SUDO
NOTE: See the Endpoint Policy Manager Cloud and SUDO support video and the Endpoint Policy Manager Cloud Mac + SUDO Using Wildcard Example video for an overview of this section.
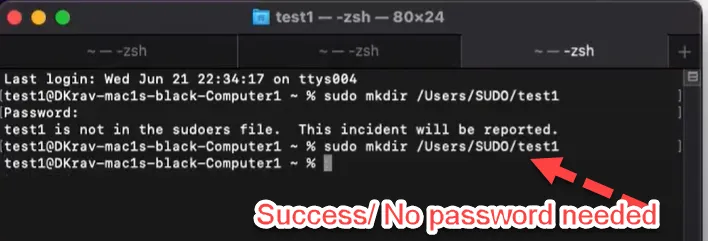
The point of SUDO policies is to enable a standard user to perform SUDO commands without needing to provide actual admin credentials. In this example the user wants to perform the command
Sudo mkdir /Users/Sudo/test1 but is blocked with a password request.
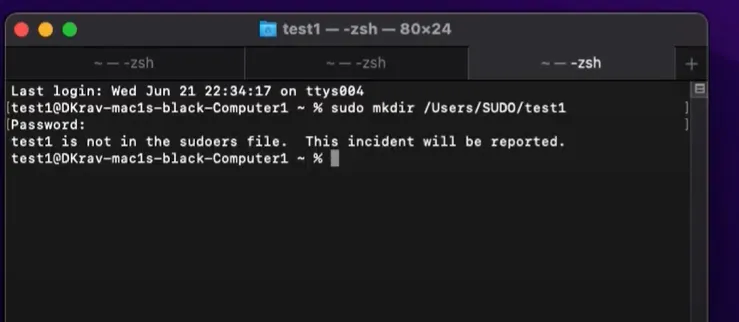
To overcome this, create a SUDO rule like this one:
: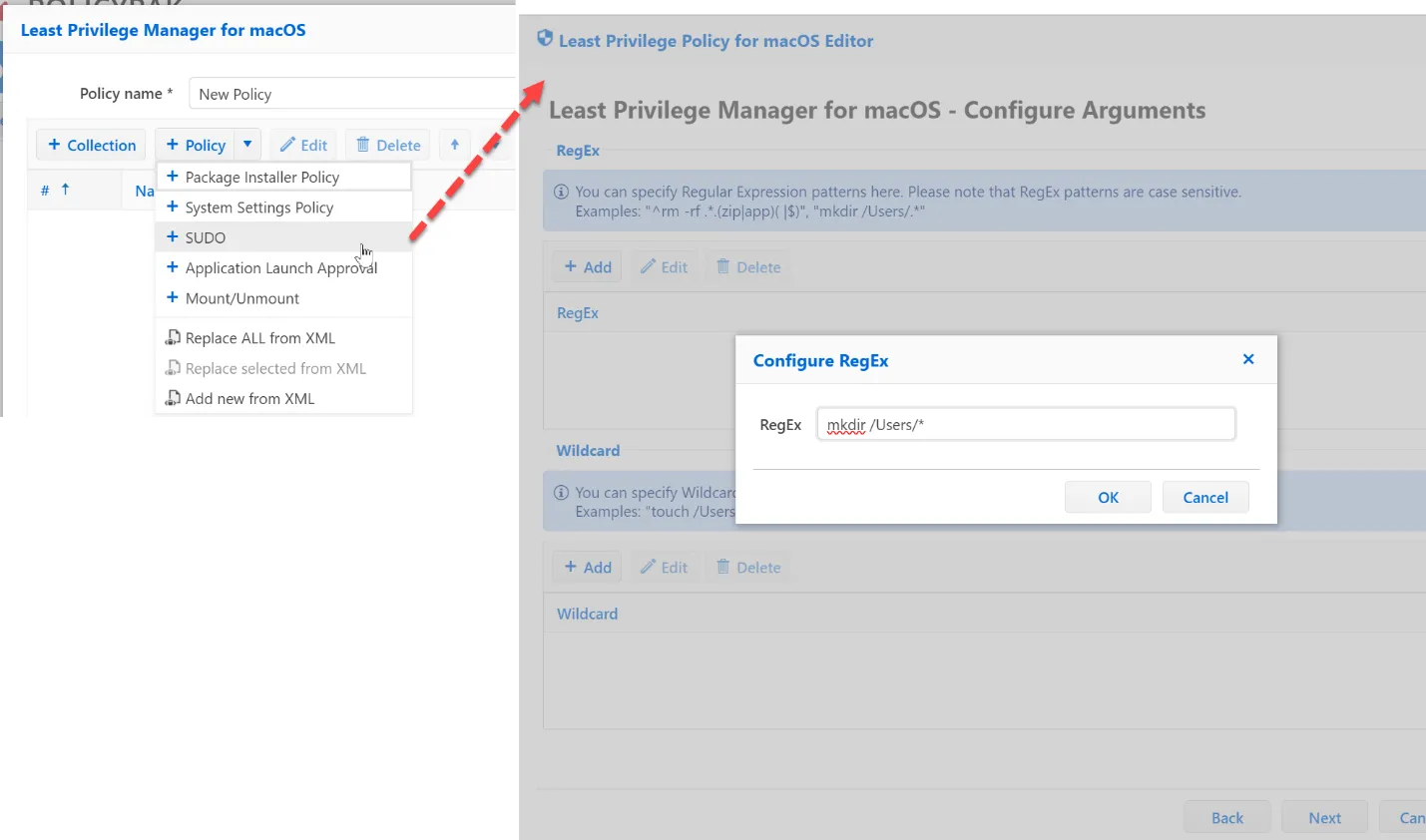
The Actions are:
- Deny Execution — Blocks the running of matching SUDO commands
- Allow Execution — Running SUDO commands is limited according to the system configuration. The PolicyPak MacOS client logs the user's actions
- Elevate — SUDO commands run without administrator password request, applicable for admin and standard users.
For this example policy, choose Elevate.
After the policy is synced, the result on the client can be seen here, where the same command now runs without password requirement.