Using Item-Level Targeting with Collections and Policies
Item-Level Targeting is used in Microsoft Group Policy Preferences and other areas of Endpoint Policy Manager to target or filter where specific policies will apply. With Endpoint Policy Manager Java Rules Manager, Item-Level Targeting can be placed on collections as well as Java Rules Manager policies within collections.
Step 1 – To start, right-click the collection, and select Change Item Level Targeting.

Step 2 – Within a Java Rules Manager policy, you can dictate an Item-Level Targeting policy by clicking on Item-Level Targeting.
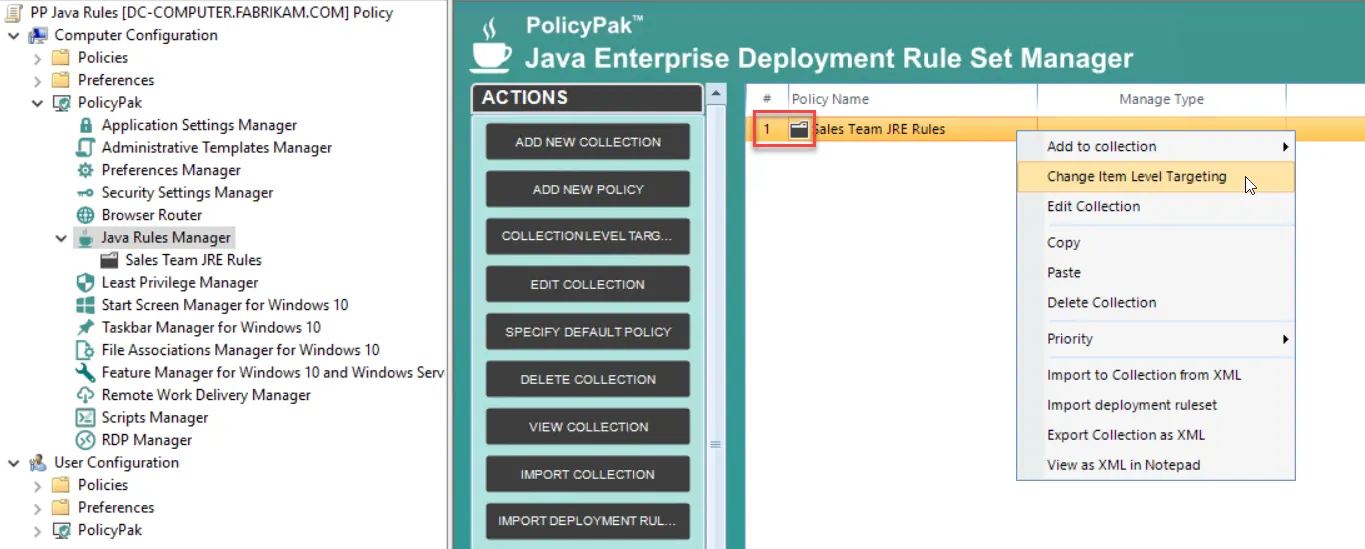
Step 3 – The Edit Item Level Targeting menu item brings up the Targeting Editor. You can select any combination of characteristics you want to test for. Administrators familiar with Group Policy Preferences' Item-Level Targeting will be at home in this interface as it is functionally equivalent.
Step 4 – You can apply one or more targeting items to a policy, which enables targeting items to be joined logically. You can also add targeting collections, which group together targeting items in much the same way parentheses are used in an equation. In this way, you can create a complex determination about where a policy will be applied. Collections may be set to And, Or, Is, or Is Not.
Below are some real-world examples of how you can use Item-Level Targeting.
- Software prerequisites — If you want to configure an application's settings, first make sure the application is installed on the user's computer before configuring it. You can use File Match or Registry Match targeting items (or both) to verify a specific version of a file or a registry entry is present. (For an example of this, look in the Uninstall registry key.)
- Mobile computers — If you want to deploy settings exclusively for users on mobile PCs, then filter the rule to apply only to mobile PCs by using the Portable Computer targeting item.
- Operating system version — You can specify different settings for applications based on the operating system version. To do this, create one rule for each operating system. Then filter each rule using the Operating System targeting item.
- Group membership — You can link the Group Policy Object (GPO) to the whole domain or organizational unit (OU), but only members within a specific group will pick up and process the rule settings.
- IP range — You can specify different settings for various IP ranges, like different settings for the home office and each field office.
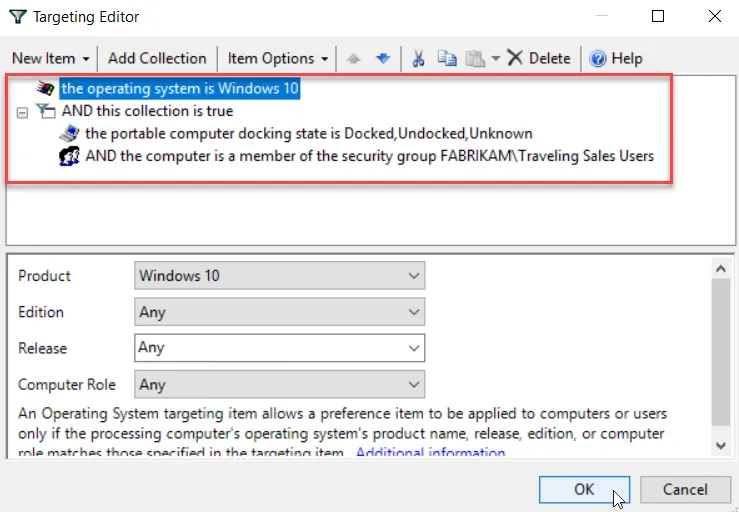
Step 5 – Close the editor when done. The collection's icon will have changed to orange, which indicates it now has Item-Level Targeting on the whole collection. In other words, none of the items in the collection will apply unless the Item-Level Targeting on the collection evaluates to True.
Within the collection, setting Item-Level Targeting within any policy results in the icon turning orange. The Item-Level Targeting column will indicate if Item-Level Targeting is on (Yes) or off (No).
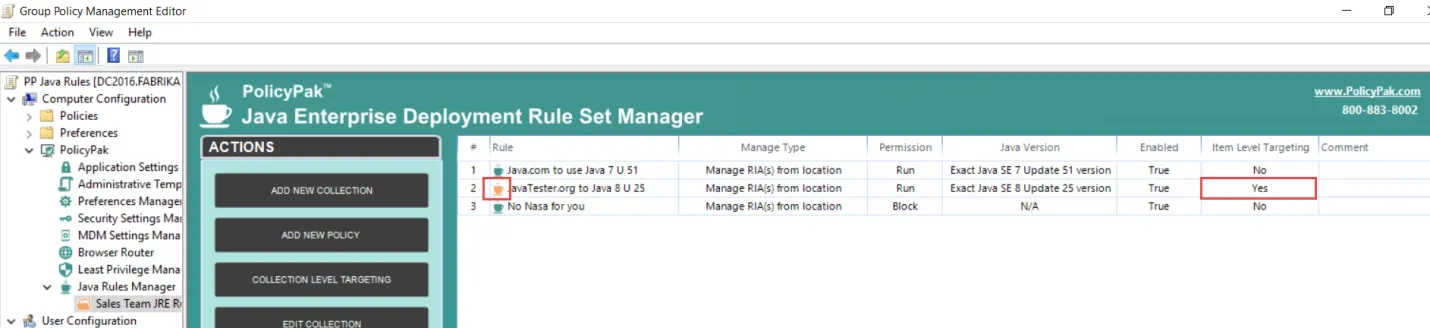
In this way, you can have granular control over policies and collections. First, filter with Item-Level Targeting on a collection, and then filter any specific rule if any Item-Level Targeting is applied there.