | Type Int32 Description Specifies the execution priority. |
| Property required | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the referenced entity property |
| PropertyCriteria optional | Type Int64 Description References the property criteria used to compute navigation properties. |
EntityType
Represents a conceptual model of a business object, such as a person entity or an organization entity. See Connector on how to configure define an EntityType.
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| DisplayName_L1 optional | Type String Description Display name of the entity type in language 1 (up to 16). |
| Identifier required | Type String Description Unique identifier of the entity type. It must is be unique to the entity model scope. Cannot be a reserved identifier. |
| LicenseTag optional | Type String Description Value of the Tag parameter of the license key (in appsettings.json) linked to the entity type. All the features allowed by the license key are enabled for this entity type, otherwise only default features are available. |
| TableName optional | Type String Description Represents the table name of hard coded entity types. Exclusively reserved to Usercube connector for Power BI. |
Child Element: Property
An entity property represents a property of an Entity Type. See Connector on how to configure/define an EntityProperty.
Examples
Populate navigational property from non primary key
Some configuration elements will be linked to an entity whose id is not known at configuration time.
In this case, another key must be used. On each entity type property, the IsKey attribute
specifies that the property can be used as a key during configuration import.
For example, the Code property of the Title entity type is marked as a key.
<EntityType Identifier="Title" DisplayName_L1="Title"> <Property Identifier="Code" Type="String" IsKey="true" TargetColumnIndex="4" /> ...
</EntityType>
All Title instances will be replicated from a managed system. So, at configuration time, Usercube's internal primary key for this Title is not known.
We hence cannot write a SingleRoleRule with a Dimension criteria based on Title as the primary key.
We can however, use a non-primary key, that is known in advance, because it depends on the managed system's data and not on Usercube.
For example, the below Dimension1 attribute references a Title entity by its Code value.
<SingleRoleRule Role="InternetAccess" Dimension1="TITLE0000" Policy="Default" />
Changing the multiplicity of a property
It is sometimes necessary to change the multiplicity of a property (Scalar property to Navigation
property or vice-versa). As long as the property was not used in any workflow, this can be properly
handled by Deploy-Configuration.exe. If it was used in one or more workflows, foreign key
conflicts (in UW_Changes database table) may occur, preventing the configuration from being
deployed. To solve this problem, references to this property must be manually cleaned up with SQL
queries directly in the database before deploying the configuration.
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| DisplayName_L1 optional | Type String Description Display name of the property in language 1 (up to 16). Note: cannot be "Id". |
| FlexibleComparisonExpression optional | Type String Description Expression used to transform the query input value for comparison using a flexible operator. |
| GroupByProperty optional | Type Int64 Description Property used to regroup navigation resources (resources used in navigation rules) by value. When defined, the Evaluate policy will enforce that one and only one item of a group can be assigned to an identity on a given date range. Warning: whenever the value of this property changes for a resource used in the defined navigation rules, the server needs to be restarted in order for the changes to be taken into account. |
| HistoryPrecision default value: 0 | Type Int32 Description Defines the number of minutes to wait, after a property change, before triggering the record history mechanism. |
| Identifier required | Type String Description Unique identifier of the property. It must be unique to the parent entity type scope. Cannot be a reserved identifier and can only contain numbers (except the first character) and letters without accents. Note: cannot be "Id". |
| IsKey default value: false | Type Boolean Description true if the property is designated to be one of the keys that uniquely identify any resource from the entity type in the configuration. Each entity type must have at least one key. Note: AD synchronization requires the dn property to have either IsKey or EntityTypeMapping > Property > IsUniqueKey set to true (key property in the UI). |
| Language optional | Type Int64 Description Language associated to the property if it is localized (optional). |
| NeutralProperty optional | Type Int64 Description Neutral property associated to the property if it is localized (optional). |
| TargetColumnIndex default value: -1 | Type Int32 Description Specifies the corresponding column in the resource entity. 0 to 3: scalar property whose value exceeds 443 characters. 4 to 127: scalar property whose value does not exceed 443 characters (or optimized mono-valued navigation property : see note). 128 to 152: optimized mono-valued navigation property only. -1: non-optimized mono or multi-valued navigation property (stored in UR_ResourceLink), or binary (stored in UR_ResourceLink). Note: optimized mono-valued navigation properties should have their TargetColumnIndex between 128 and 152 included to be fully optimized. However, if all are already taken, TargetColumnIndex from 0 to 127 included (usually for scalar properties) may also be used. In this case the first available TargetColumnIndex in ascending order should be used. |
| Type default value: 0 | Type EntityPropertyType Description Property type. 0 - String. 1 - Bytes. 2 - Int32. 3 - Int64. 4 - DateTime. 5 - Bool. 6 - Guid. 7 - Double. 8 - Binary. 9 - Byte. 10 - Int16. 12 - ForeignKey: indicates a navigation property, i.e. a property related to an association between entities. |
Metadata
-
AccessControlEntityType
-
Binding
-
Dimension
-
EntityAssociation
-
EntityPropertyExpression
-
EntityType
-
Language
-
Settings
Language
Represents a configuration entity used to create multilingual application.
Examples
The following example declares a new language.
<Language Code="en-US" IndicatorNumber="1" />
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Code required | Type String Description Unique identifier of the language (fr-FR, en-US�). |
| IndicatorNumber required | Type Int32 Description Defines the default language. |
| JsonPath optional | Type String Description The original translations file path |
AppDisplaySetting
This setting is used to customize the application display.
Examples
Set colors, logos and names
The following example sets:
- "Netwrix Usercube" as name of the application visible on the tabs;
- the logo to be displayed in the top left corner;
- the favicon to be displayed on the tabs;
- the banner color, banner gradient color, banner selected tab color, banner text color, primary color and secondary color.
<AppDisplaySetting ApplicationName="Netwrix Usercube" LogoFile="logo.webp" FaviconFile="favicon.ico" BannerColor="#512E5F" BannerGradientColor="#76D7C4" BannerSelectedTabColor="#E74C3C" BannerTextColor="#F1C40F" PrimaryColor="#0E6655" SecondaryColor="#85C1E9" />
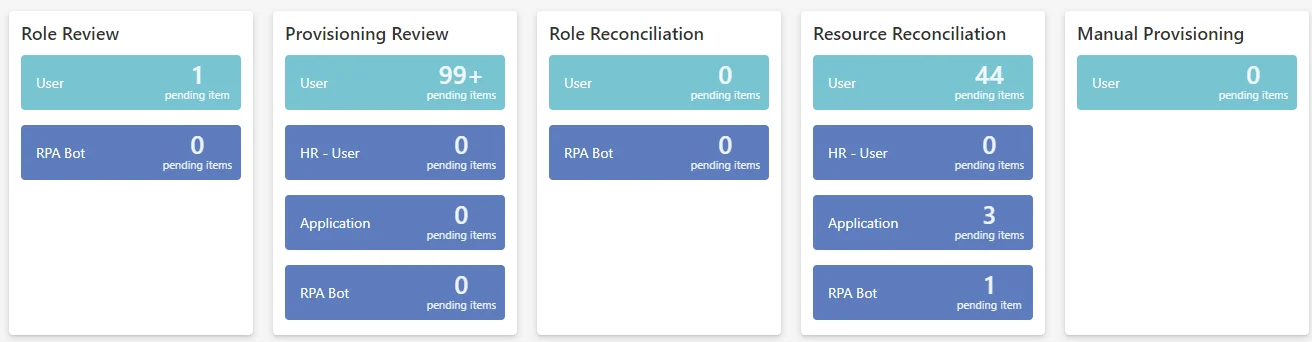
Disable counters
The following example disables the counters that are usually visible on the dashboard:
<AppDisplaySetting DisableProvisioningCounters="true" />
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| ApplicationName optional | Type String Description Name of the application, visible on the application's tabs. |
| BannerColor optional | Type String Description HEX code of the color for the banner, i.e. the header displaying logo and navigation bar. |
| BannerGradientColor optional | Type String Description HEX code of the color for the banner's gradient to be visible at the middle of the banner. |
| BannerSelectedTabColor optional | Type String Description HEX code of the color for the line that emphasizes the selected tab. |
| BannerTextColor optional | Type String Description HEX code of the color for the banner's text. |
| DisableProvisioningCounters default value: false | Type String Description true to disable the counters related to the administration screens: Role Review, Provisioning Review, Role Reconciliation, Resource Reconciliation and Manual Provisioning. |
| FaviconFile optional | Type String Description Path of the favicon to be displayed in the application's tabs. |
| FaviconMimeType optional | Type String Description Mime type of the favicon. |
| FullNameSeparator default value: � | Type String Description Separator of the full name. |
| Identifier default value: AppDisplay | Type String Description Unique identifier of the setting. |
| LogoFile optional | Type String Description Path of the logo to be displayed in the top left corner. |
| LogoMimeType optional | Type String Description Mime type of the logo. |
| Preview optional | Type String Description Documentation unavailable. |
| PrimaryColor optional | Type String Description HEX code of the color for the highlighted buttons. |
| SecondaryColor optional | Type String Description HEX code of the color for the background of the authentication screen. |
ConfigurationVersionSetting
Used to track the current configuration version.
Examples
<ConfigurationVersionSetting Version="5.0.0" Description="Demo Usercube" />
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Description optional | Type String Description Detailed description of the version. |
| Identifier default value: ConfigurationVersion | Type String Description Unique identifier of the setting. |
| Misc optional | Type String Description Misc. |
| Version optional | Type String Description Version of the configuration. |
CustomLink1Setting
Used to display a given static HTML file to a custom URL address.
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Path_L1 required | Type String Description The path (relative to the configuration root) to the HTML file for language L1. |
| Url required | Type String Description The URL from which the custom HTML should be displayed. Must start with an �/'. |
| Identifier default value: CustomLink1 | Type String Description Unique identifier of the setting. |
CustomLink2Setting
Used to display a given static HTML file to a custom URL address.
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Path_L1 required | Type String Description The path (relative to the configuration root) to the HTML file for language L1. |
| Url required | Type String Description The url from which the custom HTML should be displayed. Must start with an �/'. |
| Identifier default value: CustomLink2 | Type String Description Unique identifier of the setting. |
DashboardItemNumberSetting
Used to customize the number of links to display on each section on the Dashboard. If no value is defined, the default value is 3. The value must be greater than 0 and less than or equal to 5.
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Identifier default value: DashboardItemNumber | Type String Description Unique identifier of the setting. |
| ManualProvisioningSection optional | Type String Description Number of links to display in the Manual Provisioning section. The default value is 3. The value must be greater than 0 and less than or equal to 5. |
| MyTasksSection optional | Type String Description Number of links to display in the My Tasks section. The default value is 3. The value must be greater than 0 and less than or equal to 5. |
| ProvisioningReviewSection optional | Type String Description Number of links to display in the Provisioning Review section. The default value is 3. The value must be greater than 0 and less than or equal to 5. |
| ResourceReconciliationSection optional | Type String Description Number of links to display in the Reconciliation Review section. The default value is 3. The value must be greater than 0 and less than or equal to 5. |
| RoleReconciliationSection optional | Type String Description Number of links to display in the Role Reconciliation section. The default value is 3. The value must be greater than 0 and less than or equal to 5. |
| RoleReviewSection optional | Type String Description Number of links to display in the Role Review section. The default value is 3. The value must be greater than 0 and less than or equal to 5. |
Settings
-
AppDisplaySetting
This setting is used to customize the application display.- #### ConfigurationVersionSetting Used to track the current configuration version.- #### CustomLink1Setting Used to display a given static HTML file to a custom URL address.- #### CustomLink2Setting Used to display a given static HTML file to a custom URL address.- #### DashboardItemNumberSetting Used to customize the number of links to display on each section on the Dashboard. If no value is defined, the default value is 3. The value must be greater than 0 and less than or equal to 5.- #### MailSetting -
PasswordGenerationSetting
-
PasswordTestsSetting
This setting enables a check on the passwords set manually by users.- #### SchedulingCleanDataBaseSetting If the default value for the Task CleanDataBase needs to be overridden.- #### SelectAllPerformedByAssociationQueryHandlerSetting This setting enables task delegation to a group of people.- #### SelectPersonasByFilterQueryHandlerSetting This setting is used to filter the entity type used by authentication mechanism.- #### SelectUserByIdentityQueryHandlerSetting This attribute matches an end-user with a resource from the unified resource repository.
MailSetting
Examples
The following example indicates that notifications for users from Directory_User are to be sent to
the email addresses contained by the Email property.
<MailSetting MailProperty="Directory_User:Email"/>
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Identifier default value: MailSettings | Type String Description Unique identifier of the setting. |
| LanguageCode optional | Type String Description Language code for the notifications sent by server-side tasks, using the ISO 639-1 standard. For example, "en-US" represents American English. |
| MailProperty optional | Type String Description Property whose values are to be used by Usercube to send emails. |
PasswordGenerationSetting
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| AllowedSymbolChars required | Type String Description The documentation is not yet available. |
| Identifier default value: PasswordGenerationSetting | Type String Description Unique identifier of the setting. |
PasswordTestsSetting
This setting enables a check on the passwords set manually by users.
The strength of passwords generated by Usercube can be configured via
PasswordResetSettings's
StrengthCheck.
Examples
The following example encourages users to choose a strong password with at least 9 characters including at least one digit, one lowercase letter, one uppercase and one special character.
<PasswordTestsSetting PasswordRegex="'^..........*$','^.*[0-9].*$', '^.*[a-z].*$', '^.*[A-Z].*$', '^.*[^A-Za-z0-9].*$'"/>
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Identifier default value: PasswordTests | Type String Description Unique identifier of the setting. |
| PasswordRegex optional | Type String Description Regular expression(s) (regex) that users' passwords must match to be acceptable when set manually. When setting several regex, passwords must match all of them to be considered strong, and 70% to be considered average. Below that, a password is considered weak and cannot be confirmed. Default value:'^..*$', '^...*$', '^....*$', '^.....*$', '^......*$', '^.......*$', '^........*$', '^.........*$', '^..........*$', '^.*[0-9].*$', '^.*[a-z].*$', '^.*[A-Z].*$', '^.*[^A-Za-z0-9].*$' |
SchedulingCleanDataBaseSetting
If the default value for the Task CleanDataBase needs to be overridden.
Examples
<SchedulingCleanDataBaseSetting Timeout="2" CronTabExpression="* */2 * * *"/>
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| CronTabExpression optional | Type String Description Define the cron to launch the CleanDatabase Job. |
| Identifier default value: SchedulingCleanDataBase | Type String Description Unique identifier of the setting. |
| Timeout optional | Type String Description Defines the maximum time a Job or Task can wait after the last run. |
SelectAllPerformedByAssociationQueryHandlerSetting
This setting enables task delegation to a group of people.
Examples
<SelectAllPerformedByAssociationQueryHandlerSetting RootEntityType="AD_Entry" Binding="member" />
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Binding optional | Type String Description Defines the binding used to get the list of identities to delegate to. |
| Identifier default value: SelectAllPerformedByAssociationQueryHandler | Type String Description Unique identifier of the setting. |
| RootEntityType optional | Type String Description Indicates the entity type on which the delegation is applied. |
SelectPersonasByFilterQueryHandlerSetting
This setting is used to filter the entity type used by authentication mechanism.
Examples
<SelectPersonasByFilterQueryHandlerSetting ResourceDisplayNameProperty="AD_Entry:displayName" PersonTypeFilterProperty="AD_Entry:objectCategory" PersonTypeFilter="Person" />
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Identifier default value: SelectPersonasByFilterQueryHandler | Type String Description Unique identifier of the setting. |
| MailProperty optional | Type String Description Defines the mail property. Note: required to receive the email for two-way password reset, when relevant. |
| OwnerPhotoTagProperty optional | Type String Description Defines the photo tag property. |
| PersonTypeFilter optional | Type String Description The documentation is not yet available. |
| PersonTypeFilterProperty optional | Type String Description Defines the filter property |
| PhotoProperty optional | Type String Description The documentation is not yet available. |
| ResourceDisplayNameProperty optional | Type String Description Represents the display property. |
SelectUserByIdentityQueryHandlerSetting
This attribute matches an end-user with a resource from the central repository.
Authorization mechanisms within Usercube rely on assigning a profile to a resource that stands for the end-user digital identity.
To that end, end-user authentication credentials are linked to such an identity using the following pattern:
- authentication credentials are retrieved;
- authentication credentials are trimmed using the
AfterTokenand/orBeforeTokenattributes; - the trimmed result is matched against the
ResourceIdentityPropertyof resources with the entity type specified byOwnerEntityType; - the matching resource is used to find a profile and authorization for that digital identity.
After modifying the authentication mode via SelectUserByIdentityQueryHandlerSetting, Usercube
server must be restarted. On a SaaS environment, contact your Usercube administrator.
Examples
The following example links the authentication credentials of an end-user to its matching resource of EntityType Directory_User.
In this example, authentication has been set up using
Integrated Windows Authentication.
In that case, the login used by the end-user is in the form DOMAIN/userName.
The AfterToken attribute parses the DOMAIN/userName string into userName.
The parsed result userName is compared with AD_Entry:sAMAccountName property value of
Directory_User resources.
The matching Directory_User resource is the resource that stands for the end-user identity within Usercube.
<SelectUserByIdentityQueryHandlerSetting
ResourceIdentityProperty="AD_Entry:sAMAccountName"
ResourceDisplayNameProperty="AD_Entry:displayName"
OwnerPhotoTagProperty="Directory_User:PhotoTag"
OwnerEntityType="Directory_User"
AfterToken="\"/>
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| AfterToken optional | Type String Description Second character used to trim the authentication login. The trimmed result is the content of the authentication login between AfterToken and BeforeToken. If BeforeToken is empty, trimmed result is everything after AfterToken. If AfterToken is empty, trimmed result is everything before BeforeToken. |
| BeforeToken optional | Type String Description First character used to trim the authentication login. The trimmed result is the content of the authentication login between AfterToken and BeforeToken. If BeforeToken is empty, trimmed result is everything after AfterToken. If AfterToken is empty, trimmed result is everything before BeforeToken. |
| Identifier default value: SelectUserByIdentityQueryHandler | Type String Description Unique identifier of the setting. |
| OwnerEntityType optional | Type String Description Entity type of the resources used to store digital identities within Usercube. |
| OwnerPhotoTagProperty optional | Type String Description Photo property for Usercube users. |
| ResourceDisplayNameProperty optional | Type String Description Property used for displaying login data at the top right of the application. |
| ResourceIdentityProperty optional | Type String Description Identity-resource property supposed to match the authentication login used by the end-user. |
Automation Rule
Automation rules make automatic decisions instead of the reviewer on assignments that still need to be reviewed after a given waiting period.
There are distinct types of automation rules:
-
A composite role automation rule targets the assigned composite roles corresponding to a given composite role.
CompositeRoleAutomationRuleis equivalent toAutomationRulewith itsTypeset toCompositeRole, and requires specifying theCompositeRoleproperty; -
A single role automation rule targets the assigned single roles corresponding to a given single role.
SingleRoleAutomationRuleis equivalent toAutomationRulewith itsTypeset toSingleRole, and requires specifying theSingleRoleproperty; -
A resource type automation rule targets the assigned resource types corresponding to a given resource type.
ResourceTypeAutomationRuleis equivalent toAutomationRulewith itsTypeset toResourceType, and requires specifying theResourceTypeproperty; -
A category automation rule targets the assigned roles and resource types corresponding to a given category and a given entity type.
CategoryAutomationRuleis equivalent toAutomationRulewith itsTypeset toCategory, and requires specifying theCategoryandEntityTypeproperties; -
A policy automation rule targets the assigned roles and resource types corresponding to a given policy and a given entity type.
PolicyAutomationRuleis equivalent toAutomationRulewith itsTypeset toPolicy, and requires specifying thePolicyandEntityTypeproperties.
Remember, Netwrix recommends always using the typed syntax.
For example, you should always use SingleRoleAutomationRule, rather than AutomationRule with
Type set to CompositeRole.
All these rules target the assignments which have a specific workflow state which is specified in the rule.
Automation rules can also specify dimensions.
One assignment should be involved in the decision of only one automation rule. However, one assignment can easily be targeted by several automation rules. In this case, the Provisioning Policy algorithm prioritizes the most specific rule.
For example, considering an assigned composite role, Usercube's algorithm prioritizes a composite role automation rule, before a category automation rule, before a policy automation rule.
After this prioritization, when an assignment is still targeted by several rules due to dimensions, then Usercube prioritizes a rule implying a decline decision.
Examples
In the following example, the two first rules are equivalent (except for the workflow state's value), but the second one shows the preferred syntax.
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
This rule approves all the assignments of the "FCT0070" composite role, which are waiting for the first of two required approvals for more than one hour:
<AutomationRule Type="CompositeRole" CompositeRole="FCT0070" WorkflowState="PendingApproval1" HoursToWait="1" Decision="Approve"/>
This rule approves all the assignments of the "FCT0070" composite role, which are waiting for the second of two required approvals for more than one hour:
<CompositeRoleAutomationRule CompositeRole="FCT0070" WorkflowState="PendingApproval2" HoursToWait="1" Decision="Approve"/>
This rule approves all the assignments of the "BO028" single role, which are waiting for their required approval for more than one hour:
<SingleRoleAutomationRule SingleRole="BO028" WorkflowState="PendingApproval" HoursToWait="1" Decision="Approve"/>
This rule approves all the assignments of the "SAB_User_NominativeUser" resource type, which are waiting for their required approval for more than one hour:
<ResourceTypeAutomationRule ResourceType="SAB_User_NominativeUser" WorkflowState="PendingApproval" HoursToWait="1" Decision="Approve"/>
This rule declines all the assignments to the entity type "Directory_User" concerning the "IT Administration" category, which are waiting for the first of two required approvals for more than one hour:
<CategoryAutomationRule Category="IT Administration" WorkflowState="PendingApproval1" HoursToWait="1" Decision="Decline" EntityType="Directory_User"/>
This rule declines all the assignments to the entity type "Directory_User" concerning the "Default" policy, which are found during a synchronization without a linked automatic rule, for more than one hour:
<PolicyAutomationRule Policy="Default" WorkflowState="Found" HoursToWait="1" Decision="Decline" EntityType="Directory_User"/>
This rule declines all the assignments to the entity type "Directory_User" concerning the "Default" policy, which are found during the first synchronization without a linked automatic rule, for more than one hour:
<PolicyAutomationRule Policy="Default" WorkflowState="Historic" HoursToWait="1" Decision="Decline" EntityType="Directory_User"/>
Properties
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Category optional | Int64 | Identifier of the category targeted by the rule. |
| CompositeRole optional | Int64 | Identifier of the composite role targeted by the rule. |
| D0 optional | Int64 | Value of the dimension 0 (up to 127) that filters the assignments targeted by the rule. |
| Decision default value: 0 | AutomationRuleDecision | Decision to apply on the targeted assignments. 0 - Approve. 1 - Decline. |
| EntityType required | Int64 | Identifier of the entity type targeted by the rule. This property should not be specified when writing an automation rule among the following: composite role automation rule; single role automation rule; resource type automation rule. These rules imply the entity type. |
| HoursToWait default value: -1 | Int32 | Waiting period (in hours) from the most recent change in the workflow state of the assignments, before the decision can be applied. |
| L0 default value: false | Boolean | True to indicate that the rules targets the assignments with not only the dimension 0 (up to 127), but also this dimension's child elements. |
| Policy optional | Int64 | Identifier of the policy that the rule is part of. |
| ResourceType optional | Int64 | Identifier of the resource type targeted by the rule. |
| SingleRole optional | Int64 | Identifier of the single role targeted by the rule. |
| Type required | AutomationRuleType | Object type targeted by the rule. 0 - CompositeRole. 1 - SingleRole. 2 - ResourceType. 4 - Category. 5 - Policy. |
| WorkflowState default value: 0 | WorkflowState | Workflow state of the assignments targeted by the rule. 0 - None: used for Usercube's internal computation. 1 - Non-conforming: the assignment is not supported by a rule. 3 - Pre-existing: the assignment is not supported by a rule, and it existed before the production launch. 4 - Requested: the assignment is requested via a workflow, but not yet added. NOTE: Usually displayed in workflows' summaries. 5 - Calculated - Missing Parameters: the assignment was done by a rule which does not specify at least one required parameter for the role. 8 - Pending Approval: the assignment must be reviewed manually by a knowledgeable user. 9 - Pending Approval 1 of 2: the assignment is pending the first approval on a two-step workflow. 10 - Pending Approval 2 of 2: the assignment is pending the second approval on a two-step workflow. 11 - Pending Approval 1 of 3: the assignment is pending the first approval on a three-step workflow. 12 - Pending Approval 2 of 3: the assignment is pending the second approval on a three-step workflow. 13 - Pending Approval 3 of 3: the assignment is pending the third approval on a three-step workflow. 16 - Approved: the assignment has completed all approval steps. 17 - Declined: the assignment is explicitly declined during one of the approval steps. 18 - Calculated: the assignment is given by one of Usercube's rules. 19 - Inactive: the assignment has expired and is not yet removed. Does not appear in the UI. 20 - Cancellation: the assignment is inferred by a role that was declined. See the Reconcile a Property topic for additional information. 21 - Suggested: the assignment comes from a rule of type Suggested and appears among suggested permissions in the owner's permission basket. See the SingleRoleRule topic for additional information. 22 - Suggested: the assignment comes from a rule of type Automatic but with Validation and appears among suggested permissions for a pre-existing user. See the SingleRoleRule topic for additional information. Remember, the states 21 and 22 are both displayed in the UI as Suggested but they do not mean the exact same thing. 23 - Automatic but with Validation: the assignment comes from a rule of type Automatic but with Validation and appears in a new user's permission basket. See the SingleRoleRule topic for additional information. 24 - Approved - Questioned: the assignment was approved manually, then a change has been made in the assignment's source data via one of Usercube's workflows that should change the assignment but the manual approval is authoritative. See the Resource Type topic for additional information. 25 - Pending Approval - Risk: the assignment must be reviewed due to a risk. 26 - Blocked: the assignment is blocked due to a risk of type Blocking. Does not appear in the UI. 27 - Prolonged: the assignment has expired but it was set with a grace period. See the SingleRoleRule topic for additional information. 116 - Approved - Risk: the assignment is approved despite a risk. 118 - Given by a Role: the assignment comes from the assignment of a role. For example, when a user is assigned a SAP entitlement without having a SAP account, the account is created automatically with this state. |
Category
A category is a classification of Composite Roles, Single Roles or/and Resource Types. It can be used to group multiple roles of the same context.
Examples
The following example declares a new category called "Shares - Public".
<Category Policy="Default" Identifier="Shares - Public" DisplayName_L1="Shares - Public" />
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Description_L1 optional | Type String Description Describe this category in detail. |
| DisplayName_L1 required | Type String Description Display name of the category in language 1 (up to 16). |
| Identifier required | Type String Description Unique identifier of the category. |
| IsCollapsed default value: false | Type Boolean Description Defines if the category must be collapsed by default in the permission list of a resource (View Permissions popup and roles basket). |
| Parent optional | Type Int64 Description Represents the parent category definition. |
| Policy required | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the policy that the category is part of. |
CompositeRole
Defines basic information about a composite role. Composite roles identify affiliations or job functions by which users can be grouped. A composite role is a business role comprehensible by managers. It provides a layer of abstraction above existing entitlements, technical roles and single roles.
Roles can be used to:
- Grant various types and levels of access.
- Restrict access to sensitive information assets by grouping entitlements in a form that is meaningful to the business.
- Grant the minimum privileges required by an individual to perform his/her job.
Roles can be requested manually, or they can be configured to be assigned automatically via a Composite Role Rule. To further control access, roles can be related via required, inherited, or permitted relationships.
Examples
The following example declares a new composite role.
<CompositeRole Identifier="HR_Accounting" DisplayName_L1="HR:accounting" Category="HR" ApprovalWorkflowType="One" EntityType="Directory_User" Policy="Default"/>
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| ApprovalWorkflowType default value: 0 | Type ProvisioningPolicyApprovalWorkflow Description Number of validations required to assign manually the composite role (from None to Three). The value ManualAssignmentNotAllowed is used when a manual assignment cannot be performed. |
| Category optional | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the category that the role is part of. |
| CommentActivationOnApproveInReview default value: Inherited | Type CommentActivationWithInherited Description Indicates if a comment is enabled when reviewing a request of the role and deciding to approve it. 0 - Disabled 1 - Optional 2 - Required 3 - Inherited: comment activation in the associated policy. |
| CommentActivationOnDeclineInReview default value: Inherited | Type CommentActivationWithInherited Description Indicates if a comment is enabled when reviewing a request of the role and deciding to refuse it. 0 - Disabled 1 - Optional 2 - Required 3 - Inherited: comment activation in the associated policy. |
| CommentActivationOnDeleteGapInReconciliation default value: Inherited | Type CommentActivationWithInherited Description Indicates if a comment is enabled when reviewing a non-conforming assignment of the role and deciding to delete it. 0 - Disabled 1 - Optional 2 - Required 3 - Inherited: comment activation in the associated policy. |
| CommentActivationOnKeepGapInReconciliation default value: Inherited | Type CommentActivationWithInherited Description Indicates if a comment is enabled when reviewing a non-conforming assignment of the role and deciding to keep it. 0 - Disabled 1 - Optional 2 - Required 3 - Inherited: comment activation in the associated policy. |
| Description_L1 optional | Type String Description Detailed description of the single role in language 1 (up to 16). |
| DisplayName_L1 required | Type String Description Display name of the composite role in language 1 (up to 16). |
| EntityType required | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the entity type whose resources can receive the composite role. |
| GracePeriod optional | Type Int32 Description Duration (in minutes) for which a lost automatic composite role is prolonged. The grace period is only applied if the loss of the entitlement is due to a change in the rules (rule deletion or criteria changes). A review will be required to validate or decline the entitlement prolongation. Inferred entitlements won't be lost unless the end of the grace period is reached or the prolongation is declined. If it is not defined, the value is inherited from the policy. |
| HideOnSimplifiedView default value: false | Type Boolean Description true to show the role in a user's basket only in advanced view and not simplified view. This flag is applied only on automatic assignments. |
| Identifier required | Type String Description Unique identifier of the composite role. |
| ImplicitApproval default value: 0 | Type Byte Description Indicates if the validation steps of the composite role can be skipped. 0 - Inherited: implicit approval value in the associated policy. 1 - Explicit: all the workflow steps must be approved. 2 - Implicit: the workflow steps can be skipped if the requester has enough permissions. |
| MaxDuration optional | Type Int32 Description Duration (in minutes) after which the role will be automatically revoked, if no earlier end date is specified. It impacts only the roles which are manually assigned after the maximum duration is set. Pre-assigned roles are not impacted. If no duration is set on the role, the MaxDuration of the associated policy is applied. If the MaxDuration is set to 0 on the role, it prevents the associated policy from applying its MaxDuration to it. |
| Policy required | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the policy that the role is part of. |
| ProlongationWithoutApproval default value: 0 | Type ProlongationWithoutApproval Description Indicates whether the role can be extended without any validation. 0 - Inherited: gets the value from the policy. 1 - Enabled. 2 - Disabled. |
| R0 default value: false | Type Boolean Description true to set the dimension 0 (up to 3V following the base32hex convention) as a required parameter when assigning the role. |
| Tags optional | Type String Description Tags of the roles targeted by the campaign filter. The tag separator is �. |
CompositeRoleRule
A composite role rule assigns a composite role to users who match given criteria.
Examples
The following example declares a new rule to give the composite role "HR_Accounting" to all the "FCT0008" users.
<CompositeRoleRule Role="HR_Accounting" D1="FCT0008" Policy="Default" /> <CompositeRoleRule Role="HR_Accounting" D1="FCT0008" Type="Suggested" Policy="Default" />
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| D0 optional | Type Int64 Description Value to match for the dimension D0 (up to D127) to trigger the rule. For example, considering that D0 corresponds to users' countries, then set D0 to France to assign the composite role to users whose country is France. |
| IsDenied default value: false | Type Boolean Description true to forbid the assignment instead of applying it. |
| L0 default value: false | Type Boolean Description true to activate inheritance for D0 (up to 127). |
| ParentRole optional | Type Int64 Description Identifier of a composite role that users must have to trigger the rule. |
| Policy required | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the policy that the rule is part of. |
| Role required | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the composite role to be assigned. |
| Type default value: 0 | Type RuleType Description Type of the rule. 0 - Required: the role is automatically assigned to users matching the criteria. 1 - RequestedAutomatically: the role is listed in the permission basket of new workers, these assignments can still be modified. For existing workers, the rule's type is Suggested. 2 - Suggested: the role is listed among suggested permissions in the permission basket of users matching the criteria during an entitlement request, suggested assignments must be selected manually to be requested. |
Context
A context is the result of the combination of all identity-related entities, for example personal data, contracts or positions, so that all dimension values contained in a given context are valid for a given user on a given period of time.
Contexts define the resources' scopes of responsibility. They are used during provisioning to simplify the application of the role model's rules based on dimensions.
See more information about context generation.
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Automatic default value: false | Type Boolean Description Specifies the automatic assignments. |
| D0 optional | Type Int64 Description Dimension0 identifier, specifies the scope in which the assignment is restricted. Going from 0 to 127. |
ContextRule
A context rule configures, for the identities of a given entity type, the generation of contexts which are used in provisioning to simplify the application of the role model's rules.
A context rule should be created for each entity type for which we want to assign entitlements automatically based on users' attributes.
Without a context rule, automatic entitlements (assigned via the role model's rules):
- cannot be assigned based on users' attributes;
- don't have specific start and end dates, so they are valid from the resource creation until its deletion.
See more information about context generation.
A context rule can be configured with record sections in situations where a user needs to be modeled by several contexts over time or simultaneously.
Without record sections, a context rule can generate only one context per user. This means that users cannot have more than one contract, or position, at a time, and that data changes cannot be anticipated.
Examples
The following example generates contexts, i.e. sets of dimension-value pairs, for users from
Directory_User as resources of Directory_User:Records.
Both the start and end dates of the future contexts are defined with C# expressions based on users' contract and position start/end dates.
All contexts are to be made of the properties specified by the bindings B0 to B7.
<ContextRule Identifier="Directory_User" DisplayName_L1="Directory_User" Policy="Default" SourceEntityType="Directory_User" ResourcesBinding="Records" ResourcesStartExpression="C#:record:return record.StartDate ?? record.PositionStartDate ?? record.ContractStartDate;" ResourcesEndExpression="C#:record:return record.EndDate ?? record.PositionEndDate ?? record.ContractEndDate;"
B0="Directory_UserRecord:Organization"
B1="Directory_UserRecord:Title"
B2="Directory_UserRecord:Site"
B3="Directory_UserRecord:Site.Region.Country"
B4="Directory_UserRecord:UserType.Category"
B5="Directory_UserRecord:Organization.Type"
B6="Directory_UserRecord:Subsidiary"
B7="Directory_UserRecord:ExternalCompany"
/>
ExcludeExpression
The following example is similar to the previous one, except that we choose to exclude users declared as "draft" from the role model and provisioning calculations.
<ContextRule Identifier="Directory_User" DisplayName_L1="Directory_User" Policy="Default" SourceEntityType="Directory_User" ResourcesBinding="Records" ResourcesStartExpression="C#:record:return record.StartDate ?? record.PositionStartDate ?? record.ContractStartDate;" ResourcesEndExpression="C#:record:return record.EndDate ?? record.PositionEndDate ?? record.ContractEndDate;" ExcludeExpression="C#:record:return record.IsDraft.GetValueOrDefault();"
B0="Directory_UserRecord:Organization"
B1="Directory_UserRecord:Title"
B2="Directory_UserRecord:Site"
B3="Directory_UserRecord:Site.Region.Country"
B4="Directory_UserRecord:UserType.Category"
B5="Directory_UserRecord:Organization.Type"
B6="Directory_UserRecord:Subsidiary"
B7="Directory_UserRecord:ExternalCompany"
/>
This option can exclude workers who are not validated yet, or who have left the company, for example.
RiskFactorType
The following example is similar to the previous one, except that we force the final risk score of a user to be the maximum value of all their risk scores.
<ContextRule Identifier="Directory_User" DisplayName_L1="Directory_User" Policy="Default" SourceEntityType="Directory_User" ResourcesBinding="Records" ResourcesStartExpression="C#:record:return record.StartDate ?? record.PositionStartDate ?? record.ContractStartDate;" ResourcesEndExpression="C#:record:return record.EndDate ?? record.PositionEndDate ?? record.ContractEndDate;" ExcludeExpression="C#:record:return record.IsDraft.GetValueOrDefault();" RiskFactorType="Max"
B0="Directory_UserRecord:Organization"
B1="Directory_UserRecord:Title"
B2="Directory_UserRecord:Site"
B3="Directory_UserRecord:Site.Region.Country"
B4="Directory_UserRecord:UserType.Category"
B5="Directory_UserRecord:Organization.Type"
B6="Directory_UserRecord:Subsidiary"
B7="Directory_UserRecord:ExternalCompany"
/>
Role mining
Context rules also contain some parameters for role mining.
Users are distributed in a hypercube made of all dimensions, like in the following table (left) when
we have only 2 dimensions, where for example 1, 2, 3, etc. are users' possible locations, and
A, B, C, etc. are users' possible departments in the company. When considering one dimension
and sorting the dimension values per user percentage, we get the following table (right).
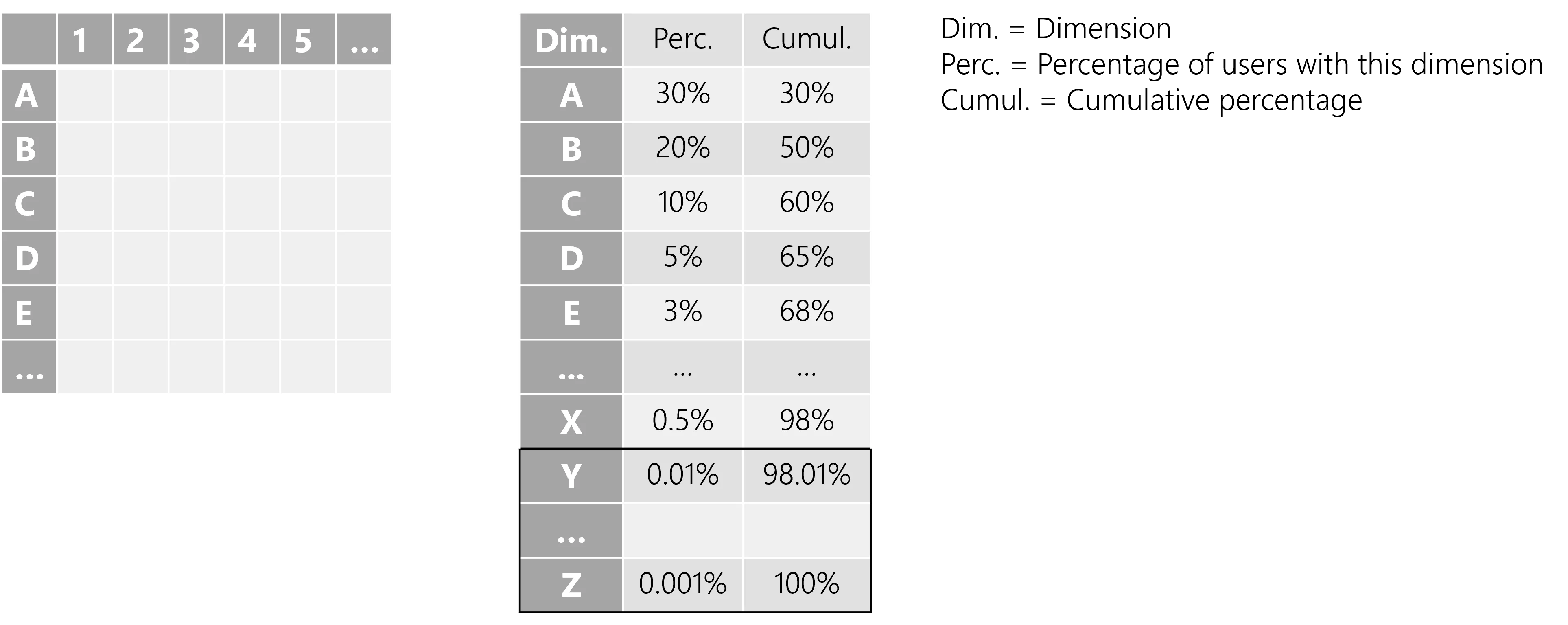
The tables here represent a simple situation with few dimensions. But the higher the number of dimensions, the more complex are role mining's computations. This is known as the curse of dimensionality.
The following example is similar to the first one, except that we customize some role mining parameters which help tackle the curse of dimensionality:
-
MinIdentitiesCountestablishes that the role mining's engine will generate a role assignment rule only when the rule is applicable to at least 5 users; -
ReductionOutlierPercentageestablishes that the role mining's engine will consider the last 2.0% dimension values (fromYtoZin the table above) to be grouped together in a single category "Others".The definition of the outlier percentage is particularly useful when managing, for example a services company with thousands of distinct organizations, where many organizations contain only one or two users. We can safely choose to group into a single fictitious organization the 2% of all users that involve the smallest organizations.
<ContextRule Identifier="Directory_User" DisplayName_L1="Directory_User" Policy="Default" SourceEntityType="Directory_User" ResourcesBinding="Records" ResourcesStartExpression="C#:record:return record.StartDate ?? record.PositionStartDate ?? record.ContractStartDate;" ResourcesEndExpression="C#:record:return record.EndDate ?? record.PositionEndDate ?? record.ContractEndDate;" MinIdentitiesCount="5" ReductionOutlierPercentage="2.0"
B0="Directory_UserRecord:Organization"
B1="Directory_UserRecord:Title"
B2="Directory_UserRecord:Site"
B3="Directory_UserRecord:Site.Region.Country"
B4="Directory_UserRecord:UserType.Category"
B5="Directory_UserRecord:Organization.Type"
B6="Directory_UserRecord:Subsidiary"
B7="Directory_UserRecord:ExternalCompany"
/>
Certification items
Unlike ResourcesStartBinding and ResourcesEndBinding, ResourcesStartExpression and
ResourcesEndExpression cannot be used to define the resources to include in the related
certification campaigns. Thus, when needing to define which resources to include with more than
start/end bindings, add a comparison based on ResourceCertificationComparisonBinding,
ResourceCertificationComparisonOperator and ResourceCertificationComparisonValue.
The following example includes in certification campaigns only the resources that have their
IsActivePosition property set to 1.
<ContextRule Identifier="Directory_User" DisplayName_L1="Directory_User" Policy="Default" ResourcesBinding="Records" ResourcesStartExpression="C#:record:return record.StartDate ?? record.PositionStartDate ?? record.ContractStartDate;" ResourcesEndExpression="C#:record:return record.EndDate ?? record.PositionEndDate ?? record.ContractEndDate;" SourceEntityType="Directory_User" ExcludeExpression="C#:record:return record.IsDraft.GetValueOrDefault();" RiskFactorType="Max" ResourceCertificationComparisonBinding="Directory_UserRecord:IsActivePosition" ResourceCertificationComparisonOperator="Equal" ResourceCertificationComparisonValue="1"
B0="Directory_UserRecord:Organization"
B1="Directory_UserRecord:Title"
B2="Directory_UserRecord:Site"
B3="Directory_UserRecord:Site.Region.Country"
B4="Directory_UserRecord:UserType.Category"
B5="Directory_UserRecord:Organization.Type"
B6="Directory_UserRecord:Subsidiary"
B7="Directory_UserRecord:ExternalCompany"
/>
Note: must be configured together with the other ResourceCertificationComparison properties.
Note: when not specified, certification items are defined by ResourcesStartBinding and
ResourcesStartBinding.
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| B0 optional | Type Int64 Description Binding of the dimension 0 (up to 3V in base32hex). The dimension can then be used in rules to filter the rules' targets. |
| DisplayName_L1 required | Type String Description Display name of the context rule in language 1 (up to 16). |
| ExcludeExpression optional | Type String Description C# expression that defines the resources to exclude from context generation, because they should not be part of the role model and provisioning calculations. See more details on C# expressions. |
| Identifier required | Type String Description Unique identifier of the context rule. |
| MinIdentitiesCount default value: 0 | Type Int32 Description Minimum number of identities to take into account to generate a rule by the role mining engine. |
| Policy required | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the policy that the rule is part of. |
| ReductionOutlierPercentage default value: 0.0 | Type Float Description Proportion of identities that are grouped together by role mining to aggregate all the small entities in one "other" category. This is used to speed up the mining process as the number of groups can be greatly reduced. |
| ResourceCertificationComparisonBinding optional | Type Int64 Description Binding of the property whose value is to be compared to ResourceCertificationComparisonValue in order to specify the resources to include in the related certification campaigns. Note: must be configured together with the other ResourceCertificationComparison... properties. Note: when not specified, certification items are defined by ResourcesStartBinding and ResourcesStartBinding. And when they are not specified either, there is no filtering, so all valid resources (those with ValidTo later than today's date) are included. |
| ResourceCertificationComparisonOperator optional | Type QueryComparisonOperator Description Operator of the comparison that specifies the resources to include in the related certification campaigns. Note: must be configured together with the other ResourceCertificationComparison... properties. Note: when not specified, certification items are defined by ResourcesStartBinding and ResourcesStartBinding. And when they are not specified either, there is no filtering, so all valid resources (those with ValidTo later than today's date) are included. |
| ResourceCertificationComparisonValue optional | Type String Description Value to be compared to the value of ResourcesCertificationComparisonBinding in order to specify the resources to include in the related certification campaigns. Note: must be configured together with the other ResourceCertificationComparison... properties. Note: when not specified, certification items are defined by ResourcesStartBinding and ResourcesStartBinding. And when they are not specified either, there is no filtering, so all valid resources (those with ValidTo later than today's date) are included. |
| ResourcesBinding optional | Type Int64 Description Binding that represents the entity type of the contexts to be created from the SourceEntityType. It can also be defined via ResourcesExpression. |
| ResourcesEndBinding optional | Type Int64 Description Binding of the date property among those from ResourcesBinding which specifies the end of validity for all properties of the context. It can also be defined via ResourcesEndExpression. Note: a context rule's start and end dates are ignored when the related identities are also configured with record sections. |
| ResourcesEndExpression optional | Type String Description Expression based on the ResourcesBinding entity type that defines the end of validity for all properties of the context. It can also be defined via ResourcesEndBinding. See more details on C# expressions. Note: a context rule's start and end dates are ignored when the related identities are also configured with record sections. |
| ResourcesExpression optional | Type String Description Expression based on SourceEntityType that defines the entity type of the contexts to be created. It can also be defined via ResourcesBinding. See more details on C# expressions. |
| ResourcesStartBinding optional | Type Int64 Description Binding of the date property among those from ResourcesBinding which specifies the beginning of validity for all properties of the context. It can also be defined via ResourcesStartExpression. Note: a context rule's start and end dates are ignored when the related identities are also configured with record sections. |
| ResourcesStartExpression optional | Type String Description Expression based on the ResourcesBinding entity type that defines the beginning of validity for all properties of the context. It can also be defined via ResourcesStartBinding. See more details on C# expressions. Note: a context rule's start and end dates are ignored when the related identities are also configured with record sections. |
| RiskFactorType optional | Type RiskFactorType Description Operator used to aggregate a user's risk scores together to compute the user's global risk score. 0 - None. 1 - Max: a user's final risk score is the maximum value among all their risk scores. 2 - Average: a user's final risk score is the average value of all their risk scores. |
| SourceEntityType required | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the entity type of the parent resource. |
Provisioning
This section describes different entities that manages the process of granting, changing, or removing user permissions to systems, applications and databases based on the security policy.
-
AutomationRule
-
BulkChange
-
Category
-
CompositeRole
-
CompositeRoleRule
-
Context
-
ContextRule
-
IndirectResourceRule
-
MiningRule
-
Policy
-
RecordSection
-
ResourceClassificationRule
-
ResourceCorrelationRule
-
ResourceType
-
Risk
-
RoleMapping
-
SingleRole
-
SingleRoleRule
IndirectResourceRule
An indirect resource rule is a link between a resource and its indirect groups, equivalent in another system and the indirect groups of the equivalent in the other system.
Examples
For example:
<IndirectResourceRule
ResourceType="MicrosoftEntraID_DirectoryObject_NominativeUser"
Property="memberOf"
Correspondence="SharePointObject"
CorrespondenceMembershipProperty="Group"
Entitlement="Entitlement"
/>
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Correspondence optional | Type Int64 Description Property used to link the resource with an associated resource in another system, like Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Microsoft Azure AD) or SharePoint groups. |
| CorrespondenceMembershipProperty optional | Type Int64 Description Same as Property but for the associated resource found in the external system. |
| Entitlement optional | Type Int64 Description Property used if the assignment is not given by the property in the external system. In the example, the assignment that we are looking for is not whether a user is in a group. Instead, it is the entitlement(s) given by the groups of which the user is a member. |
| Property required | Type Int64 Description Resource property for membership. Example: if our entity is a group, the group(s) it belongs to. |
| ResourceType required | Type Int64 Description Represents the Id of the ResourceType you want to use the rule on. |
MiningRule
After roles are assigned to users, Usercube can use mining rules to perform role mining. Role mining means that Usercube analyzes existing assignments in order to suggest single role rules which will assign single roles to certain users matching given criteria.
The role mining task replaces the existing single role rules in the specified rule policy with the new generated ones.
Examples
The following example set of mining rules targets the roles owned by users from Directory_User.
These mining rules are part of the Default policy while the role assignment rules are to be
generated to be part of the Mining policy.
The following rules have a different impact whether they are applied individually, or all together.
Indeed, during role mining, the first mining rule of type Required applies to given roles with a
given precision, then the second mining rule applies to a larger group of roles but only to those
still with no linked single role rules.
-
The first rule will generate required rules (i.e. automatic assignments) for sensitive assignments that require 2 or 3 validations, with a high precision (via
PrecisionMinPercentageandFalsePositiveMaxPercentage).
<MiningRule EntityType="Directory_User" RulePolicy="Mining" Policy="Default" IncludeNoValidation="false" IncludeSimpleValidation="false" FalsePositiveMaxPercentage="0.03" PrecisionMinPercentage="97.0" RuleType="0" Priority="10" /> -
The second rule will generate required rules (i.e. automatic assignments) for all assignments, with a lower precision.
<MiningRule EntityType="Directory_User" RulePolicy="Mining" Policy="Default" FalsePositiveMaxPercentage="0.05" PrecisionMinPercentage="95.0" RuleType="0" Priority="1" /> -
The third rule will generate suggested rules (i.e. assignments listed as suggested in users' permission baskets) for all assignments, with an even lower precision.
<MiningRule EntityType="Directory_User" RulePolicy="Mining" Policy="Default" FalsePositiveMaxPercentage="20.0" PrecisionMinPercentage="80.0" RuleType="2" Priority="1" />
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Category optional | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the category containing the roles targeted by role mining's analysis. |
| EntityType required | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the entity type that represents the owners of the roles targeted by role mining's entitlement analysis. |
| ExcludeRole default value: false | Type Boolean Description true to ignore the specified roles during the mining process triggered by the next mining rules (in terms of priority). |
| FalsePositiveMaxPercentage default value: 0.0 | Type Float Description Maximum authorized percentage of false positive assignments, i.e. roles that are assigned to users who should not have them. NETWRIX recommends around 1%, to be lowered when working on a sensitive application and/or a large user population, and vice versa. |
| IncludeDoubleValidation default value: true | Type Boolean Description true to include in role mining's analysis the roles requiring two validations. |
| IncludeNoValidation default value: true | Type Boolean Description true to include in role mining's analysis the roles requiring zero validations. |
| IncludeSimpleValidation default value: true | Type Boolean Description true to include in role mining's analysis the roles requiring one validation. |
| IncludeTripleValidation default value: true | Type Boolean Description true to include in role mining's analysis the roles requiring three validations. |
| Policy required | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the policy that the mining rule is part of. |
| PrecisionMinPercentage default value: 100.0 | Type Float Description Minimum authorized percentage of correct role assignments, considering both the roles that are assigned to users who should have them, and the roles that are not assigned to users who should not have them. NETWRIX recommends around 99.5%, to be lowered when working on a sensitive application and/or a large user population, and vice versa. |
| Priority default value: 0 | Type Int32 Description Priority order of the mining rule. Usercube applies mining rules one after the other in descending order. Info: a mining rule can generate single role rules only for the single roles that were not already associated with a single role rule by another mining rule during the same role mining task. |
| RulePolicy optional | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the policy that the generated single role rules are to be part of. Note: NETWRIX recommends using a policy dedicated to role mining in order not to remove existing assignment rules. |
| RuleType default value: 0 | Type Int32 Description Represents the type of the generated single role rules. 0 - Required: the role is automatically assigned to users matching the criteria. 1 - RequestedAutomatically: the role is listed in the permission basket of new workers. These assignments can still be modified. For existing workers, the rule's type is Suggested. 2 - Suggested: the role is listed among suggested permissions in the permission basket of users matching the criteria during an entitlement request. Suggested assignments must be selected manually to be requested, and will go through the validation process. |
Policy
A policy is a next generation access control (NGAC) which works by assigning permissions to users based on their roles within an organization, and other dimensions and attributes. A policy is a sub-group of the role model, containing roles and rules, that allows an administrator to manage the access specific to their applications.
Examples
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
<Policy Identifier="Default" DisplayName_L1="Default Policy" IsProvisioningEnabled="true" />
All ResourceType, SingleRole, CompositeRole and Category must belong to a Policy. This is
done by specifying the Policy attribute.
<Category Policy="Default" Identifier="AD" DisplayName_L1="Active Directory" />
Properties
| Property | Type | Details |
|---|---|---|
| CommentActivationOnApproveInReview default value: Optional | CommentActivation | Indicates if a comment is enabled when reviewing a role request associated with the policy, and deciding to approve it. 0 - Disabled. 1 - Optional. 2 - Required. |
| CommentActivationOnDeclineInReview default value: Required | CommentActivation | Indicates if a comment is enabled when reviewing a role request associated with the policy, and deciding to refuse it. 0 - Disabled. 1 - Optional. 2 - Required. |
| CommentActivationOnDeleteGapInReconciliation default value: Optional | CommentActivation | Indicates if a comment is enabled when reviewing a non-conforming role assignment associated with the policy, and deciding to delete it. 0 - Disabled. 1 - Optional. 2 - Required. |
| CommentActivationOnKeepGapInReconciliation default value: Required | CommentActivation | Indicates if a comment is enabled when reviewing a non-conforming role assignment associated with the policy, and deciding to keep it. 0 - Disabled. 1 - Optional. 2 - Required. |
| D0 optional | Int64 | Value of the dimension 0 (up to 127) that filters the access to the policy and its roles. |
| DisplayName_L1 required | String | Display name of the policy in language 1 (up to 16). |
| GracePeriod default value: 0 | Int32 | Duration (in minutes) for which a lost automatic entitlement associated with this policy is prolonged. The grace period is only applied if the loss of the entitlement is due to a change in the rules (rule deletion or criteria changes). A review will be required to validate or decline the entitlement prolongation. Inferred entitlements won't be lost unless the end of the grace period is reached or the prolongation is declined. This value can be overwritten for each composite role and single role. |
| HasImplicitApproval default value: false | Boolean | True to skip the approval circuit when the requester has the appropriate review permissions. This value can be overwritten for each policy object (composite role, single role, resource type). |
| Identifier required | String | Unique identifier of the policy. |
| IsExternal default value: false | Boolean | True to indicate that the policy's roles are outside Usercube's scope. The roles are managed by an external source, and Usercube cannot add, update nor delete any role. |
| IsProvisioningEnabled default value: false | Boolean | True to enable the provisioning policy. |
| IsSimulationEnabled default value: false | Boolean | True to enable the provisioning policy simulation. |
| MaxDuration default value: 0 | Int32 | Duration (in minutes) after which the assignments induced by the policy will be automatically revoked, if no earlier end date is specified. It impacts only the assignments which are performed after the maximum duration is set. Pre-existing assignments are not impacted. |
| ProlongationWithoutApproval default value: false | Boolean | True to allow the policy's roles to be extended without any validation. |
RecordSection
Record sections shape identity data for a given entity type, by grouping properties into sections, for example personal data, contract or position.
Record sections impact the generation of identities' contexts which contain users' dimension values valid on a given period of time. The aim is to simplify the application of the role model' rules for provisioning.
Thanks to this data organization in sections, the identities of a given entity type can be modeled by more than one context over time, even simultaneously. This means that users can have more than one contract, or position, at a time, and that data changes can be anticipated.
See more details about identity modeling.
Configuration recommendations:
As record sections cannot be configured without a context rule, NETWRIX recommends starting with the configuration of the context rule before configuring record sections.
NETWRIX recommends defining at least two record sections: a default section for the properties shared by all records, and another section for a given set of properties which differentiate between records. The default section must contain zero properties, the shared properties are those that are not defined in the other section(s).
For example, to model several positions for a single user, we configure the default record section to contain the properties shared by all positions such as personal data, and we configure the position section to contain the properties specific to each position. Similar to the position section, we can also typically configure a section for contracts.
Examples
The following example models users from the Directory_User entity type with three sets of
properties: user properties, contract properties and position properties. All created records will
be resources from the Directory_UserRecord entity type.
The properties from the contract (or position) section are the properties specific to each contract
(or position). The properties from Directory_User that are not specified in the record sections
are the properties shared between all records, here user properties.
Each section must be defined with start and end dates, so that Usercube's engine is able to combine all periods of validity and apply the rules with the right input at any time.
Default section:
<RecordSection Identifier="Directory_UserRecord_Default" DisplayName_L1="User Properties" SourceEntityType="Directory_User" ResourceEntityType="Directory_UserRecord" StartProperty="StartDate" EndProperty="EndDate"> ...
</RecordSection>
Contract section:
<RecordSection Identifier="Directory_UserRecord_Contract" DisplayName_L1="Contract Properties" SourceEntityType="Directory_User" ResourceEntityType="Directory_UserRecord" StartProperty="ContractStartDate" EndProperty="ContractEndDate"> ...
<Property Property="UserType"/> <Property Property="ExternalCompany"/> <Property Property="Subsidiary"/></RecordSection>
Position section:
<RecordSection Identifier="Directory_UserRecord_Position" DisplayName_L1="Position Properties" SourceEntityType="Directory_User" ResourceEntityType="Directory_UserRecord" StartProperty="PositionStartDate" EndProperty="PositionEndDate"> ...
<Property Property="PositionIdentifier" /> <Property Property="JobTitle" /> <Property Property="OfficeNumber" /> <Property Property="Organization" /> <Property Property="Site"/> <Property Property="Title" /> <Property Property="Office" /> <Property Property="Manager" /> <Property Property="IGAManager" /> <Property Property="EffectiveIGAManager" /> <Property Property="IsMainPosition" /></RecordSection>
InstanceKeyExpression
The following example computes a unique key for each record section instance. This way, we can distinguish between contracts thanks to their identifiers, same for positions, and between user property sets thanks to a C# expression based on the start date.
Default section:
<RecordSection Identifier="Directory_UserRecord_Default" DisplayName_L1="User Properties" SourceEntityType="Directory_User" ResourceEntityType="Directory_UserRecord" StartProperty="StartDate" EndProperty="EndDate" InstanceKeyExpression="C#:record:return record.StartDate.HasValue ? record.StartDate.Value.ToString("yyyyMMdd") : string.Empty;"></RecordSection>
Contract section:
<RecordSection Identifier="Directory_UserRecord_Contract" DisplayName_L1="Contract Properties" SourceEntityType="Directory_User" ResourceEntityType="Directory_UserRecord" StartProperty="ContractStartDate" EndProperty="ContractEndDate" InstanceKeyExpression="C#:record:return record.ContractIdentifier;"> <Property Property="UserType"/> ...
</RecordSection>
Position section:
<RecordSection Identifier="Directory_UserRecord_Position" DisplayName_L1="Position Properties" SourceEntityType="Directory_User" ResourceEntityType="Directory_UserRecord" StartProperty="PositionStartDate" EndProperty="PositionEndDate" InstanceKeyExpression="C#:record:return record.PositionIdentifier;"> <Property Property="PositionIdentifier" /> ...
</RecordSection>
An instance key is required when we need to uniquely identify a context, i.e. when we may have several simultaneous contexts.
For example, an instance key is required for the position section when users can have overlapping positions.
IsDefaultBoundariesSection
The following example uses the contract start/end dates as default boundaries in users' validity period, instead of those from the default section. It may be because, for example, HR services do not enter an end date for the personal data of users on permanent contracts. So we prefer to use the start and end dates of their contracts.
Contract section:
<RecordSection Identifier="Directory_UserRecord_Contract" DisplayName_L1="Contract Properties" SourceEntityType="Directory_User" ResourceEntityType="Directory_UserRecord" StartProperty="ContractStartDate" EndProperty="ContractEndDate" IsDefaultBoundariesSection="true"> <Property Property="UserType"/> ...
</RecordSection>
Context extension
There can be some time gap where no context is defined, for example a time gap with a position but no contract or vice versa. Usercube offers the possibility to choose whether an existing context is to be extended to the period without context. And in case we decide to use another context and extend its values, which context should it be?
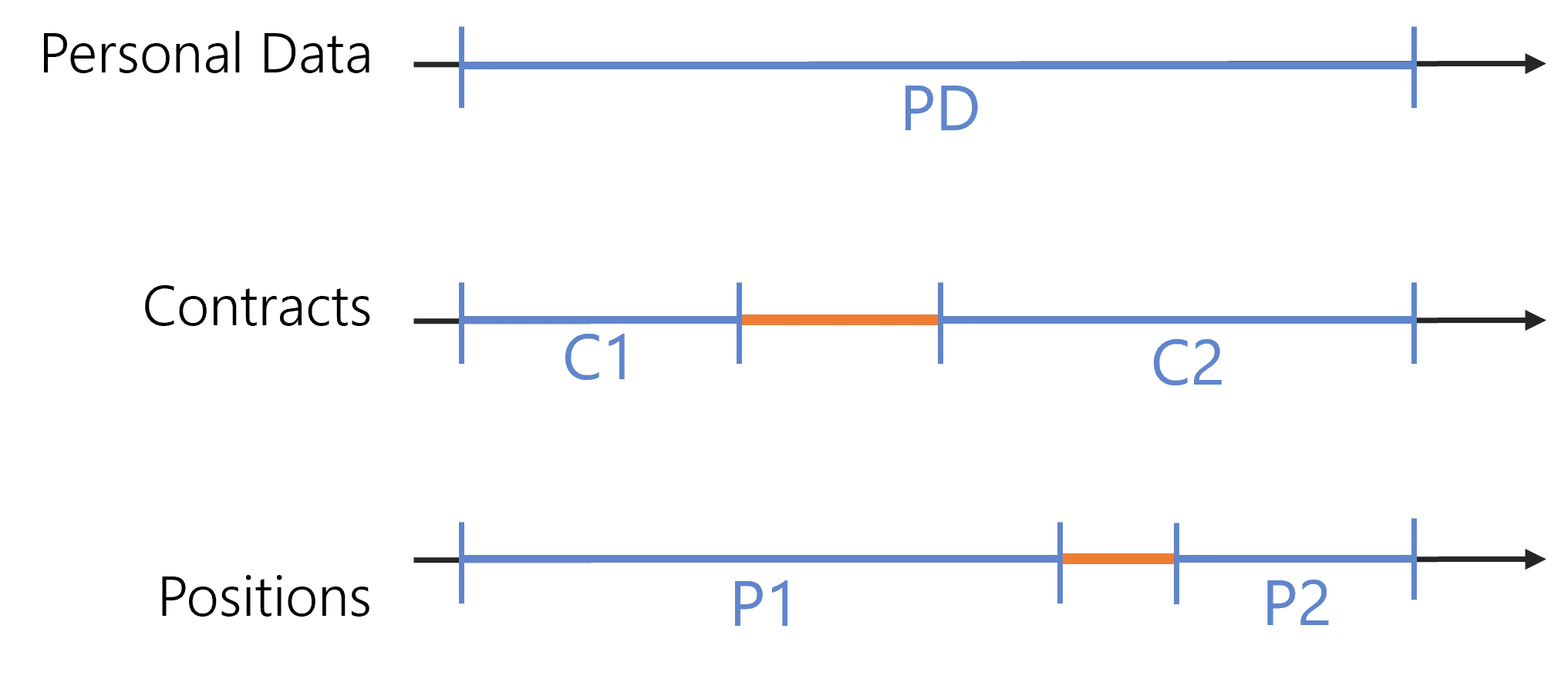
Here, we decide to extend an existing contract to the gap, for example because users' email
addresses are built using the contract type to add -ext for external users. And we decide to not
extend the position.
In the following example, the contract section uses SortKeyExpression to establish between
existing contracts a priority order that will determine which contract should be extended to the
gap. Based on this C# expression that returns a value A, B or C, the ExtendedSortKey
considers as extendable only the contract(s) whose expression returns C.
The position section uses ExtensionKind set to None to block the extension mechanism.
Contract section:
<RecordSection Identifier="Directory_UserRecord_Contract" DisplayName_L1="Contract Properties" SourceEntityType="Directory_User" ResourceEntityType="Directory_UserRecord" StartProperty="ContractStartDate" EndProperty="ContractEndDate" SortKeyExpression="C#:record:return record.Main.GetValueOrDefault() && record.UserType.Id == -018 ? "C" : (!record.Main.GetValueOrDefault() && record.UserType.Id == -018 ? "B" : "A");" ExtendedSortKey="C"> <Property Property="UserType"/> ...
</RecordSection>
Position section:
<RecordSection Identifier="Directory_UserRecord_Position" DisplayName_L1="Position Properties" SourceEntityType="Directory_User" ResourceEntityType="Directory_UserRecord" StartProperty="PositionStartDate" EndProperty="PositionEndDate" ExtensionKind="None"> <Property Property="PositionIdentifier" /> ...
</RecordSection>
When not specifying any sort key nor extended sort key, Usercube will select a context to extend to the gap. However, it may not be functionally the most meaningful context.
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| BoundaryKind default value: 0 | Type RecordBoundaryKind Description Defines how the section dates are computed for a resource, when the current start/end dates are null. 0 - None: start date and end date are equal respectively to the minimum value of StartProperty and maximum value of EndProperty when comparing the default sections of all records. 1 - Kept: start and end dates are equal respectively to the default start date (1900/01/01 00:00:00) and end date (2079/06/06 00:00:00). Info: the boundary has no effect on the default section which is the reference to compute the default dates in other sections. When the default section's start/end dates are null, then they equal the default start/end dates. |
| DisplayName_L1 required | Type String Description Display name of the section in language 1 (up to 16). |
| EndProperty optional | Type Int64 Description Date property among those from the ResourceEntityType which specifies the end of validity for all properties of the section. It cannot be a property computed by an EntityPropertyExpression. |
| ExtendedSortKey optional | Type String Description Value used as a threshold for SortKeyExpression values to determine whether the property values of a given record section can be extended from a context where the values are defined to another context where no properties from the section are defined. This extension is enabled only when the value of SortKeyExpression of the section is higher (with an ordinal comparison) than ExtendedSortKey. |
| ExtensionKind default value: 0 | Type RecordExtensionKind Description Defines whether the section's property values can be extended (copied) from a context where the properties are defined to another context where no properties from the section are defined. 0 - Default: the section's property values can be extended. 4 - None: the section's property values cannot be extended. |
| Identifier required | Type String Description Unique identifier of the section. |
| InstanceKeyExpression optional | Type String Description Expression returning a key to uniquely identify a context, i.e. distinguish between job positions for example when users can have several concurrent positions, or between contracts. See more details on C# expressions. |
| IsDefaultBoundariesSection default value: false | Type Boolean Description true to use the start/end dates of this section as the default boundaries, i.e. the start/end dates of users' validity period. When no section has IsDefaultBoundaries set to true, the default section (the one without properties) is automatically selected. |
| ResourceEntityType required | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the entity type of the multiple records to be created. |
| SortKeyExpression optional | Type String Description C# expression used to compute a value for each record, to be used as a priority, following an ordinal comparison. See more details on C# expressions. When a record section has ExtensionKind set to Default and a priority value higher than ExtendedSortKey, then the record property values can be extended from a context where the values are defined to another context where no properties from the section are defined. |
| SourceEntityType required | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the entity type of the parent resource. |
| StartProperty optional | Type Int64 Description Date property among those from the ResourceEntityType which specifies the beginning of validity for all properties of the section. It cannot be a property computed by an EntityPropertyExpression. |
Child Element: Property
A record section is a set of record properties which belong to the resource entity type.
Examples
In the following example, the position section gathers the properties Organization, Location and
Title, while the default section gathers all the other properties from Directory_UserRecord.
The property Location can be extended from a context where the location is defined to a context
where it is not. The two other properties cannot be extended.
See more details about record extension.
Default section:
<RecordSection Identifier="Directory_UserRecord_Default" DisplayName_L1="Contract Properties" SourceEntityType="Directory_User" ResourceEntityType="Directory_UserRecord" StartProperty="ContractStartDate" EndProperty="ContractEndDate">
</RecordSection>
Position section:
<RecordSection Identifier="Directory_UserRecord_Position" DisplayName_L1="Position Properties" SourceEntityType="Directory_User" ResourceEntityType="Directory_UserRecord" StartProperty="StartDate" EndProperty="EndDate">
<Property Property="Organization" ExtensionKind="None" /> <Property Property="Location"/> <Property Property="Title" ExtensionKind="None" />
</RecordSection>
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| ExtensionKind default value: 0 | Type RecordExtensionKind Description Defines whether the property value can be extended (copied) from a context where the section properties are defined to another context where no properties from the section are defined. 0 - Default: the property value can be extended. 4 - None: the property value cannot be extended. Note: a property value can be extended only if the section is extendable too. |
| IsExcluded default value: false | Type Boolean Description Excludes the given property from the section. This is used only in the default section to remove properties such as the RecordIdentifier that are always different between all the records and that are thus not interesting for the provisioning rules. |
| Property required | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the property from the record section's ResourceEntityType that is to be part of the section. |
ResourceClassificationRule
In Usercube, this type of rule is used to classify the resources based on a C# expression.
Examples
The following example declares a rule to classify the Active Directory accounts based on the dn values.
<ResourceClassificationRule ResourceType="AD_Entry_TechnicalEntry" Policy="Default" ResourceTypeIdentificationConfidenceLevel="100"
TargetExpression="C#:resource:return resource.dn.Contains(",CN=Roles,");" />
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Policy required | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the policy that the rule is part of. |
| ResourceType required | Type Int64 Description Represents the resource type definition. |
| ResourceTypeIdentificationConfidenceLevel default value: 0 | Type Int32 Description Defines the confidence level used to match the resources. |
| SourceMatchedConfidenceLevel default value: false | Type Boolean Description Defines the confidence level used to match the sources. |
| TargetExpression optional | Type String Description Defines the C# expression used to classify the resources. See more details on C# expressions. |
ResourceCorrelationRule
A correlation rule is used to correlate the resources, i.e. link resources to their owners.
Examples
Correlation based on unchanged attributes
The following example creates an Active Directory correlation rule based on the mail property:
<ResourceCorrelationRule ResourceType="AD_Entry_To_Directory_UserRecord" TargetBinding="Directory_UserRecord:Mail" Policy="Default" SourceMatchedConfidenceLevel="100" SourceBinding="AD_Entry:mail" />
Correlation based on attributes changed by a function
The following example copies the previous example (based on unchanged attributes), but using a
predefined function (ToLower) in source and target bindings' expressions, to compare the email
attributes:
<ResourceCorrelationRule ResourceType="AD_Entry_To_Directory_UserRecord" TargetBinding="Mail" TargetExpression="ToLower" Policy="Default" SourceMatchedConfidenceLevel="100" SourceBinding="mail" SourceExpression="ToLower" />
A list of predefined functions is available.
Correlation based on attributes within a C# expression
The following example creates an Active Directory correlation rule based on the comparison between the AD's simplified display name and an expression from the external system:
<ResourceCorrelationRule ResourceType="AD_Entry_NominativeUser" TargetBinding="displayName" TargetExpression="Simplify" Policy="Default" SourceMatchedConfidenceLevel="80" SourceExpression="C#:person:return (person.LastName + person.FirstName).Simplify();" />
This example also uses a confidence rate equals to 80%.
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Policy required | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the policy that the rule is part of. |
| ResourceType required | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the resource type. |
| SourceBinding optional | Type Int64 Description Binding property from the source system. |
| SourceExpression optional | Type String Description Binding expression based on properties from the source system. See more details on C# expressions. |
| SourceMatchedConfidenceLevel default value: 0 | Type Int32 Description Defines the correlation confidence rate of this rule. If the value is less than 100, we process a manual review step to confirm the choice. |
| TargetBinding optional | Type Int64 Description Binding property from the target system. |
| TargetExpression optional | Type String Description Binding expression based on properties from the target system. See more details on C# expressions. |
Resource Type
In Usercube, a resource type is a conceptual model used to categorize resources. It groups together, with a meaningful name, resources sharing the same intent and the same authorization system. Resource types are assigned directly to a resource rather than mapped to a role. A resource type can be assigned manually, or configured to be assigned automatically via a resource type rule.
Examples
The following example declares a new resource type to provision the LDAP service accounts:
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
<ResourceType Identifier="LDAP_Entry_ServiceEntry" DisplayName_L1="LDAP Entry (service)" Policy="Default" TargetEntityType="LDAP_Entry" Category="LDAP" SourceEntityType="Directory_Application" />
ArgumentsExpression
This option is used to use provisioning orders to compute useful arguments.
Most standard situations use only one workflow per action type on a resource (addition, update, deletion). But in some more complex situations (like using multi records), several workflows are available for one type of action. As the configuration JSON file of an InternalWorkflow connection cannot contain expressions, a resource type can be configured with the ArgumentsExpression attribute to explicit the arguments of provisioning orders, based on conditions and variables. See the InternalWorkflow topic for additional information.
The following example computes the identifier of the workflow to launch, based on the provisioning order as a variable (the returned value depends here mostly on the type of change):
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
<ResourceType Identifier="HR_Person_To_Directory_UserRecord" DisplayName_L1="User Record (from HR)" DisplayName_L2="Fiche de collaborateur (source RH)" Category="HR" Policy="Default" TargetEntityType="Directory_UserRecord" SourceEntityType="HR_Person" CorrelateMultipleResources="true" ArgumentsExpression="C#:resource:
if ((provisioningOrder == null) || (provisioningOrder.ChangeType.IsNone() {
return null;
}
var arguments = new System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary<string, string>();
var workflowIdentifier = "Directory_User_UpdateFromHR";
if ((provisioningOrder.ChangeType.IsAdded()) || (provisioningOrder.HasChanged("Employee_Id") {
workflowIdentifier = "Directory_User_StartInternalByHR";
}
else if (provisioningOrder.ChangeType.IsDeleted()) {
workflowIdentifier = "Directory_User_DeleteFromHR";
}
arguments.Add("WorkflowIdentifier", workflowIdentifier);
return arguments;" />
ResourceIdToCopy
Now consider a record creation for a given identity, inside a multi-record organization. Suppose that records are defined by their position and location, while other properties are the same for all records (usually the identity's personal data like the name and birth date). When creating a new record for an existing identity, you will want to copy an existing record from the database to modify only the values specific to the new record.
The following example computes the identifier of the record to copy, if the identity has already any:
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
<ResourceType Identifier="HR_Person_To_Directory_UserRecord" DisplayName_L1="User Record (from HR)" DisplayName_L2="Fiche de collaborateur (source RH)" Category="HR" Policy="Default" TargetEntityType="Directory_UserRecord" SourceEntityType="HR_Person" CorrelateMultipleResources="true" ArgumentsExpression="C#:resource:
if ((provisioningOrder == null) || (provisioningOrder.ChangeType.IsNone() {
return null;
}
var arguments = new System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary<string, string>();
if (provisioningOrder.TryGetScalar("EmployeeId", out var employeeId) && (employeeId != null)) {
var resources = queryHandler.Select<Directory_UserRecord>("Select Id Where EmployeeId="\" + employeeId.ToString() + "\"");
if (resources.Any()) {
arguments.Add("ResourceIdToCopy", resources.FirstOrDefault().Id.ToString());
}
}
return arguments;" />
DependsOn
This option is used to configure another resource type as prerequisite for this resource type.
For example, a Microsoft Exchange account requires the email address of a related Active Directory account.
In this case, we want to configure the Exchange Account resource type so that a user cannot own an Exchange account when they do not own an AD account.
The following example is meant to perform an automatic check to prevent the execution of any provisioning order for the creation of an Exchange account when the user does not own an AD nominative account.
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
<ResourceType Identifier="Exchange" DisplayName_L1="Exchange Account" Policy="Default" TargetEntityType="Exchange" Category="Accounts" SourceEntityType="Directory_User" ApprovalWorkflowType="ManualAssignmentNotAllowed" DependsOn="AD_Entry_NominativeUser">
DependsOnOwnerProperty
This option is used to configure a property as prerequisite for the resource type.
Consider an Active Directory administrator account which should be able to perform manual provisioning to ServiceNow. Then it requires the random identifier computed by ServiceNow.
In this case, we want to configure the AD_Entry_AdministrationUser resource type so that a user cannot own an AD administrator account when they do not have an identifier in ServiceNow.
NOTE: The DependsOnOwnerProperty of a resource type should only refer to scalar values that are part of the properties of the SourceEntityType.
The following example is meant to perform an automatic check to prevent the execution of any provisioning order for the creation of an AD administrator account when the user does not have an identifier in ServiceNow.
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
<ResourceType Identifier="AD_Entry_AdministrationUser" DisplayName_L1="AD User (Administration)" Policy="Default" TargetEntityType="AD_Entry" Category="Accounts" SourceEntityType="Directory_User" ApprovalWorkflowType="ManualAssignmentNotAllowed" DependsOnOwnerProperty="ServiceNow:identifier">
DiscardManualAssignments
This option is used to set Usercube as authoritative following a manual change in a managed system.
Suppose a resource type managing the provisioning of Active Directory nominative accounts based on users data in Usercube (Directory_User). Suppose a scalar rule that provisions the AD's sn property based on users' last names.
The following scenario is about a user named Cedric Blanc, whose AD's sn property is set by the scalar rule to Blanc.

Let's see what happens when the user's name is changed manually directly in the AD.
Suppose that we change in the AD the last name to White. As the scalar rule computes the sn value based on the user's data which still states the last name Blanc, such a change induces a difference between the value calculated by the rule and the actual value in the AD. This difference is spotted by the next synchronization, triggering a non-conforming assignment on the Resource Reconciliation page.

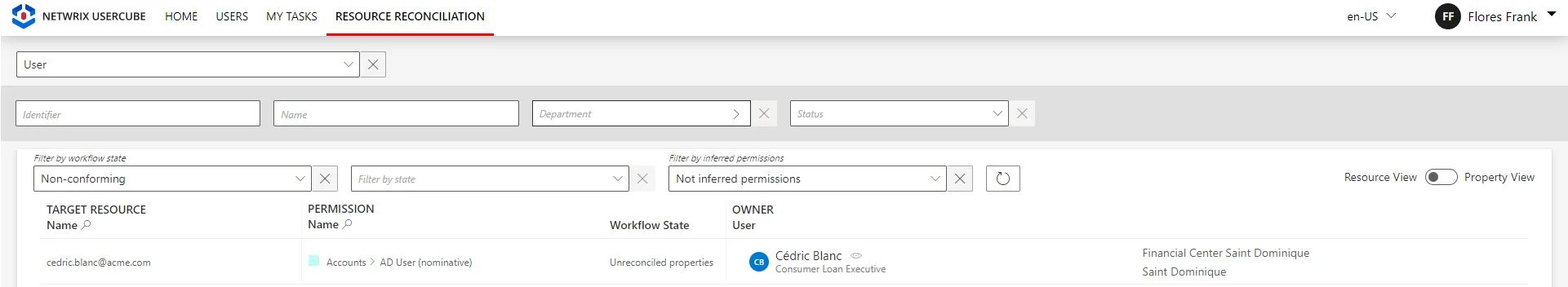
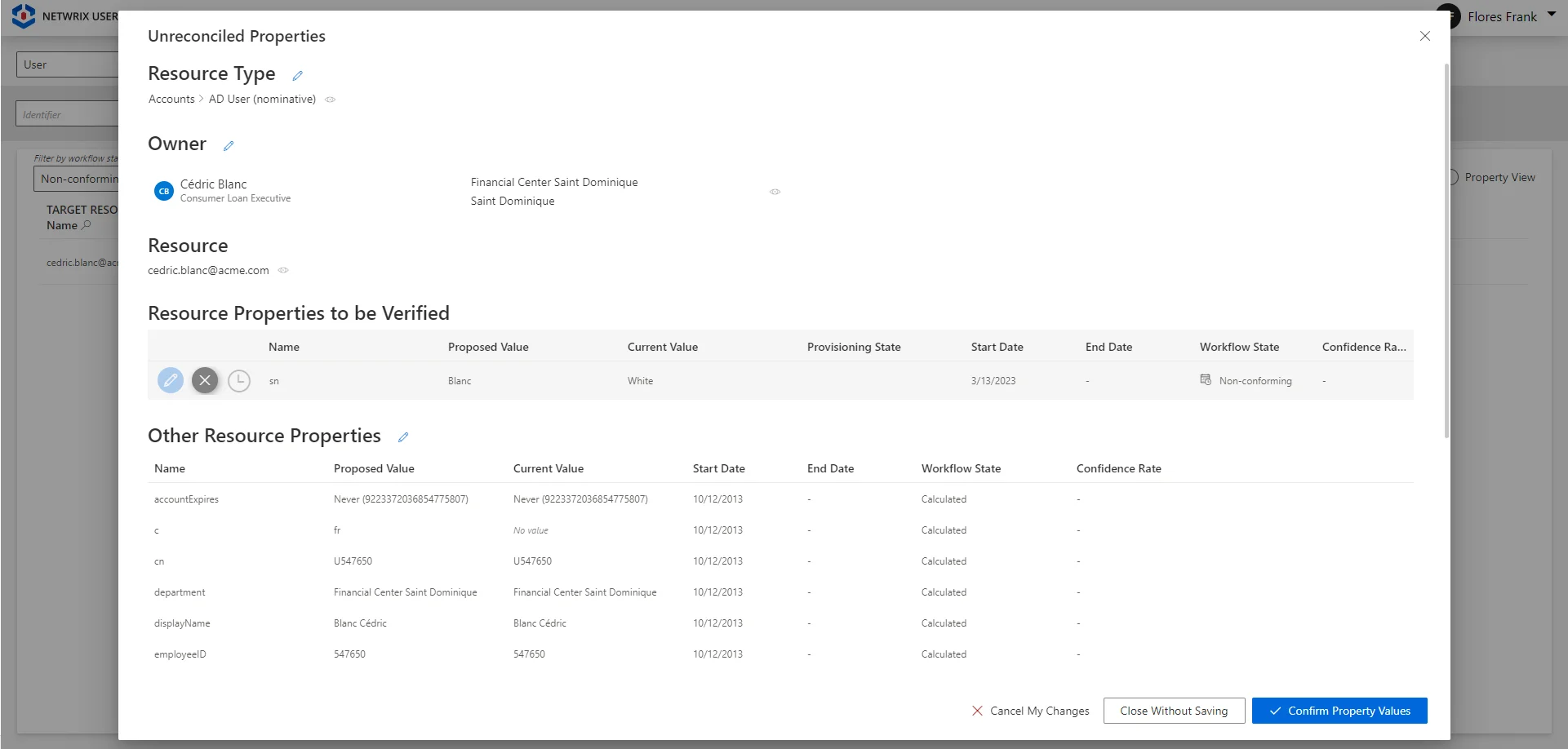
Once this manual new value is confirmed, the property is stated as Approved.

Now suppose that the user's last name is changed to Black via Usercube's workflows. As the source data is changed, the scalar rule computes a new value for sn. There are two options:
-
The default configuration (DiscardManualAssignments set to false) considers manual assignments, i.e. changes made directly in the managed system, as authoritative. So there will be no provisioning of the newly computed value for sn. The current sn value that was written manually in the AD stays as is, no matter the changes in the source data (here the user's last name). Usercube only states the property's value as Questioned.

NOTE: No change in the source data can affect the property's value. However, any manual change made in the managed system will trigger a non-conforming assignment. Then, reconciling the property by choosing to keep Usercube's suggested value will make the property's value go back to Calculated and thus follow the changes in the source data.
NOTE: If DiscardManualAssignments is changed from False to True, then the state of the property's value does not matter. Usercube applies the rules of the role model, and generates a provisioning order to overwrite the manual change White with the newly computed value Black.

In this scenario for Cedric Blanc, these behaviors can be summed up like the following:
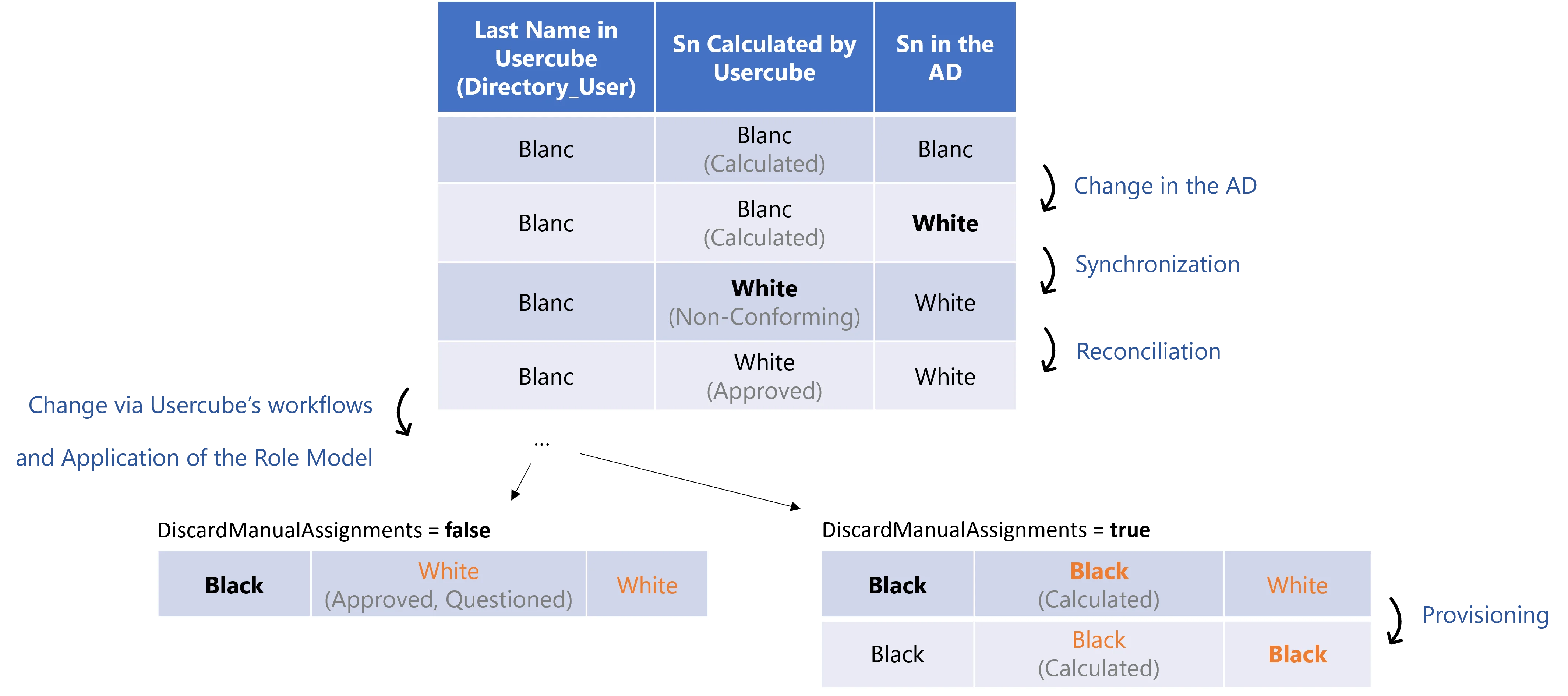
Correlate Multiple Resources
With the Correlation Multiple Resources option, Usercube can link a single owner to several existing target objects of the same resource type. This setting can be used in conjunction with the Suggest all resources option to fine tune the behavior.
Below, we illustrate the different scenarios that are possible, taking into consideration whether a resource type has previously been correlated to the owner or not.
-
The value for both Correlate Multiple Resources and Suggest All Correlations is No there is no Resource already correlated so the first match with the highest confidence rate is Correlated if it is
>100or Suggested if it is<100. As for all other matches with lower confidence rate they will be ignored.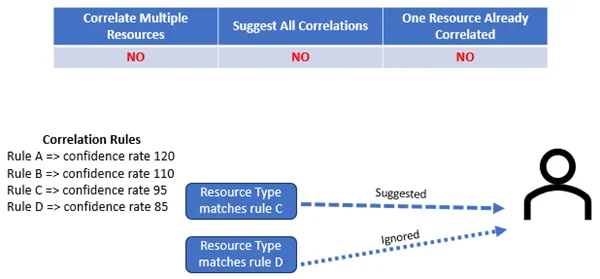
If there are no Resources to be correlated with a confidence rate
>100, the ones below with confidence rate below 100 are Suggested or Ignored.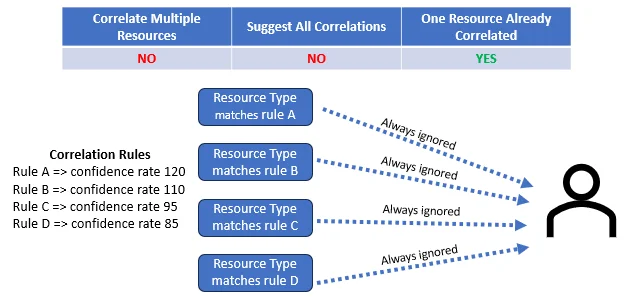
-
The value for both Correlate Multiple Resources and Suggest All Correlations is No there is one Resource already correlated so due to this all future correlations will be ignored.
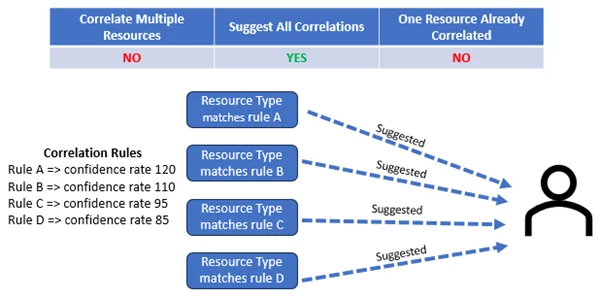
-
The value for Correlate Multiple Resources is No, Suggest All Correlations is Yes there is no Resource already correlated so all Resource Types will be Suggested.
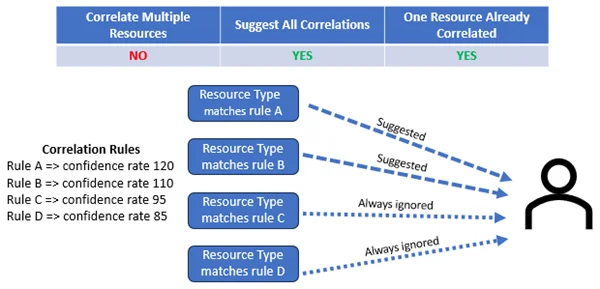
-
The value for Correlate Multiple Resources is No, Suggest All Correlations is Yes there is one Resource already correlated so the Resource Types that have a confidence rate
>100will be Suggested. As for all other matches with lower confidence rate they will be ignored.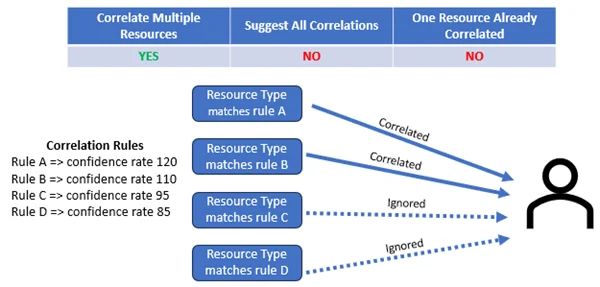
-
The value for Correlate Multiple Resources is Yes, Suggest All Correlations is No, and there is no Resource already correlated so Resource Types that have a confidence rate
>100will be Correlated and the ones<100will be Suggested if there are no higher matches otherwise they will be ignored.
If there are no Resources to be correlated with a confidence rate
>100, the ones with confidence rate below 100 are Suggested.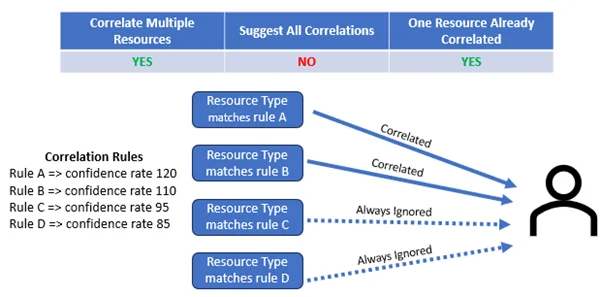
-
The value for Correlate Multiple Resources is Yes, Suggest All Correlations is No there is one Resource already correlated so the matches with confidence rate
>100will be Correlated and the ones<100will be ignored.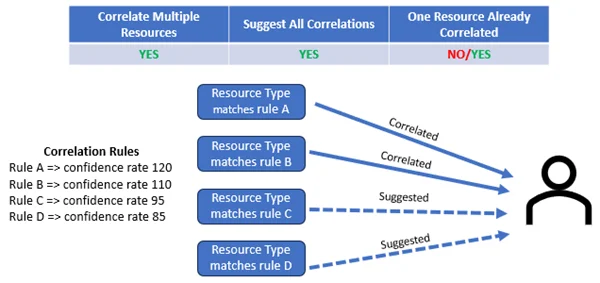
-
The value for Correlate Multiple Resources is Yes, Suggest All Correlations is Yes one Resource could be already correlated or not so the matches with confidence rate
>100will be Correlated and the ones<100will be Suggested.
Properties
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| AllowAdd default value: true | Boolean | Enables Usercube to automatically create new resources in the managed system when their owners are given the right entitlements. Otherwise, resource managers must create resources manually directly in the managed system. |
| AllowRemove default value: true | Boolean | Enables Usercube to automatically deprovision resources in the managed system when their owners are deprived of the right entitlements. Otherwise, Usercube is able to delete resources in the managed system only with a manual approval on the Resource Reconciliation screen. |
| ApprovalWorkflowType default value: 0 | ProvisioningPolicyApprovalWorkflow | Indicates the number of validation to give to a role given manually (from None to Three). The value ManualAssignmentNotAllowed is used when a manual assignment cannot be performed. Netwrix recommends using ManualAssignmentNotAllowed for all resource types. |
| ArgumentsExpression optional | String | C# expression used to compute the arguments of provisioning orders, for example a workflow identifier, in a situation where it is not obvious. The aim is to enable an InternalWorkflow connector to fulfill correctly a virtual managed system by launching the right workflows based on a given provisioning order. This expression must return a dictionary of string. ArgumentsExpression is useful only when provisioning via the following packages: Active Directory, Apache Directory, Generic LDAP, Open LDAP, Oracle LDAP, Red Hat Directory Server and Workflow. |
| BlockProvisioning default value: true | Boolean | True to block the provisioning policy orders. |
| Category optional | Int64 | Resource type category. |
| CorrelateMultipleResources default value: false | Boolean | True to extend the QueryRule/CorrelationRule to match as many target resources as possible (no blocking like this is normally the case). |
| DependsOn optional | Int64 | Identifier of another resource type that must be provisioned for a given identity before the current resource type can be provisioned for said identity. |
| DependsOnOwnerProperty optional | Int64 | Identifier of one of the owner properties that must be filled before the current resource type can be provisioned for said identity. |
| Description_L1 optional | String | Describe this resource type in detail. |
| DiscardManualAssignments default value: false | Boolean | True to always allow the provisioning of a new property value, i.e. re-computed by a provisioning rule after a change in the source data, no matter the property's current workflow state. Set to false, any manual change of a property's value made directly in the target system will be "protected" (only after the change is approved in Usercube in Resource Reconciliation). It means that a future change in the source data will not trigger the provisioning of the new value to the target system. Instead, Usercube will keep the value of the manual change, and state the value as Questioned. This option should be set to true when: * using multiple authoritative sources and the latest value should be provisioned; * a source system is not often synchronized to Usercube but should stay the authoritative source. |
| DisplayName_L1 required | String | Display name of the resource type in language 1 (up to 16). |
| FulfillHoursAheadOfTime default value: 0 | Int32 | Anticipate resource fulfill order hours ahead of they start time. It is helpful for manual fulfillment and/or long fulfillment process. It differs from TimeOffset because the start date of the resource to fulfill is not impacted. |
| HideOnSimplifiedView default value: false | Boolean | True to hide this resource type in the basket simplified view. This flag is applied only on automatic assignments. |
| Identifier required | String | Unique identifier of the resource type. |
| ImplicitApproval default value: 0 | Byte | Indicates if the validation steps of the resource type can be skipped. 0 - Inherited: implicit approval value in the associated policy. 1 - Explicit: all the workflow steps must be approved. 2 - Implicit: the workflow steps can be skipped if the requester has enough permissions. |
| ManualAssignmentEndDateLockedToContextMode default value: inherited | RoleManualAssignmentEndDateLockedToContextMode | Inherited (default value) it uses the policy's ManualAssignmentEndDateLockedToContextMode value. The values are: - Explicit, by default not context bound: By default, the assignment's end date will not be context bound in order to encourage the manual entry of an end date - Explicit, by default context bound: By default, the assignment's end date will be context bound and therefore locked, but a manual date can be entered. - Never: The assignment's end date will never be locked and needs to be specified manually - Always: The assignment's end date is always locked according to the applicable context rule. |
| MaximumDelete default value: 0 | Int32 | Deleted lines threshold. Sets the maximum number of resources that can be removed from the resource type when running the provisioning job. |
| MaximumDeletePercent default value: 30 | Int32 | Deleted lines threshold in percent. |
| MaximumInsert default value: 0 | Int32 | Inserted lines threshold. Sets the maximum number of resources that can be added into the resource type when running the provisioning job. |
| MaximumInsertPercent default value: 30 | Int32 | Inserted lines threshold in percent. |
| MaximumUpdate default value: 0 | Int32 | Updated lines threshold. Sets the maximum number of resources that can be modified within the resource type when running the provisioning job. |
| MaximumUpdatePercent default value: 30 | Int32 | Updated lines threshold in percent. |
| P0 default value: false | Boolean | True to indicate that the resource type is parametrized, i.e. there is at least one type rule configured to assign the resource type based on the dimension 0 (up to 3V following the base32hex convention). See the Base32 Parameter Names topic for additional information. |
| Policy required | Int64 | Identifier of the policy that the resource type is part of. |
| ProlongationWithoutApproval default value: 0 | ProlongationWithoutApproval | Indicates whether the resource type can be extended without any validation. 0 - Inherited: gets the value from the policy. 1 - Enabled. 2 - Disabled. |
| R0 default value: false | Boolean | True to set the dimension 0 (up to 3V following the base32hex convention) as a required parameter when assigning the resource type. See the Base32 Parameter Names topic for additional information. |
| RemoveOrphans default value: false | Boolean | True to authorize the deprovisioning of this resource when it does not have an owner. Can only be true when AllowRemove property is also true. |
| SourceEntityType required | Int64 | Identifier of the source entity type. |
| SuggestAllCorrelations optionalAttribute | Boolean | Allows correlation suggestions for rules with a confidence rate below 100, even if other correlations with a confidence rate above 100 have been found. |
| TargetEntityType required | Int64 | Identifier of the target entity type. |
| TransmittedStateValidityPeriod default value: 0 | Int32 | Time period (in minutes) after which fulfillment orders in Transmitted/Executed states are automatically set in Error state. - when provisioning automatically, then set 1, 2 or 3 times the period between two synchronizations. - when provisioning manually and synchronizing regularly, then set around 15 days. - when provisioning manually with few synchronizations, then don't set it. |
Child Element: BinaryRule
A ResourceBinaryRule allows to specify the file that must be set to an assigned resource binary
property. It is defined by a child element <BinaryRule> of the <ResourceType> element. The
source file should already be synchronized and stored inside and reference as an EntityType
property.
Examples
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
<ResourceType Identifier="AD_Entry_To_Directory_User" ...> ...
<BinaryRule Property="Photo" Binding="thumbnailPhoto" /> </ResourceType>
Properties
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Binding optional | Int64 | Defines the binding expression to get the file property. |
| Policy required | Int64 | Identifier of the policy that the rule is part of. |
| Property required | Int64 | Identifier of the property used to represent the file on the target EntityType. |
| SingleRole optional | Int64 | Identifier of the single role. The single role must be assigned to the owner so that the file can be provisioned on the resource. See the SingleRole topic for additional information. |
| TimeOffsetAfterReference default value: 0 | Int32 | Defines the offset after reference (in minutes). |
| TimeOffsetBeforeReference default value: 0 | Int32 | Defines the offset before reference (in minutes). |
| TimeOffsetReference default value: 0 | TimeOffsetReference | Offset mode defining which dates to use as references, in order to apply the time offset. The time period for which the rule is applied is adjusted accordingly. 0 - Default: the offset inherited from the type rule. 1 - Around: the offset before reference is applied from the start date of the resource, and the offset after reference is applied from the end date. 2 - Before: the offset before and after reference are both applied from the start date of the resource. 3 - After: the offset before and after reference are both applied from the end date of the resource. in a situation with several binary rules, the order of application is: After, then Before, then Around, then Default. Each rule is able to overwrite those previously applied in case they overlap. two offsets of the same mode should never overlap. Resources' start and end dates can be configured through record sections and/or context rules. |
Child Element: NavigationRule
A navigation rule computes the value of a given navigation property for target resources, based on the properties of their owners (source resources and entitlements). These properties are to be provisioned, i.e. written to the managed system. Contrary to query rules, navigation rules assign resources regardless of the attributes of source resources.
A navigation rule is defined by the child element <NavigationRule> of the <ResourceType>
element.
NOTE: Both navigation and query rules compute navigation properties. The value of one navigation property should be computed by either navigation or query rules, not both.
See the Compute a Navigation Property topic for additional information.
Examples
Computation based on other properties
The following example declares a new rule to give the SG_APP_SharePoint_HR_Owner group to all users who had the SharePoint_HR_Owner role.
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
<NavigationRule Property="memberOf" Resource="SG_APP_SharePoint_HR_Owner" SingleRole="SharePoint_HR_Owner" Policy="Default" />
The following rule will set users' Active Directory nominative account in the CN=SG_APP_DL-INTERNET-Restricted,OU=Applications,DC=acme,DC=internal group for people having the DL-INTERNET-Restricted role.
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
<ResourceType Identifier="AD_Entry_NominativeUser"> ...
<NavigationRule Property="memberOf" Resource="CN=SG_APP_DL-INTERNET-Restricted,OU=Applications,DC=acme,DC=internal" SingleRole="DL-INTERNET-Restricted" />
</ResourceType>
Parametrized roles
The role catalog can be optimized by reducing the number of roles, by configuring parametrized roles. See the Configure a Parameterized Role topic for additional information.
This optimization will simplify the functional understanding of the role catalog, and speed up Usercube's calculations.
Supposing that the 10th dimension (dimension A following the base32hex convention) is created for time slots, the following example creates a single role Access/A_Brune_HR for all time slots. Each time-slot-related entitlement will be assigned to users by configuring one navigation rule per entitlement, using the dimension as a required parameter. See the Dimension and Base32 Parameter Names topics for additional information.
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
<SingleRole Identifier="Access/A_Brune_HR" DisplayName_L1="Zone - Brune - HR" DisplayName_L2="Zone - Brune - RH" Category="Access" ApprovalWorkflowType="One" EntityType="Directory_User" Policy="Default" RA="1" /><ResourceType ... > <NavigationRule Property="TimeSlot" Resource="TS_5/7_8/24" SingleRole="Access/A_Brune_HR" DA="TS_5/7_8/24" /> <NavigationRule Property="TimeSlot" Resource="TS_5/7_12/24" SingleRole="Access/A_Brune_HR" DA="TS_5/7_12/24" /> <NavigationRule Property="TimeSlot" Resource="TS_7/7_24/24" SingleRole="Access/A_Brune_HR" DA="TS_7/7_24/24" /></ResourceType>
Properties
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| D0 optional | Int64 | Value to match for the dimension D0 (up to D127) to trigger the rule. For example, considering that D0 corresponds to users' countries, then set D0 to France to compute the navigation property for users whose country is France. Specifying at least one dimension makes the linked role parametrized. |
| IsDenied default value: false | Boolean | True to forbid the resource assignment instead of applying it. |
| L0 default value: false | Boolean | True to activate inheritance for D0 (up to 127). |
| Policy required | Int64 | Identifier of the policy that the rule is part of. |
| Property required | Int64 | Identifier of the navigation property to be computed. |
| Resource required | Int64 | Identifier of the resource to be assigned as a value of the impacted navigation property. Said resource must be part of the entity type that the navigation property points to. |
| SingleRole optional | Int64 | Identifier of a single role, which users must have to trigger the property computation. |
| TimeOffsetAfterReference default value: 0 | Int32 | Time period (in minutes) after the reference end date, which shifts the end of the rule's application. A negative value for the time offset means that the time period is before the reference date. |
| TimeOffsetBeforeReference default value: 0 | Int32 | Time period (in minutes) after the reference start date, which shifts the start of the rule's application. A negative value for the time offset means that the time period is before the reference date. |
| TimeOffsetReference default value: 0 | TimeOffsetReference | Offset mode defining which dates to use as references, in order to apply the time offset. The time period for which the rule is applied is adjusted accordingly. 0 - Default: the offset inherited from the type rule. 1 - Around: the offset before reference is applied from the start date of the resource, and the offset after reference is applied from the end date. 2 - Before: the offset before and after reference are both applied from the start date of the resource. 3 - After: the offset before and after reference are both applied from the end date of the resource. In a situation with several navigation rules, the order of application is descending (After-Before-Around-Default). Thus each time offset is able to overwrite those previously applied in case they overlap, for mono-valued properties. two offsets of the same mode should never overlap for mono-valued properties. Overlapping rules on a multi-valued property do not conflict with each other, Usercube stores all computed values. Resources' start and end dates can be configured through record sections and/or context rules. |
Child Element: QueryRule
A query rule computes the value of a given navigation property for target resources, based on the properties of their owners (source resources and entitlements). These properties are to be provisioned, i.e. written to the managed system. Contrary to navigation rules, query rules assign resources to target resources according to a query via a C# expression with conditions, based on the attributes of the source resources. See the Expressions topic for additional information.
A query rule is defined by the child element <QueryRule> of the <ResourceType> element.
Both navigation and query rules compute navigation properties. The value of one navigation property should be computed by either navigation or query rules, not both.
See the Compute a Navigation Property topic for additional information.
Examples
Computation based on other properties
The following example declares a new rule to compute the parent distinguished name for guest users. Here we do not use source properties, but a literal expression for all guest users.
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
<ResourceType Identifier="AD_Entry_Guest"> ...
<QueryRule Property="parentdn" Policy="Default" TargetBinding="AD_Entry:dn" SourceExpression="C#:resource:return "OU=Guests,DC=acme,DC=internal";" TargetMatchedConfidenceLevel="100" />
</ResourceType>
Properties
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Policy required | Int64 | Identifier of the policy that the rule is part of. |
| Property required | Int64 | Identifier of the navigation property to be computed. |
| SourceBinding optional | Int64 | Binding of the property from the source entity type to be compared with the target binding/expression, in order to find a matching resource to be the value of Property. |
| SourceExpression optional | String | C# expression to compare with the target binding/expression in order to compute the value of Property with the matching resource. See the Expressions topic for additional information. |
| TargetBinding optional | Int64 | Binding of the property from the entity type pointed by Property, which will be the value of Property if it matches the source binding/expression. |
| TargetExpression optional | String | C# expression to compare with the source binding/expression in order to compute the value of Property with the matching resource.See the Expressions topic for additional information. The TargetExpression must contain at least one target property, it cannot be a literal expression. |
| TargetMatchedConfidenceLevel default value: 0 | Int32 | Percentage rate expressing the confidence in the rule according to data quality and sensitivity. Usercube considers the rules in descending order of confidence rate, the first matching rule is applied. 0 to 99: imposes that a resource manager reviews the property computation on the Resource Reconciliation page. 100 to 150: computes the property automatically. |
| TimeOffsetAfterReference default value: 0 | Int32 | Time period (in minutes) after the reference end date, which shifts the end of the rule's application. A negative value for the time offset means that the time period is before the reference date. |
| TimeOffsetBeforeReference default value: 0 | Int32 | Time period (in minutes) after the reference start date, which shifts the start of the rule's application. A negative value for the time offset means that the time period is before the reference date. |
| TimeOffsetReference default value: 0 | TimeOffsetReference | TypeDescriptionOffset mode defining which dates to use as references, in order to apply the time offset. The time period for which the rule is applied is adjusted accordingly. 0 - Default: the offset inherited from the type rule. 1 - Around: the offset before reference is applied from the start date of the resource, and the offset after reference is applied from the end date. 2 - Before: the offset before and after reference are both applied from the start date of the resource. 3 - After: the offset before and after reference are both applied from the end date of the resource. In a situation with several query rules, the order of application is descending (After-Before-Around-Default). Thus each time offset is able to overwrite those previously applied in case they overlap, for mono-valued properties. two offsets of the same mode should never overlap for mono-valued properties. Overlapping rules on a multi-valued property do not conflict with each other, Usercube stores all computed values. Resources' start and end dates can be configured through record sections and/or context rules. |
Child Element: ScalarRule
A scalar rule computes the value of a given scalar property for target resources, based on the properties of their owners (source resources and entitlements). These properties are to be provisioned, i.e. written to the managed system.
A scalar rule is defined by the child element <ScalarRule> of the <ResourceType> element.
See the Compute a Scalar Property topic for additional information.
Examples
Computation based on other properties
The following example shows two scalar rules. The first one computes users' emails based on AD values. The other one contains a C# expression to compute AccountExpires.
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
<ResourceType Policy="Default" Identifier="App1_Standard_Account" TargetEntityType="App1_Account" SourceEntityType="Bot"> ...
<ScalarRule Property="Mail" Binding="AD_Entry:mail" Policy="Default" />
<ScalarRule Property="accountExpires" Expression="C#:person:return !person.EndDate.HasValue ? null : person.EndDate.Value.ToSince1601DateString();" />
</ResourceType>
The next example computes the firstName property of a App1_Account from the resource type App1_Standard_Account, indicating that it must be equal to the firstName of the source resource.
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
<ResourceType Policy="Default" Identifier="App1_Standard_Account" TargetEntityType="App1_Account" SourceEntityType="User"> ...
<ScalarRule Property="firstName" Binding="User:FirstName" />
</ResourceType>
Computation via a literal expression
The following example translates to "the userAccountControl property of a App1_Account of resource type App1_Standard_Account must be equal to 66048. It uses a literal expression. See the Expressions topic for additional information.
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
<ResourceType Policy="Default" Identifier="App1_Standard_Account" TargetEntityType="App1_Account" SourceEntityType="Bot"> ...
<ScalarRule Property="userAccountControl" Expression="Literal:66048" />
</ResourceType>
Binding
The Binding attribute complies with the binding expression syntax or the calculation expression syntax. So, it can use the C# language to specify a more complex binding. See the Bindings and Expressions topics for additional information.
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
<ScalarRule Property="email" Binding="C#:user:user.firstName+"."+user.lastName+"@acme.com"" />
IsMapped
Consider a system that we want to connect to Usercube , let's call it SYST, using a title property. Consider also that SYST needs to be provisioned with the value of title, but does not allow any other system to retrieve the said value.
In this case, we set IsMapped to false so that Usercube sends the adequate provisioning order when
needed, and then is able to change the provisioning state to Executed without synchronization.
See the
Provision Synchronize Data
topic for additional information.
The following example computes users' title in a given managed system, based on Usercube's
PersonalTitle property without ever retrieving the value:
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
<ScalarRule Property="title" Binding="PersonalTitle" IsMapped="false" />
TimeOffset
A scalar rule is applied according to reference start and end dates (configured through record sections and context rules), usually users' arrival and departure days. It means that, for a user matching the rule's criteria, a property is to be computed, by default, from the user's arrival day until their departure day. See the RecordSection and ContextRule topics for additional information.
A time offset adjusts the period for which the rule applies and computes a property's value.
The following example impacts the property for the activation of nominative AD accounts:
- The first rule deactivates the account from its creation, i.e. 1 month before the user's arrival day, until the arrival day;
- The second rule activates the account from the user's arrival day until their departure;
- The third rule deactivates the account from the user's departure day and until its deletion, i.e. 6 months after the departure day.
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
<ResourceType Identifier="AD_Entry_NominativeUser" Policy="Default" TargetEntityType="AD_Entry" Category="Accounts" SourceEntityType="Directory_User" ApprovalWorkflowType="None"> <ScalarRule Property="accountEnabled" Expression="C#:person:return "false";" TimeOffsetReference="Before" TimeOffsetBeforeReference="-43200" TimeOffsetAfterReference="0" /> <ScalarRule Property="accountEnabled" Expression="C#:person:return person.Leave.GetValueOrDefault() ? "false" : "true";" TimeOffsetReference="Around" TimeOffsetBeforeReference="0" TimeOffsetAfterReference="0" /> <ScalarRule Property="accountEnabled" Expression="C#:person:return "false";" TimeOffsetReference="After" TimeOffsetBeforeReference="0" TimeOffsetAfterReference="259200" /> ...
</ResourceType>
If the time period of property computation exceeds the limits of the period of resource type assignment, then the period of resource type assignment is extended accordingly.
Note that the rules are applied in a specific order according to their offset reference: After, Before, Around and Default. Each rule overwrites pre-existing values. Thus in case of overlapping rules, Default-offset rules overwrite the values of Around-offset rules, which overwrite the values of Before-offset rules, which overwrite the values of After-offset rules. We could have the following:

Properties
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Binding optional | Int64 | Defines the binding expression. |
| ComparisonType default value: 0 | ComparisonType | Defines the comparison type for the computed value, when Usercube retrieves it from the managed system during synchronization, and compares it to the value stored in Usercube's database. 0 - CaseSensitive: compares words exactly as they are. 1 - IgnoreCase: ignores the difference between upper and lower case. 2 - IgnoreDiacritics: considers all letters with diacritics (é, à, ç) to be equivalent to their base letters (e, a, c...). 3 - Simplified: ignores diacritics, case and characters which are not letters. 4 - Approximate: does the same as Simplified but also ignores some spelling mistakes. Some letters are considered equivalent (Z and S, Y and I, W and V, K and C, SS and C). All H can be missing. A T, D or S can be missing at the very end. Finally, it ignores all duplicate letters (other than SS). There is no comparison for unmapped properties (IsMapped set to false). |
| Expression optional | String | Expression used to compute the target property specified in Property. See the Expressions topic for additional information. for C# expressions, Usercube provides an implicit variable called "assignment" that contains basic information about the linked assigned resource type, i.e. StartDate, EndDate and ParametersValues. |
| IsMapped default value: true | Boolean | True to use the scalar rule's computation to both provision the managed system and synchronize the property back to Usercube, thus both create and update. Otherwise, the scalar rule's computation is used only to provision the managed system and the property will be ignored during synchronization, thus create only. This way the property can never be displayed as non-conforming. IsMapped is usually set to false in order to adapt the configuration to the constraints of the managed system, when Usercube does not retrieve and/or update the property value. |
| Policy required | Int64 | Identifier of the policy that the rule is part of. |
| Property required | Int64 | Identifier of the scalar property to be computed. |
| SingleRole optional | Int64 | Identifier of a single role that users must have to trigger the property computation. scalar rules must not be dependent on dimensions or role as far as possible as, according to Usercube, a good rights policy must be based on group membership and not on mono-valued properties. |
| TimeOffsetAfterReference default value: 0 | Int32 | Time period (in minutes) after the reference end date, which shifts the end of the rule's application. A negative value for the time offset means that the time period is before the reference date. |
| TimeOffsetBeforeReference default value: 0 | Int32 | Time period (in minutes) after the reference start date, which shifts the start of the rule's application. A negative value for the time offset means that the time period is before the reference date. |
| TimeOffsetReference default value: 0 | TimeOffsetReference | Offset mode defining which dates to use as references, in order to apply the time offset. The time period for which the rule is applied is adjusted accordingly. 0 - Default: the offset inherited from the type rule. 1 - Around: the offset before reference is applied from the start date of the resource, and the offset after reference is applied from the end date. 2 - Before: the offset before and after reference are both applied from the start date of the resource. 3 - After: the offset before and after reference are both applied from the end date of the resource. in a situation with several scalar rules, the order of application is: After, then Before, then Around, then Default. Each rule is able to overwrite those previously applied in case they overlap. two offsets of the same mode should never overlap. Resources' start and end dates can be configured through record sections and/or context rules. |
Child Element: TypeRule
A resource type rule assigns resources to given users if they match specific criteria. These resources are to be provisioned, i.e. written to the managed system.
A resource type rule is defined by the child element <TypeRule> of the <ResourceType> element.
NOTE: The specification of several resource type rules for one resource type implies the union of all rules, i.e. the combination of all rules (and all sets of criteria) with an OR operator.
Examples
With a dimension criterion
The following rule will assign an App1_Standard_Account resource (resource of type App1_Account) to any User whose organization dimension (dimension binded to column 0) identifier is Marketing.
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
<ResourceType Policy="Default" Identifier="App1_Standard_Account" TargetEntityType="App1_Account" SourceEntityType="User">
<TypeRule D0="Marketing">
...
</ResourceType>
With a single role criterion
In addition to dimensions, a single role can be used as a criterion for a rule.
The following rule will assign an App1_Standard_Account resource to all User whose organization dimension identifier is Marketing and having the single role Multimedia_Designer.
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
<ResourceType Policy="Default" Identifier="App1_Standard_Account" TargetEntityType="App1_Account" SourceEntityType="User">
<TypeRule D0="Marketing" SingleRole="Multimedia_Designer">
...
</ResourceType>
Without any criterion
Di and SingleRole conditions are not mandatory. A type rule with no condition entails the creation of an AssignedResourceType, and hence of a target resource (from the target entity type), for every source resource (from the source entity type). See the AssignedResourceType topic for additional information.
The following example declares a new rule to give the resource type "AD_Entry_NominativeUser" to all users.
Code attributes enclosed with <> need to be replaced with a custom value before entering the
script in the command line.
<ResourceType Identifier="AD_Entry_NominativeUser" Policy="Default" TargetEntityType="AD_Entry" Category="Accounts" SourceEntityType="Directory_User" Type="Suggested" ApprovalWorkflowType="None">
<TypeRule Policy="Default" />
...
</ResourceType>
Properties
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| D0 optional | Int64 | Value to match for the dimension D0 (up to D127) to trigger the rule. For example, considering that D0 corresponds to users' countries, then set D0 to France to assign the resource type to users whose country is France. specifying at least one dimension makes the linked resource type parametrized. |
| IsDenied default value: false | Boolean | True to forbid the assignment instead of applying it. |
| L0 default value: false | Boolean | True to activate inheritance for D0 (up to 127). |
| Policy required | Int64 | Identifier of the policy that the rule is part of. |
| SingleRole optional | Int64 | Identifier of a single role, which users must have to trigger the resource type assignment. |
| TimeOffsetAfterReference default value: 0 | Int32 | Time period (in minutes) after the reference end date, which shifts the end of the rule's application. A negative value for the time offset means that the time period is before the reference date. |
| TimeOffsetBeforeReference default value: 0 | Int32 | Time period (in minutes) after the reference start date, which shifts the start of the rule's application. A negative value for the time offset means that the time period is before the reference date. |
| TimeOffsetReference default value: 0 | TimeOffsetReference | Offset mode defining which dates to use as references, in order to apply the time offset. The time period for which the rule is applied is adjusted accordingly. 0 - Default: no offset. 1 - Around: the offset before reference is applied from the start date of the resource, and the offset after reference is applied from the end date. 2 - Before: the offset before and after reference are both applied from the start date of the resource. 3 - After: the offset before and after reference are both applied from the end date of the resource. In a situation with several resource type rules, the order of application is descending (After-Before-Around-Default). Thus each time offset is able to overwrite those previously applied in case they overlap. two offsets of the same mode should never overlap. Resources' start and end dates can be configured through record sections and/or context rules. |
| Type default value: 0 | RuleType | Represents the type of the rule. 0 - Required: the resource type is automatically assigned to users matching the criteria. 1 - Requested Automatically: the resource type is listed in the permission basket of new workers. These assignments can still be modified. For existing workers, the rule's type is Suggested. 2 - Suggested: the resource type is listed among suggested permissions in the permission basket of users matching the criteria during an entitlement request. Suggested assignments must be selected manually to be requested, and will go through the validation process. |
Risk
A risk defines a security threat triggered by the assignment of one or more entitlements to an identity. A risk is linked to risk rules, each of which can trigger the risk.
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Description_L1 optional | Type String Description Message that describes the risk. It will be displayed during the manual request of a risk-triggering entitlement. |
| DisplayName_L1 required | Type String Description Display name of the risk in language 1 (up to 16). |
| EntityType required | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the entity type targeted by the risk. |
| ExemptionPolicy default value: Warning | Type RiskExemptionPolicy Description Behavior of Usercube during the manual request of a risk-triggering entitlement. 0 - Warning: a message is displayed and the request can be continued or cancelled. 1 - Blocking: a message is displayed and the whole request must be cancelled. 2 - Approval required: the request will need an additional approval. A message is displayed and the request can be continued or cancelled. |
| Identifier required | Type String Description Identifier of the risk. |
| Level default value: 0 | Type Byte Description Risk score on a scale from 0 to 100. The higher the level, the higher the risk. |
| Policy required | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the policy in which the risk exists. |
| Remediation_L1 optional | Type String Description Message that describes the way to solve the risk. It will be displayed during the manual request of a risk-triggering entitlement. |
| RiskType default value: SoD | Type RiskType Description Nature of the situation described by the risk. 0 - Segregation of Duties: threat due to the conjunction of two or more entitlements for an identity. A risk rule must contain at least two rule items. 1 - High Privileges: threat due to the assignment of one or more highly sensitive entitlements. A risk rule must contain at least one rule item. |
Child Element: Rule
A risk rule is a set of risk rule items. The intersection of all rule items triggers the assignment of a risk to an identity, depending on the identity's entitlements.
Child Element: Item
A risk rule item is a filter that identify risk-triggering resources. The intersection of all rule items in a risk rule triggers the associated risk.
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Property required | Type Int64 Description Property (scalar or navigation) that represents the risk-triggering entitlement. |
| Resource optional | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the resource assigned to Property, if navigation, that triggers the risk. |
| ResourceType required | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the resource type targeted by the risk analysis. |
RoleMapping
Defines a naming rule to create a single role in a specific category based on a property. A navigation rule will also be created by the naming rule, giving the property to the target user when the created single role is assigned to this user.
Examples
Additional condition
The following example uses WhereExpression to condition the application of the rule.
NETWRIX recommends using this property only when the properties from the rule items do not suffice.
Here the naming convention says that we should create a single role for each group (memberOf
value) whose dn starts with SG_and whose dn's second part (between two _) is made of three
characters.
<RoleMapping Identifier="AD_dn" Policy="Default" Property="AD_Entry:memberOf" ResourceType="AD_Entry_NominativeUser" WhereExpression="C#:resource:return resource.dn?.Split('_')[1].Length == 3;" > <Rule> <Item Property="AD_Entry:dn" Operator="StartWith" Value="SG_"/> </Rule></RoleMapping>
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| ApprovalRequired default value: false | Type Boolean Description Indicates that the generated role must be approved before being used by a policy. |
| ApprovalWorkflowType default value: None | Type ProvisioningPolicyApprovalWorkflow Description Indicates the number of validation to give to a manual role (from 0 to 3 inclusive). The value 4 is used when a manual assignment cannot be performed. |
| Category optional | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the category. |
| CategoryDisplayNameBinding optional | Type Int64 Description Defines the binding used to compute the category display name. |
| CategoryDisplayNameExpression optional | Type String Description References the C# or literal expression used to compute the category display name. See more details on C# expressions. |
| CategoryIdentifierBinding optional | Type Int64 Description Binding used to compute the category identifier. |
| CategoryIdentifierExpression optional | Type String Description C# or literal expression used to compute the category identifier. See more details on C# expressions. |
| CommentActivationOnApproveInReview default value: Inherited | Type CommentActivationWithInherited Description Indicates if a comment is enabled when reviewing a request of the role and deciding to approve it. 0 - Disabled 1 - Optional 2 - Required 3 - Inherited: comment activation in the associated policy. |
| CommentActivationOnDeclineInReview default value: Inherited | Type CommentActivationWithInherited Description Indicates if a comment is enabled when reviewing a request of the role and deciding to refuse it. 0 - Disabled 1 - Optional 2 - Required 3 - Inherited: comment activation in the associated policy. |
| CommentActivationOnDeleteGapInReconciliation default value: Inherited | Type CommentActivationWithInherited Description Indicates if a comment is enabled when reviewing a non-conforming assignment of the role and deciding to delete it. 0 - Disabled 1 - Optional 2 - Required 3 - Inherited: comment activation in the associated policy. |
| CommentActivationOnKeepGapInReconciliation default value: Inherited | Type CommentActivationWithInherited Description Indicates if a comment is enabled when reviewing a non-conforming assignment of the role and deciding to keep it. 0 - Disabled 1 - Optional 2 - Required 3 - Inherited: comment activation in the associated policy. |
| DisplayNameBinding optional | Type Int64 Description Defines the binding used to compute the role display name. |
| DisplayNameExpression optional | Type String Description References the C# or literal expression used to compute the role display name. See more details on C# expressions. |
| HideOnSimplifiedView default value: false | Type Boolean Description true to hide this role in the basket simplified view. This flag is applied only on automatic assignments. |
| Identifier required | Type String Description Identifier of the role mapping. |
| IdentifierBinding optional | Type Int64 Description Binding used to compute the role identifier. |
| IdentifierExpression optional | Type String Description C# or literal expression used to compute the role identifier. See more details on C# expressions. |
| ImplicitApproval default value: 0 | Type Byte Description Indicates if the validation steps of the single role can be skipped. 0 - Inherited: implicit approval value in the associated policy. 1 - Explicit: all the workflow steps must be approved. 2 - Implicit: the workflow steps can be skipped if the requester has enough permissions. |
| ParentCategoryIdentifierBinding optional | Type Int64 Description Defines the binding used to compute the parent category. |
| ParentCategoryIdentifierExpression optional | Type String Description References the C# or literal expression used to compute the parent category. See more details on C# expressions. |
| Policy required | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the policy that the rule is part of. |
| Property required | Type Int64 Description Property on which the naming rule will be applied. |
| ResourceType required | Type Int64 Description Resource type on which the naming rule will be applied. |
| RolePolicy optional | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the policy used for the roles created by the naming rule. |
| WhereExpression optional | Type String Description C# expression returning a boolean, used to condition the application of the naming convention. See more details on C# expressions. |
Child Element: Rule
Represent the sets of conditions which will determine the enforcement of the naming rule.
Child Element: Item
Represents one of the conditions used to determine the enforcement of the naming rule.
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Operator default value: 0 | Type QueryComparisonOperator Description Operator used in the condition for the naming rule enforcement. |
| Property required | Type Int64 Description Property on which the condition for the naming rule enforcement is based. |
| Value optional | Type String Description Value used in the condition for the naming rule enforcement. |
SingleRole
A single role is a way to represent an entitlement that is to be assigned to an identity. It brings a layer of abstraction through a user-friendly name, close to the business view.
Roles can be used to:
- grant accesses of various types and levels;
- restrict access to sensitive information assets, by grouping entitlements in a form that is meaningful from a business point of view;
- grant the minimum privileges required by an individual to perform his/her job.
Roles can be requested manually, or they can be configured to be assigned automatically via single role rules depending on identities' attributes.
Examples
The following example declares a new single role in the default policy; in the category Internet;
for resources from Directory_User; with one approval needed.
<SingleRole Identifier="DL-INTERNET-ALL" DisplayName_L1="Unlimited Internet access"
Category="Internet" ApprovalWorkflowType="One" EntityType="Directory_User" Policy="Default" />
Parameterized roles
The role catalog can be optimized by reducing the number of roles, by configuring parameterized roles. See how to via the UI.
This optimization will simplify the functional understanding of the role catalog, and speed up Usercube's calculations.
Supposing that the 10th
dimension
(dimension A following the
base32hex convention)
is created for time slots, the following example creates a single role Access/A_Brune_HR for all
time slots. Each time-slot-related entitlement will be assigned to users by configuring one
navigation rule per entitlement, using the dimension as a required parameter.
<SingleRole Identifier="Access/A_Brune_HR" DisplayName_L1="Zone - Brune - HR" DisplayName_L2="Zone - Brune - RH" Category="Access" ApprovalWorkflowType="One" EntityType="Directory_User" Policy="Default" RA="1" /><ResourceType ... > <NavigationRule Property="TimeSlot" Resource="TS_5/7_8/24" SingleRole="Access/A_Brune_HR" DA="TS_5/7_8/24" /> <NavigationRule Property="TimeSlot" Resource="TS_5/7_12/24" SingleRole="Access/A_Brune_HR" DA="TS_5/7_12/24" /> <NavigationRule Property="TimeSlot" Resource="TS_7/7_24/24" SingleRole="Access/A_Brune_HR" DA="TS_7/7_24/24" /></ResourceType>
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| ApprovalWorkflowType default value: 0 | Type ProvisioningPolicyApprovalWorkflow Description Number of validations required to assign manually the single role (from None to Three). The value ManualAssignmentNotAllowed is used when a manual assignment cannot be performed. |
| Category optional | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the category that the role is part of. |
| CommentActivationOnApproveInReview default value: Inherited | Type CommentActivationWithInherited Description Indicates if a comment is enabled when reviewing a request of the role and deciding to approve it. 0 - Disabled. 1 - Optional. 2 - Required. 3 - Inherited: comment activation in the associated policy. |
| CommentActivationOnDeclineInReview default value: Inherited | Type CommentActivationWithInherited Description Indicates if a comment is enabled when reviewing a request of the role and deciding to refuse it. 0 - Disabled. 1 - Optional. 2 - Required. 3 - Inherited: comment activation in the associated policy. |
| CommentActivationOnDeleteGapInReconciliation default value: Inherited | Type CommentActivationWithInherited Description Indicates if a comment is enabled when reviewing a non-conforming assignment of the role and deciding to delete it. 0 - Disabled. 1 - Optional. 2 - Required. 3 - Inherited: comment activation in the associated policy. |
| CommentActivationOnKeepGapInReconciliation default value: Inherited | Type CommentActivationWithInherited Description Indicates if a comment is enabled when reviewing a non-conforming assignment of the role and deciding to keep it. 0 - Disabled. 1 - Optional. 2 - Required. 3 - Inherited: comment activation in the associated policy. |
| D0 optional | Type Int64 Description Value that will be set for the dimension 0 (up to 3V following the base32hex convention) for all users with the role. |
| Description_L1 optional | Type String Description Detailed description of the single role in language 1 (up to 16). |
| DisplayName_L1 required | Type String Description Display name of the single role in language 1 (up to 16). |
| EntityType required | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the entity type whose resources can receive the single role. |
| GracePeriod optional | Type Int32 Description Duration (in minutes) for which a lost automatic single role is prolonged. The grace period is only applied if the loss of the entitlement is due to a change in the rules (rule deletion or criteria changes). A review will be required to validate or decline the entitlement prolongation. Inferred entitlements won't be lost unless the end of the grace period is reached or the prolongation is declined. If it is not defined, the value is inherited from the policy. |
| HideOnSimplifiedView default value: false | Type Boolean Description true to show the role in a user's basket only in advanced view and not simplified view. This flag is applied only on automatic assignments. |
| Identifier required | Type String Description Identifier of the single role. |
| ImplicitApproval default value: 0 | Type Byte Description Indicates whether the validation steps of the single role can be skipped. 0 - Inherited: implicit approval value from the associated policy. 1 - Explicit: all the workflow steps must be approved. 2 - Implicit: the workflow steps can be skipped if the requester has enough permissions. |
| MaxDuration optional | Type Int32 Description Duration (in minutes) after which the role will be automatically revoked, if no earlier end date is specified. It impacts only the roles which are manually assigned after the maximum duration is set. Pre-assigned roles are not impacted. If no duration is set on the role, the MaxDuration of the associated policy is applied. If the MaxDuration is set to 0 on the role, it prevents the associated policy from applying its MaxDuration to it. |
| Policy required | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the policy in which the role exists. |
| ProlongationWithoutApproval default value: 0 | Type ProlongationWithoutApproval Description Indicates whether the role can be extended without any validation. 0 - Inherited: gets the value from the policy. 1 - Enabled. 2 - Disabled. |
| R0 default value: false | Type Boolean Description true to set the dimension 0 (up to 3V following the base32hex convention) as a required parameter when assigning the role. |
| State default value: Manual | Type RoleState Description Mark that differentiates the roles analyzed in the role mining process. 0 - Manual: the role was created manually. 1 - Generated: the role was generated by a role mapping rule. |
| Tags optional | Type String Description Label(s) that can later be used to filter the target roles of access certification campaigns. The tag separator is �. |
SingleRoleRule
A single role rule assigns a single role to users who match given criteria.
Examples
The following example declares a new rule to give the single role to all the "FCT0000" users.
<SingleRoleRule Role="DL-INTERNET-ALL" D1="FCT0000" Policy="Default" /> <SingleRoleRule Role="DL-INTERNET-ALL" D1="FCT0000" Type="Suggested" Policy="Default" />
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| CompositeRole optional | Type Int64 Description Identifier of a composite role that users must have to trigger the rule. |
| D0 optional | Type Int64 Description Value to match for the dimension D0 (up to D127) to trigger the rule. For example, considering that D0 corresponds to users' countries, then set D0 to France to assign the single role to users whose country is France. |
| IsDenied default value: false | Type Boolean Description true to forbid the assignment instead of applying it. |
| L0 default value: false | Type Boolean Description true to activate inheritance for D0 (up to 127). |
| Policy required | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the policy that the rule is part of. |
| Role required | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the single role to be assigned. |
| Type default value: 0 | Type RuleType Description Type of the rule. 0 - Required: the role is automatically assigned to users matching the criteria. 1 - RequestedAutomatically: the role is listed in the permission basket of new workers, these assignments can still be modified. For existing workers, the rule's type is Suggested. 2 - Suggested: the role is listed among suggested permissions in the permission basket of users matching the criteria during an entitlement request, suggested assignments must be selected manually to be requested. |
Reporting
ReportQuery
Allows the user to define queries to generate a report in a CSV file. When creating a new ReportQuery it is recommended to also create the linked MenuItem.
Examples
<ReportQuery Identifier="SingleRoles" ReturnedEntityType="SingleRole" Query="select Identifier, DisplayName" DisplayName_L1="Single Roles" /> <ReportQuery Identifier="ResourceTypes" ReturnedEntityType="ResourceType" Query="select Identifier, DisplayName" DisplayName_L1="Resource Types" /> <ReportQuery Identifier="PersonRecords" ReturnedEntityType="PersonRecord" Query="join Person Person join PersonalTitle PersonalTitle join EmployeeType EmployeeType select InternalDisplayName, PersonalTitle.DisplayName, LastName, FirstName, DisplayedCR, Login, DisplayedFonction, DisplayedEDS, EmployeeType.DisplayName, EmployeeType.Category" DisplayName_L1="Users" />
<ReportQuery Identifier="SGS_Report" ReturnedEntityType="SGS_User" Query="join UserMetier metier join UserDepartement dpt join ResourceAssignedResourceTypes art join art.Owner of type Person person join person.Records personRecord join personRecord.EmployeeType employeeType join personRecord.Organization eds join personRecord.Fonction fonction join personRecord.Company cr select IDUser,NomPrenomUserSgs, metier.IDMetier, dpt.IDDepartement, person.Identifier, personRecord.FirstName, personRecord.LastName,employeeType.DisplayName,eds.DisplayName,fonction.DisplayName,cr.DisplayName" DisplayName_L1="SGS Accounts" />
<ReportQuery Identifier="AD_Report" ReturnedEntityType="AD_Entry" Query="join memberOf memberof join ResourceAssignedResourceTypes art join art.Owner of type Person person join person.Records personRecord join personRecord.EmployeeType employeeType join personRecord.Organization eds join personRecord.Fonction fonction join personRecord.Company cr select sAMAccountName,memberof.dn, person.Identifier, personRecord.FirstName, personRecord.LastName, employeeType.DisplayName, eds.DisplayName, fonction.DisplayName,cr.DisplayName" DisplayName_L1="AD Entries" />
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| DisplayName_L1 required | Type String Description Display name of the report query in language 1 (up to 16). |
| Identifier required | Type String Description Report query Identifier. |
| Query required | Type String Description The report query written following Usercube EBNF Grammar rules. |
| ReturnedEntityType required | Type Int64 Description Returned Entity Type ID. The entity type can be seen as the FROM of a sql query. |
Resources
Resource
The <Resource> element also allows the definition of a resource entity directly from within the
configuration. Such element must specify:
- the entity type using the
Typeattribute - a unique
Id - property values using corresponding column names as attributes
When inserting resource-identity in the resource table this way, the Id attribute must be a positive integer. Negative Ids are reserved for Usercube's engine.
Examples
The following sample inserts two entities of type User: John Smith and Anthony Baker. John Smith
is the manager of Anthony Baker.
The User Entity Type is defined as follows:
<EntityType Identifier="User"> <Property Identifier="FirstName" Type="String" TargetColumnIndex="4" /> <Property Identifier="LastName" Type="String" TargetColumnIndex="5" /> <Property Identifier="Manager" Type="String" TargetColumnIndex="128" /> </EntityType>
The two new resources are inserted in the database using the <Resource> tag.
They are assigned the ids 300 and 301, they are positive integers (since User type resources are
resource-identity) and not yet used in the UR_Resource table.
The User resource properties (FirstName, LastName and Manager) are matched to a UR_Resource
table column, such as C4, C5 or I40 according to their data column index, in the above
Entity Type definition.
- FirstName: index 4 => column C4
- LastName: index 5 => column C5
- Manager: index 128 => column I40
<Resource Type="User" Id="300" C4="John" C5="Smith" /><Resource Type="User" Id="301" C4="Anthony" C5="Baker" I40="-300" />
Most encountered use cases in real life is populating very tiny datasets like employee categories (Internal, External) or personal titles (Mr, Ms). Identities are almost never insert this way. This contrived example aims at illustrating the method.
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| C0 optional | Type String Description A column of storage. Going from 0 to 127. |
| Dirty default value: false | Type Boolean Description Flag set by the Usercube-Set-RecentlyModifiedFlag task. |
| DisplayName_L1 optional | Type String Description Display name of the resource in language 1 (up to 16). |
| I40 optional | Type Int64 Description This columns are used to store the id of an linked entity. When an entity type has a mono-valued association we usually use this columns to store the information. By default there are 10 columns for the storage of the mono-valued associations. |
| Type required | Type Int64 Description The type of the resource. References the internal id of an EntityType. |
DisplayEntityAssociation
Entity referencing the Entity Association that can be displayed in the Usercube interface. An association can be established between two properties of the same display entity type.
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| IsHierarchical default value: false | Type Boolean Description Is hierarchical entity association. |
DisplayEntityType
The <DisplayEntityType> element sets information about how an entity type is to be displayed by
the UI.
Examples
<DisplayEntityType PluralDisplayName_L1="Companies" IconCode="Suitcase" Identifier="Directory_Company"> <Property DisplayOrder="-1" IsRequired="true" Identifier="Identifier" /> <Property IsRequired="true" Identifier="DisplayName" /> <Property OutputType="BasicCollection" Identifier="UserRecords" NavigationBinding="Directory_UserRecord:User" /> <Property OutputType="BasicCollection" Identifier="Guests" /> </DisplayEntityType>
Zoom on Priority
The Priority property controls the order in which entity types are displayed in the entity type selection dropdown of the following administration screens:
- Role Review
- Provisioning Review
- Role Reconciliation
- Resource Reconciliation
- My Tasks (also known as Workflow Management)
- Workflow Overview
- Access Rules
By default, the entity type with the highest priority is selected first. The end user can later change the selection using the top-left dropdown.
Priorities are integer values, positive or negative. The most important priority is assigned to the lowest value.
Entity Types with the same priority are sorted by Identifier, in the alphabetical order, where
relevant.
Entity Types for which a priority isn't set by a <DisplayEntityType> configuration element are
assigned an equally less important priority than the least important priority set by a
<DisplayEntityType> element.
Example
This example shows how to define priorities between the main Entity Types of the organizational
model. The highest priority is assigned to Directory_User and the lowest priority to
Directory_Application. All other entity types are assigned an equally low priority, below
Directory_Application. In the dropdown they will be sorted by alphabetical order.
dashboard.xml
<DisplayEntityType Identifier="Directory_User" Priority="0" /> <DisplayEntityType Identifier="Directory_Guest" Priority="1" /> <DisplayEntityType Identifier="Directory_Bot" Priority="2" /> <DisplayEntityType Identifier="Directory_Application" Priority="3" />
Priorities for workflows
The dropdown in My Tasks (also known as Workflow Management) and Workflow Overview screens is related to workflows, not to entity types per se.
In Usercube, each workflow is associated with a workflow-entity type.
To configure the priority order for elements in the dropdown in these screens, the user should
remember to take the workflow-entity types in the <DisplayEntityType elements, not just the
entities themselves.
Example
Let's take the following organizational model:
- a Directory_User entity type for employee
- a Directory_Guest entity type for contractors and the like
When workflows are defined to handle resources for these entity types, the following workflow-entity types are created too:
- Workflow_Directory_User
- Workflow_Directory_Guest
The order in which Directory_User and Directory_Guest appear in the role review dropdown is configured like this
dashboard.xml
<DisplayEntityType Identifier="Directory_User" Priority="0" /> <DisplayEntityType Identifier="Directory_Guest" Priority="1" />
But the order in which "Workflow for Directory_User" and "Workflow for Directory_Guest" appear in the My Tasks screen is configured like this.
dashboard.xml
<DisplayEntityType Identifier="Directory_Workflow_User" Priority="0" /> <DisplayEntityType Identifier="Directory_Workflow_Guest" Priority="1" />
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| AutocompleteBinding optional | Type Int64 Description Defines the binding of the property used for search in the auto complete picker (this activates the auto complete picker). |
| Color optional | Type String Description Defines the color used when displaying this entity type (it must be a 6 digit hexadecimal value, preceded by a �#'). |
| D0IsActive default value: false | Type Boolean Description Is dimension0 active for this entity type (D0IsActive to D3VIsActive following the base32hex convention. |
| HideRoles default value: false | Type Boolean Description true to skip the Access Permissions step (the one containing the roles) in the default forms for this entity type. |
| IconCode optional | Type String Description Defines the icode code ("People", "MapPin", "Suitcase"�). |
| IsHierarchical default value: false | Type Boolean Description Is hierarchical entity type. |
| MinSearchLength optional | Type Int32 Description Defines the minimum number of characters from which the search in the auto complete picker starts - 4 if it is not defined (the AutocompleteBinding must be defined). |
| PluralDisplayName_L1 optional | Type String Description Display name of the entity type in plural in language 1 (up to 16). |
| Priority default value: 2147483647 | Type Int32 Description Sets the display priority of the Entity Type in the administration screens dropdown and the dashboard. A priority is an integer value, positive or negative. The highest priority is assigned to the lowest number. See the Priority section above. |
Child Element: Property
Entity referencing the Entity properties (with which it share the same ID) that can be displayed in the Usercube interface.
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| AddedMinutes optional | Type Int32 Description Add minutes to the date field with this property. Can be overwritten in every form control, display table column or tile item that displays the property. |
| AutocompleteBinding optional | Type Int64 Description Defines the binding of the property used for search in the auto complete picker (this activates the auto complete picker if the input type of the display property is a picker). |
| DisplayOrder default value: 0 | Type Int32 Description Defines the property display order. |
| DisplayTable optional | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the display table. |
| Format optional | Type String Description Defines a formating method on the property values ("ParseSince1601Date", "ToStringUserAccountControl", "FormatDate" and "ParseBoolean"). |
| Group optional | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the display property group, i.e. the fieldset, that the property is part of in the default UI form. |
| IconCode optional | Type String Description Defines the icode code. |
| InputType default value: Auto | Type Enumeration Description Identifier of the input type. |
| IsHidden default value: false | Type Boolean Description Property is hidden. |
| IsReadOnly default value: false | Type Boolean Description Property is readOnly. |
| IsRequired default value: false | Type Boolean Description Property is required. |
| MinSearchLength optional | Type Int32 Description Defines the minimum number of characters from which the search in the auto complete picker starts - 4 if it is not defined (the input type of the display property must be a picker and the AutocompleteBinding must be defined). |
| NavigationBinding optional | Type Int64 Description Defines the binding of the resource on which the user will be redirected when he clicks on an element of a BasicCollection. |
| OutputType default value: Auto | Type Enumeration Description Identifier of the output type. |
| PlaceHolderText_L1 optional | Type String Description Property place holder text. |
| Tile optional | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the tile. |
| ToolTipText_L1 optional | Type String Description Property tool tip text. |
DisplayPropertyGroup
A display property group bundles a list of entity properties together in a fieldset in the UI.
Examples
The following example will group a specific set of properties together, when displaying AD entries.
<DisplayPropertyGroup Identifier="AD_General" DisplayName_L1="General" />
Knowing that we have the following properties:
<DisplayEntityType Identifier="AD_Entry"> <Property Identifier="displayName" Group="AD_General" DisplayOrder="100" /> <Property Identifier="givenName" Group="AD_General" DisplayOrder="101" /> <Property Identifier="initials" Group="AD_General" DisplayOrder="102" /> <Property Identifier="sn" Group="AD_General" DisplayOrder="103" /> <Property Identifier="description" Group="AD_General" DisplayOrder="104" /> <Property Identifier="thumbnailPhoto" Group="AD_General" DisplayOrder="105" /> <Property Identifier="telephoneNumber" Group="AD_General" DisplayOrder="106" /> <Property Identifier="mobile" Group="AD_General" DisplayOrder="107" /> <Property Identifier="mail" Group="AD_General" DisplayOrder="108" /> ...
</DisplayEntityType>
Any property without a value is not displayed.
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| DisplayName_L1 optional | Type String Description Display name of the fieldset in language 1 (up to 16). |
| Identifier required | Type String Description Unique identifier of the property group. |
DisplayTable
A table displays a collections of entity type data grouped into rows.
Examples
DisplayTableDesignElement
table
The following example displays sites as a table.
<DisplayTable Identifier="Directory_Site" EntityType="Directory_Site" DisplayTableDesignElement="table" IsEntityTypeDefault="true"> <Column DefaultSortPriority="1" DisplayBinding="Region.Country.DisplayName" IsDisplayInSummaryView="true" IsResizable="true" IsSortable="true" CanBeFiltered="true" ColumnSize="2" DisplayName_L1="Country" /> <Column DefaultSortPriority="2" DisplayBinding="Region.DisplayName" IsDisplayInSummaryView="true" IsResizable="true" IsSortable="true" CanBeFiltered="true" ColumnSize="2" DisplayName_L1="State" /> <Column DefaultSortPriority="3" DisplayBinding="DisplayName" IsDisplayInSummaryView="true" IsResizable="true" IsSortable="true" CanBeFiltered="true" ColumnSize="8" /></DisplayTable>
list
The following example displays users as a list.
<DisplayTable Identifier="Directory_User" EntityType="Directory_User" DisplayTableDesignElement="list" IsEntityTypeDefault="true"> <Column DefaultSortPriority="1" ColumnSize="6" IsDisplayInSummaryView="true" SortBinding="MainRecord.LastName" Tile="Directory_User_Tile1" /> <Column ColumnSize="3" IsDisplayInSummaryView="true" Tile="Directory_User_Tile2" SortBinding="MainRecord.FirstName" /> <Column ColumnSize="3" Tile="Directory_User_Tile3" /></DisplayTable>
For resources to be displayed as a list, the display table must also be configured with tiles.
resourcetable
The following example displays AD entries as a table, with an "Owner/Type" column.
<DisplayTable Identifier="AD_Entry" EntityType="AD_Entry" DisplayTableDesignElement="resourcetable" IsEntityTypeDefault="true"> <Column DefaultSortPriority="1" DisplayBinding="dn" IsDisplayInSummaryView="true" IsResizable="true" IsSortable="true" CanBeFiltered="true" ColumnSize="5" /> <Column DisplayBinding="displayName" IsDisplayInSummaryView="true" IsResizable="true" IsSortable="true" CanBeFiltered="true" ColumnSize="2" /> <Column DisplayBinding="userPrincipalName" IsDisplayInSummaryView="true" IsResizable="true" IsSortable="true" CanBeFiltered="true" ColumnSize="4" /> <Column DisplayBinding="objectCategory" IsDisplayInSummaryView="true" IsResizable="true" IsSortable="true" CanBeFiltered="true" ColumnSize="1" /></DisplayTable>
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| DisplayTableDesignElement required | Type Enumeration Description Design of the display table. -1 - table: resources are displayed in a table. -2 - list: resources are displayed in a list. -3 - resourcetable: resources are displayed in a table containing an "Owner/Type" column. -4 - adaptable: resources are displayed in a table with an "Owner/Type" column only if the entity type is the target of a resource type, otherwise the table is without said column. |
| EntityType required | Type Int64 Description Represents the linked entity type. |
| HomonymEntityLink optional | Type Int64 Description Defines the homonym display table. |
| Identifier required | Type String Description Unique identifier of the table. |
| IsEntityTypeDefault default value: false | Type Boolean Description Default display table used in the application. |
| LinesPerPage default value: 15 | Type Int32 Description Defines the maximum lines per page. |
| ParentProperty optional | Type Int64 Description Property to navigate to the parent level when the table displays a tree of values (for example Organization.ParentOrganization). |
Child Element: Column
Contains all the display table columns.
Examples
<Column DefaultSortPriority="1" DisplayBinding="dn" IsDisplayInSummaryView="true" IsResizable="true" IsSortable="true" CanBeFiltered="true" ColumnSize="4" /> <Column DisplayBinding="userPrincipalName" IsDisplayInSummaryView="true" IsResizable="true" IsSortable="true" CanBeFiltered="true" ColumnSize="2" /> <Column DisplayBinding="userAccountControl" IsDisplayInSummaryView="true" IsResizable="true" IsSortable="true" CanBeFiltered="true" ColumnSize="1" /> <Column DisplayBinding="rdn" IsDisplayInSummaryView="true" IsResizable="true" IsSortable="true" CanBeFiltered="true" ColumnSize="2" /> <Column DisplayBinding="displayName" IsDisplayInSummaryView="true" IsResizable="true" IsSortable="true" CanBeFiltered="true" ColumnSize="2" /> <Column DisplayBinding="objectCategory" IsDisplayInSummaryView="true" IsResizable="true" IsSortable="true" CanBeFiltered="true" ColumnSize="2" />
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| AddedMinutes optional | Type Int32 Description Add minutes to the date field with this property. If the value is not defined, the default value is the one defined for the associated display entity property. |
| CanBeFiltered default value: false | Type Boolean Description Can filter the column data. |
| ColumnSize default value: 1 | Type Int32 Description Defines the column size. |
| DefaultSortPriority optional | Type Int32 Description Defines the default sort priority. |
| DisplayBinding optional | Type Int64 Description Represents the linked binding path to a scalar property. |
| DisplayName_L1 optional | Type String Description Display name of the column in language 1 (up to 16). |
| IsDisplayInDropDownList default value: false | Type Boolean Description Is a drop down list column. |
| IsDisplayInSummaryView default value: false | Type Boolean Description Is a summary view column. |
| IsResizable default value: false | Type Boolean Description Is resizable column. |
| IsSortable default value: false | Type Boolean Description Is sortable column. |
| OptimizedDisplayBinding optional | Type Int64 Description Optimized Binding allows DisplayTables to be faster displayed. If it is filled in, it takes priority over the DisplayBinding located in the DisplayTableColumn. |
| OptimizedSortBinding optional | Type Int64 Description An optimized sort binding allows display tables to be faster displayed. If it is filled in, it takes priority over the sort binding located in the display table column. |
| SearchOperator default value: 0 | Type QueryComparisonOperator Description Defines the search operator (Equal, NotEqual, Contain, StartWith�). |
| SortBinding optional | Type Int64 Description Represents the sort binding path to a scalar property. |
| Tile optional | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the tile. |
Form
A form contains a set of input fields (called controls) to be filled by a user, in a structured way. A form must have a form type to be displayed and used in the UI. A form without a type can be called in another form.
Examples
The following example shows a form called Directory_UserRecord_View that involves resources from
the entity type Directory_UserRecord to collect personal data and contract information via some
structured fields to fill.
<Form Identifier="Directory_UserRecord_View" EntityType="Directory_UserRecord">
<Control DisplayName_L1="Personal Data" OutputType="LayoutFieldset"> <Control DisplayName_L1="Full Name" OutputType="LayoutRowset"> <Control Binding="LastName" /> <Control Binding="FirstName" /> </Control> <Control Binding="Mail" ColumnSize="8" /> </Control> <Control DisplayName_L1="Contract" OutputType="LayoutFieldset"> <Control Binding="EmployeeId" /> <Control Binding="ContractStartDate" /> <Control Binding="ContractEndDate" /> ...
</Control>
</Form>
Display settings
Hide the "Access Permissions" tab
When HideRoles is set to true, then the Access Permissions tab is not accessible.
Adjust the request type
When WorkflowRequestType is set to Self, then the finalization step looks like:
When WorkflowRequestType is set to Helpdesk, then the finalization step looks like:
Display records in a table
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Activity optional | Type Int64 Description Defines the linked activity template. |
| ActivityState optional | Type Enumeration Description Defines the linked activity state template. |
| AddRowLabel_L1 optional | Type String Description Defines the "add row" button label when using WorkflowUpdateSeveralRecordsEntityForm. |
| EntityType required | Type Int64 Description Represents the linked entity type. |
| FormTitle_L1 optional | Type String Description Title of the form in language 1 (up to 16). |
| FormType default value: Auto | Type FormType Description Represents the linked form type. |
| HideRecordAddButton default value: false | Type Boolean Description true to hide the button used to add a new record. |
| HideRecordRemoveButton default value: false | Type Boolean Description true to hide the button used to remove an existing record. |
| HideRoles default value: false | Type Boolean Description true to hide the Access Permissions tab. |
| Identifier required | Type String Description Unique identifier of the form. |
| IsDefaultSelfForm default value: false | Type Boolean Description Entity type default self form. |
| IsDefaultViewForm default value: false | Type Boolean Description Entity type default view form. |
| IsDeleteForm default value: false | Type Boolean Description Is a delete form. |
| MainProperty optional | Type Int64 Description Represents the form main property. |
| MainPropertyLabel_L1 optional | Type String Description Defines the main property label text. |
| Menu optional | Type Int64 Description Defines the linked menu item. |
| RecordEndProperty optional | Type Int64 Description Defines the workflow end date property. If not specified, the property �EndDate' of the record entity type is considered as RecordEndProperty. |
| RecordFilter default value: CurrentAndFuture | Type RecordFilter Description Defines the record display option. 0 - Current: shows current positions. 1 - CurrentAndFuture: shows current and future positions. Recommended. 2 - All: shows past, present and future positions. Not recommended for clarity issues. |
| RecordProperty optional | Type Int64 Description Defines the workflow record property. |
| RecordSortProperty optional | Type Int64 Description Defines the workflow sort property. |
| RecordStartProperty optional | Type Int64 Description Defines the workflow start date property. If not specified, the property �StartDate' of the record entity type is considered as RecordStartProperty. |
| RecordTable optional | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the display table to be used to display resources' records in a workflow. |
| RemoveRowLabel_L1 optional | Type String Description Defines the "remove row" button label when using WorkflowUpdateSeveralRecordsEntityForm. |
| TableTitle_L1 optional | Type String Description Defines the table title when using WorkflowUpdateSeveralRecordsEntityForm. |
| WorkflowRequestType default value: 0 | Type WorkflowRequestType Description Type of the request of the related workflow. 0 - None. 1 - Self. 2 - Helpdesk. 3 - Administration. |
Child Element: Control
A form control is an input field to be filled by a user. Controls can be inserted in other controls in order to display the form fields in a structured way.
Examples
The following example shows a form called Directory_UserRecord_View that collects first personal
data via some controls, and then calls another form Workflow_Directory_User_AddRecord_Base to
collect record information. In this example is a tree control which defines the relationships
between a worker and their managers (N+1 to N+3). The aim is to display in the form (in the UI) the
organization chart made of the worker and their managers.
<Form Identifier="Directory_UserRecord_View" EntityType="Directory_UserRecord"> <Control DisplayName_L1="Personal Data" OutputType="LayoutFieldset"> <Control DisplayName_L1="Full Name" OutputType="LayoutRowset"> <Control Binding="LastName" /> <Control Binding="FirstName" /> </Control> <Control Binding="Mail" ColumnSize="8" /> </Control> <Control DisplayName_L1="Contract" OutputType="TransformImport" EmbeddedForm="Workflow_Directory_User_AddRecord_Base" /> </Control>
</Form>
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| AddedMinutes optional | Type Int32 Description Add minutes to the date field with this property. If the value is not defined, the default value is the one defined for the associated display entity property. |
| Binding optional | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the binding property. Note: when displaying an organization chart, this binding is meant to represent the first manager level (N+1). In this case, it must be a mono-valued navigation. |
| Binding2 optional | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the binding property used to represent the second manager level (N+2) in the organization chart. It must be a mono-valued navigation. Cannot be used when Binding is not defined. |
| Binding3 optional | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the binding property used to represent the third manager level (N+3) in the organization chart. It must be a mono-valued navigation. Cannot be used when Binding2 is not defined. |
| ColumnSize optional | Type Int32 Description Defines the control column size. |
| DefaultValueBinding optional | Type Int64 Description Automatically sets the value in the control depending on this binding and the selected value in another corresponding picker. It's only available for controls with picker. For example: <Control Binding="Location" DefaultValueBinding="Organization.Manager.MainLocation" /> After a selection of an organization in another picker in the form, the field location will be automatically set by the main location of the manager of the selected organization. |
| DisplayName_L1 optional | Type String Description Display name of the control in language 1 (up to 16). |
| DisplayTable optional | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the table. |
| EmbeddedForm optional | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the form to insert in the control. With this method, one form can be imported to several forms. Warning: can be used only with OutputType set to TransformImport. |
| EntityType optional | Type Int64 Description Represents the linked entity type. |
| ExtensionIdentifier optional | Type String Description This property is used to extend the Usercube UI. |
| FilterBinding1 optional | Type Int64 Description Coupled with LinkedBinding1, it allows filtering on a list of items. FilterBinding1 defines the binding that determines the search value. Linked filters are only available for controls with the Picker InputType. |
| FilterBinding2 optional | Type Int64 Description Coupled with LinkedBinding2, it allows filtering on a list of items. FilterBinding2 defines the binding that determines the search value. Linked filters are only available for controls with the Picker InputType. |
| HomonymEntityLink optional | Type Int64 Description Defines the homonym form control. |
| InputType default value: Inherited | Type Enumeration Description Input type of the control. |
| IsReadOnly optional | Type Boolean Description Is a readonly form control. |
| IsRequired optional | Type Boolean Description Is a required form control. |
| LinkedBinding1 optional | Type Int64 Description Coupled with FilterBinding1, it allows filtering on a list of items. LinkedBinding1 defines the binding on which the search will be carried out. Linked filters are only available for controls with the Picker InputType. |
| LinkedBinding2 optional | Type Int64 Description Coupled with FilterBinding2, it allows filtering a list of items. LinkedBinding2 defines the binding on which the search will be carried out. Linked filters are only available for controls with the Picker InputType. |
| Name optional | Type String Description Identifies the control inside the Form. This is used for translation files when a control cannot be identified by its binding such as for FieldSet. |
| NavigationBinding optional | Type Int64 Description Defines the binding of the resource on which the user will be redirected when he clicks on an element of a BasicCollection. If not defined, the one defined in DisplayEntityProperty is used. |
| OutputType default value: Inherited | Type Enumeration Description Output type of the control. |
| ParentControl optional | Type Int64 Description Defines the parent form control. |
| PlaceHolderText_L1 optional | Type String Description Defines the place holder text. |
| Tile optional | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the tile. |
User Interface
-
DisplayEntityAssociation
-
DisplayEntityType
-
DisplayPropertyGroup
-
DisplayTable
-
Form
-
Indicator
-
MenuItem
-
SearchBar
-
Tile
Indicator
An Indicator displays a banner alongside the resource information whenever it meets a specific criteria.
More precisely, an indicator displays the appropriate banner whenever the Binding matches the Item Value according to the Comparison operator, as can be seen on the example below.
The banner is displayed wherever the associated resource appears.
For example, if we create an indicator pointing out the risk score of a user, the banner will show on the left-side of the user tile and the user form. If we create an indicator pointing out whether an AD account is unused or disabled, the banner will show on the left-side of the AD Entries tile and form.
One entity can show several banners, one for several different properties. They appear one above the other if there are four banners or less, one next to the other if there are more.
One indicator can posess several items, that define the information for the banner to be displayed. The indicators order is important because the banner will get the information of the first item matching the observed property.
Examples
The following example entails the display of a red banner for a user with a high risk score and an orange banner for a user with a medium risk.
The XML file below states that if the risk score is greater than 75, only the indicator "High risk" will be displayed and not "Medium risk". If it is lower than 75 and greater than 30, the indicator will be "Medium risk". If it is lower than 30, there will be no indicator.
<Indicator EntityType="Directory_User" Binding="RiskScore" ComparisonOperator="GreaterThanOrEqual" Order="0"> <Item Value="75" Color="#9D0E0E" DisplayName_L1="High risk" /> <Item Value="30" Color="#E37C14" DisplayName_L1="Medium risk" /> </Indicator>
Note that if you write the "Medium risk" item before the "High risk" one, even if the score if greater than 75, the banner will be orange according to the first item:
<Indicator EntityType="Directory_User" Binding="RiskScore" ComparisonOperator="GreaterThanOrEqual" Order="0"> <Item Value="30" Color="#E37C14" DisplayName_L1="Medium risk" /> <Item Value="75" Color="#9D0E0E" DisplayName_L1="High risk" /> </Indicator>
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Binding optional | Type Int64 Description Defines the binding path to a scalar property. |
| ComparisonOperator required | Type QueryComparisonOperator Description Defines how to compare the given binding to an indicator item value. All possible values: - Auto: The SearchOperator is calculated by the engine according to the type of element. - NotEqual: finds the elements that are not equal to the desired value. - Equal: finds the elements that are strictly equal to the desired value. - Contain: finds the elements that contain the desired value. - StartWith: finds the elements that start with the desired value. - EndWith: finds the elements that end with the desired value. - NotContain: finds the elements that do not contain the desired value. - NotStartWith: finds the elements that do not start with the desired value. - NotEndWith: finds the elements that do not end with the desired value. - GreaterThan: finds the elements that are greater than the desired value. - LessThan: finds the elements that are less than the desired value. - GreaterThanOrEqual: finds the elements that are greater than or equal to the desired value. - LessThanOrEqual: finds the elements that are less than or equal to the desired value. - Flexible*: The Flexible search operators transform the desired value according to the FlexibleComparisonExpression defined in Property then search. The flexible operators are: - FlexibleEqual. - FlexibleContain. - FlexibleStartWith. - FlexibleEndWith. |
| EntityType required | Type Int64 Description Represents the linked entity type. |
| OptimizedBinding optional | Type Int64 Description Optimized Binding allows Indicators to be faster displayed. If it is filled in, it takes priority over the Binding located in the Indicator. |
| Order required | Type Int32 Description Defines the order in which the banners are displayed. If there is no order needed, its value is zero for all indicators. |
Child Element: Item
Defines the banner to be displayed informations. See Indicator for more details.
Examples
<Item Value="75" Color="#9D0E0E" DisplayName_L1="High risk" /> <Item Value="30" Color="#E37C14" DisplayName_L1="Medium risk" />
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Color required | Type String Description Defines the color of the item. |
| DisplayName_L1 optional | Type String Description Display name of the banner in language 1 (up to 16). |
| Value optional | Type String Description Defines the value with which the indicator binding will be compared to. |
MenuItem
A menu item displays grouped navigation actions.
Examples
<MenuItem Identifier="View_AD_Entry" DisplayName_L1="AD Entry"> <MenuItem Identifier="View_AD_Entry_ResetPassword" DisplayName_L1="Reset Password" IconCode="Edit" Workflow="AD_Entry_ResetPassword" /> </MenuItem>
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| DisplayName_L1 optional | Type String Description Display name of the menu item in language 1 (up to 16). |
| EntityType optional | Type Int64 Description Represents the linked entity type. |
| IconCode optional | Type String Description Code of one of Microsoft's fabric icons to be displayed with the menu item. Note: on Microsoft page, see the icons' codes by moving the mouse over the icons, or using the detailed view. |
| Identifier required | Type String Description Unique identifier of the item. |
| IsExpandedByDefault default value: true | Type Boolean Description Is an expanded by default menu item. |
| IsSelfForm default value: false | Type Boolean Description Is a self form menu item. |
| ParentMenuItem optional | Type Int64 Description Defines the parent menu item. Five ParentMenuItem are hard coded: - Dashboard: Allow to display MenuItem in dashboard (Home page) - Nav: Allow to display MenuItem in navigation section (the left part in dashboard) - UserMenu: Allow to display MenuItem in links list on click on user account in the top right corner - Reports: Define all the reports downloadable in the application - Top: Allow to display MenuItem in top bar of the application, between "Home" and "My tasks" |
| ReportQuery optional | Type Int64 Description Represents the linked report query. |
| URI optional | Type String Description Represents the menu URI. |
| Workflow optional | Type Int64 Description Represents the linked workflow. |
SearchBar
The SearchBar is an element of the user interface that allows you to search from a list of properties of an EntityType.
Examples
<SearchBar EntityType="Directory_User" Menu="Menu_Search_Directory_User" SearchBarDesignElement="Inline"> <Criterion Binding1="MainRecord.EmployeeId" PlaceHolderText_L1="Employee Id" InputType="Auto" ColumnSize="2" /> <Criterion Binding1="MainRecord.LastName" InputType="Auto" ColumnSize="2" /> <Criterion Binding1="MainRecord.FirstName" InputType="Auto" ColumnSize="2" /> <Criterion Binding1="MainRecord.Organization" PlaceHolderText_L1="Department" InputType="Auto" ColumnSize="2" /></SearchBar>
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| EntityType required | Type Int64 Description References the linked entity type. |
| Menu optional | Type Int64 Description References the linked Menu. Each MenuItem of this Menu is a link to an entity's workflow displayed under the search bar on the visualization page of the entity's resource list. |
| SearchBarDesignElement required | Type Enumeration Description Defines the type of the searchBar(Block,Inline). |
| SearchedBinding optional | Type Int64 Description Defines the binding on which the search will be applied. |
| SearchedEntityType required | Type Int64 Description Defines the entity type on which the search will be applied. |
Child Element: Criterion
A SearchBarCriteria defines a search criterion on a given property. See SearchBar for more details.
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| ColumnSize required | Type Int32 Description Size of the insertion or selection element of the property. |
| DefaultValue optional | Type String Description Basic filter on the properties on the value or values entered in parameters. |
| DisplayName_L1 optional | Type String Description Display name of the criteria in language 1 (up to 16). |
| InputType required | Type Enumeration Description Type of the research property. (Auto: takes by default the type of the EntityType property.) |
| IsVisibleInAdvancedView default value: false | Type Boolean Description true to make the property visible in the advanced search but not in the main search properties. |
| Operator default value: 0 | Type QueryComparisonOperator Description Defines how to do the research. All possible values: - Auto: The SearchOperator is calculated by the engine according to the type of element - NotEqual: finds the elements that are not equal to the desired value - Equal: finds the elements that are strictly equal to the desired value - Contain: finds the elements that contain the desired value - StartWith: finds the elements that start with the desired value - EndWith: finds the elements that end with the desired value - NotContain: finds the elements that do not contain the desired value - NotStartWith: finds the elements that do not start with the desired value - NotEndWith: finds the elements that do not end with the desired value - GreaterThan: finds the elements that are greater than the desired value - LessThan: finds the elements that are less than the desired value - GreaterThanOrEqual: finds the elements that are greater than or equal to the desired value - LessThanOrEqual: finds the elements that are less than or equal to the desired value - Flexible*: The Flexible search operators transform the desired value according to the FlexibleComparisonExpression defined in Property then search. The flexible operators are: - FlexibleEqual - FlexibleContain - FlexibleStartWith - FlexibleEndWith |
| OptimizedBinding1 optional | Type Int64 Description Represents the first optimized binding definition. An optimized binding allows searches to be faster displayed. If it is filled in, it takes priority over the binding located in the search bar criterion column. |
| PlaceHolderText_L1 optional | Type String Description Overloads the DisplayName of the search property with this string. |
| ToolTipText_L1 optional | Type String Description Text displayed in the tool tip. |
Tile
A tile displays customizable data in one block. This block is displayed in display table. There are two types of tiles: multilines with optional icons and multilines with photo (or failing this, the initials of a defined data).
Examples
<Tile Identifier="Referentiel_User_Tile1" DisplayName_L1="Collaborateur : pr�nom, nom" EntityType="Referentiel_User" TileDesignElement="picture-text"> <Item Binding="MainRecord.FirstName" LineDisplayOrderIndicator="1" LineNumber="2" /> <Item Binding="MainRecord.LastName" LineDisplayOrderIndicator="2" LineNumber="2" /> <Item Binding="Id" LineNumber="5" /> </Tile> <Tile Identifier="Referentiel_User_Tile2" DisplayName_L1="Collaborateur : organisation, site" EntityType="Referentiel_User" TileDesignElement="inline data-icon"> <Item Binding="MainRecord.Site.Label" LineNumber="1" /> <Item Binding="MainRecord.Service.Label" LineNumber="2" /> </Tile>
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| DisplayName_L1 required | Type String Description Display name of the tile in language 1 (up to 16). |
| EntityType required | Type Int64 Description Identifier of the entity type. |
| Identifier required | Type String Description Unique identifier of the tile. |
| TileDesignElement required | Type Enumeration Description Defines the design element ("inline data-icon" or "picture-text"). |
Child Element: Item
One data to display in a tile.
Examples
<Item Binding="MainRecord.FirstName" LineDisplayOrderIndicator="1" LineNumber="2" /> <Item Binding="MainRecord.LastName" LineDisplayOrderIndicator="2" LineNumber="2" /> <Item Binding="MainRecord.EmployeeId" LineDisplayOrderIndicator="2" LineNumber="3" />
Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| AddedMinutes optional | Type Int32 Description Add minutes to the date field with this property. If the value is not defined, the default value is the one defined for the associated display entity property. |
| Binding required | Type Int64 Description Defines the binding path to a scalar property. |
| LineDisplayOrderIndicator required | Type Int32 Description Defines the display position of the data in the row. |
| LineNumber required | Type Int32 Description Defines the number of the line in which the data is displayed. When the tileDesignElement of the tile is "picture-text", four lines are customizable, and 2 lines are hard coded: - 5: id of the resource to navigate on click - 6: photoTag |
| OptimizedBinding optional | Type Int64 Description Optimized Binding allows DisplayTables to be faster displayed. If it is filled in, it takes priority over the binding located in the TileItem. |