Elasticsearch and Replication
Searches performed in GroupID are catered through Elasticsearch.
Elasticsearch relies on two services:
-
Elasticsearch Service is responsible for searching the Elasticsearch repository and displaying search results when a search is performed through GroupID. If this service stops, Elasticsearch will not work.
-
Replication Service is responsible for replicating attributes of the following objects from the provider (such as Active Directory) to Elasticsearch.
- Group
- User
- Contact
- Computers
- Organizational Unit
The Replication service only replicates changes that are made to these objects on the directory server. Changes made to these objects using Admin Center, GroupID portal, Management Shell, or the GroupID mobile app, are directly saved in the Elasticsearch repository and replicated to the GroupID database by the Data service. See the Data Service topic.
Synchronize directly updates objects in the directory. As soon as objects are provisioned, de-provisioned, or updated in the directory using Synchronize, the Replication service replicates them to Elasticsearch.
Synchronize history is saved to Elasticsearch when Active Directory, Microsoft Entra ID, Generic LDAP, or Google Workspace is the destination provider in the respective Synchronize job. This history is replicated to the GroupID database by the Data s ervice.
NOTE: The Recycle Bin in the GroupID portal fetches data from the directory server and not from Elasticsearch.
Replication Settings
In Admin Center, you can specify settings for the Replication service at the global and local levels. Global settings apply to all identity stores in GroupID while local settings are specific to an identity store.
- At the global level, you can schedule the service to run every x minutes to replicate object attributes to Elasticsearch. You can also manually restore object data to Elasticsearch. See the Manage Global Replication Settings topic.
- For an identity store, you can specify the object attributes the service should replicate to Elasticsearch. See the Manage Local Replication Settings topic.
NOTE: The Replication service does not replicate excluded domains for an identity store. See the Exclude an Active Directory Domain from Replication topic.
Replication Service Logs
Logs for the Replication service are stored in the folder for the service on the GroupID server.
To view the logs:
- Launch IIS on the GroupID server and navigate to:
…\Sites\GroupIDSite11\GroupIDReplicationService - Right-click this folder and select Explore.
- Locate the Logs folder to read the logs.
Events are logged in a text file. When the file size reaches 100 MB, GroupID archives it in the same directory by replacing the file extension with the suffix .Log.X and then creating a new text file with the original name. X in .Log.X is a number from 1 to 10 representing the archiving order; where ‘1’ denotes the most recent file.
See Also
Manage Global Replication Settings
The Replication service is responsible for replicating attributes of the group, user, contact, computer, and organizational unit objects from a provider (such as Active Directory) to Elasticsearch.
You can configure certain settings for the Replication service in Admin Center. You can schedule it to run every x minutes, force run it at any time, set a threshold for triggering replication error notifications, and view the Elasticsearch health status.
On every successful run of the Replication service, GroupID generates the replication status of object types for each domain in an identity store and alerts you to any errors that may have occurred during the replication process.
NOTE: The Replication service does not replicate excluded domains for an identity store. See the Exclude an Active Directory Domain from Replication topic.
How to Resolve Replication Errors
Possible actions to eliminate replication errors are:
- Make sure the Replication service and Elasticsearch service are running.
- Make sure Search Guard or any other security plugin you use for Elasticsearch is operational.
- Consult the Replication service logs. They provide elaborate information about the object type in the specific domain of the identity store the error occurred for, and whether that error comes from the identity provider or Elasticsearch. See the Replication Service Logs topic.
What do you want to do?
- Monitor Elasticsearch Health Status
- Specify a Replication Interval for Objects
- Force Run the Replication Service (for Object Replication)
- View the Replication Status for Objects
- Specify Interval for Deleting Tombstone Objects
- Force Run the Replication Service (for Deleting Objects)
- Restore Object Data to Elasticsearch
- Clear Unused Indices
- Change the Search Guard Password
- Set a Threshold to Trigger Replication Error Notifications
Monitor Elasticsearch Health Status
GroupID enables you to monitor the Elasticsearch service for the following:
-
The status of the Elasticsearch service. See the Elasticsearch Service card on the Admin Center dashboard.
-
Elasticsearch cluster health stats, which include:
- Cluster name, health status, node info and shards info
- Cluster indices information, like health, number of documents, and status
GroupID checks if the Elasticsearch service is running, if all nodes are working, and if the cluster is intact. It also checks the health of each index.
To view Elasticsearch health status:
-
In Admin Center, click Replication in the left pane.
-
On the Replication page, click Elasticsearch Health Monitor.
This dialog box lists the Elasticsearch clusters in your environment, with the following information for each cluster:
-
Health: the cluster health status denoted by the following colors:
- Green – the service is running and the cluster is intact. Moreover, two or more nodes exist within the cluster.
- Yellow – the cluster is running but with warnings. It also indicates that a single node exists within the cluster. Elasticsearch recommends a three-node topology for improved performance and high availability.
- Red – the service has stopped or the cluster is broken (for reasons such as network connectivity.
-
Nodes: the number of nodes in the cluster.
-
Master: the name of the master node in the cluster.
-
-
To refresh the information displayed, click the Refresh icon.
-
Click a cluster name to view it in detail.
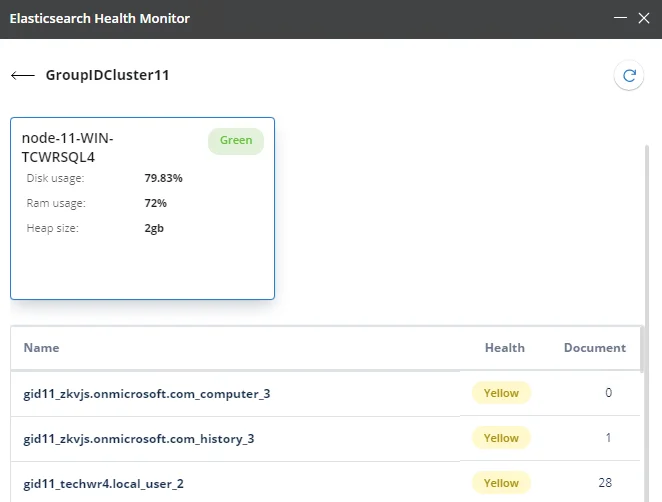
This dialog box displays the total number of nodes in the cluster. Each node is represented by a card, that displays the following for the node:
-
The name of the node
-
The system resources the node uses, such as hard disk space, RAM, and heap size
-
Node health with respect to disk space usage, denoted by the following colors:
- Green – when hard disk space usage is 79.99% or less
- Yellow – when hard disk space usage is 80-89.99%
- Red – when hard disk space usage is 90% or more
-
-
The indices in the cluster are listed in the gird.
-
The Name column displays the names of the indices.
-
The Health column displays the health of the index, which is denoted by the following colors:
- Green – the index is replicated to all nodes within the cluster.
- Yellow – the index is replicated to some but not all nodes within the cluster.
- Red – the index is not replicated to any node within the cluster.
-
The Document column shows the number of documents in the index.
-
-
Click the back arrow to return to the Elasticsearch Health Monitor dialog box.
Specify a Replication Interval for Objects
The Replication service interval applies to all identity stores defined in Admin Center. Object attributes to be replicated are specified in the respective identity store settings. See the Manage Local Replication Settings topic.
To set global replication interval:
-
In Admin Center, click Replication in the left pane.
-
On the Replication page, the Replication Service Interval card displays:
- the date and time the Replication service last ran
- the date and time the service will run next
- the interval (in minutes) between each run of the service
-
By default, the interval is set to 10 minutes, which indicates that the service is triggered every 10 minutes. In this way, changes made to objects in the directory during the last 10 minutes are replicated to Elasticsearch. In Active Directory, the whenChanged attribute stores the time and date the object was last changed. This service checks the value of this attribute and replicates any changes to Elasticsearch.
To change the interval, click Edit next to Service Interval on the on the Replication Service Interval card. Specify the interval (in minutes) between each run of the service and click the check mark.
Force Run the Replication Service (for Object Replication)
- In Admin Center, click Replication in the left pane.
- On the Replication page, click Force Replication Now on the Replication Service
Interval card to run the Replications service instantly.
Changes made to objects in the directory between the last and current run are replicated to Elasticsearch. Force-starting the service has no impact on the interval set in the Service Interval box for triggering the service.
View the Replication Status for Objects
After every run of the Replication service, you can view the replication status of each object type for each domain in an identity store. You can view which object types were successfully replicated and which ones failed to replicate.
To view the replication status:
-
In Admin Center, click Replication in the left pane.
-
On the Replication page, click Advanced Replication Status. The Advanced Replication Status dialog box displays the status of object types for each domain in an identity store.
-
The domains or object types that failed to replicate in the last run of the Replication service are displayed in red. Reasons could be inaccessibility or partial failure. Replication errors are brought to the administrator’s notice in the following ways:
- On the Identity Stores page, the card for the identity store turns red and Errors is displayed as the identity store status.
- A notification is sent to relevant personnel. See the Set a Threshold to Trigger Replication Error Notifications topic.
These alerts are triggered when replication fails in the last run of the Replication service, or if the service does not run at the required triggering interval. To resolve replication errors, see the How to Resolve Replication Errors topic.
-
The ‘Never replicated’ status indicates that the particular object type is not replicated yet. Similarly, a child domain that is not being used will have its status marked in red. To avoid these recurring errors, set the dates for these objects to a distant future date in the GroupID database. Or you can exclude a domain from replication. See the Exclude an Active Directory Domain from Replication topic.
-
Specify Interval for Deleting Tombstone Objects
Objects that are deleted from the directory must also be removed from Elasticsearch. For this purpose, you can specify a triggering interval for the Replication service to remove tombstone objects from the Elasticsearch repository. By default, the interval is set to 60 minutes, indicating that the service is triggered every 60 minutes. As a result, objects deleted in the directory during the last 60 minutes are removed from Elasticsearch.
To identify objects that have been deleted in the directory but exist in Elasticsearch, the Replication service compares the objects in both, and deletes objects that do not exist in the directory anymore.
To specify an interval:
-
In Admin Center, click Replication in the left pane.
-
On the Replication page, the Deleted Objects Replication Interval card displays:
- the date and time the Replication service last ran to remove tombstone objects from Elasticsearch
- the date and time the service will run again
- the interval (in minutes) between each run of the service
-
By default, the interval is set to 60 minutes, which indicates that the service is triggered every 60 minutes. In this way, objects that are deleted in the directory during the last 60 minutes are removed from Elasticsearch.
To change the interval, click Edit next to Service Interval on the Deleted Objects Replication Interval card. Specify the interval (in minutes) between each run of the service and click the check mark. This Replication service interval applies to all identity stores in GroupID.
Force Run the Replication Service (for Deleting Objects)
- In Admin Center, click Replication in the left pane.
- On the Replication page, click Force Replication Now on the Deleted Objects Replication
Interval card to run the Replication service instantly.
Objects deleted in the directory between the last and current run of the service, will be removed from Elasticsearch. Force-starting the service has no impact on the interval set in the Service Interval box for triggering the service.
Restore Object Data to Elasticsearch
You may need to restore object data to Elasticsearch. The restore object data function restores the following for all identity stores in GroupID:
- the current attribute values of objects (groups, users, contacts, computers, and OUs) from the provider (for example, Active Directory)
- the GroupID pseudo attributes of these objects from the GroupID database to Elasticsearch
To restore object data:
- In Admin Center, click Replication in the left pane.
- On the Replication page, click Restore Now in the Restore Objects Data area to restore data to Elasticsearch.
Clear Unused Indices
GroupID stores object attributes and their values in Elasticsearch, where each object type in an identity store is distinctly indexed. In a situation where an identity store is deleted from GroupID, its indices are not required anymore. So, you can clear them from Elasticsearch to avoid glut.
To clear unused indices:
- In Admin Center, click Replication in the left pane.
- On the Replication page, click Clear Now in the Clear Unused Indices area. The system checks if there exist any indices in Elasticsearch for an identity store that no longer exists in GroupID.
- The Delete Unused Indices dialog box displays the indices that will be deleted from
Elasticsearch. Click Delete to proceed or click Don't Delete to close the dialog box
without clearing the indices.
In case no unused indices are found, a notification pops up in the bottom right corner to inform that no unused indices were found.
Change the Search Guard Password
Search Guard is a security plugin used to induce an authentication mechanism in Elasticsearch. The option to change the Search Guard password is available when you install and manage Elasticsearch with GroupID. Users who use their own instance of Elasticsearch cannot change the Search Guard password using GroupID.
You can change the password of the admin account that GroupID uses to access Elasticsearch.
To change the password:
- In Admin Center, click Replication in the left pane.
- On the Replication page, click Change Password in the Search Guard Settings area.
- On the Change Password dialog box, provide the current password for the Search Guard admin account in the Your current password box.
- Specify a new password in the New Password and Confirm Password boxes.
- Click Change Password.
Set a Threshold to Trigger Replication Error Notifications
The Replication service runs every x minutes to replicate objects in an identity store. In case it fails to replicate during a run, a replication error is displayed, as discussed in the View the Replication Status for Objects topic.
GroupID generates notifications to alert administrators to replication errors. By default, the triggering threshold is set to ‘3 attempts’, which means that notifications will be sent when errors occur in three consecutive runs of the Replication service. You can change the threshold value as required.
Replication error notifications are sent to recipients whose email addresses are specified in the To and CC boxes on the Notifications page. See the Specify Notification Recipients topic.
To set a triggering threshold:
- In Admin Center, click Replication in the left pane.
- On the Replication page, the Replication Error Notification area displays ‘3 Attempts’ as
the default threshold for initiating notifications. This means that notifications will be sent
when three consecutive runs of the replication service result in error. Notifications will not be
sent when errors occur say, in two consecutive runs but no error shows in the third consecutive
run.
To change the threshold value, click Edit. Specify a threshold value to trigger replication error notifications and click the check mark.
See Also
GroupID Entitlement Schedule
An Entitlement schedule is automatically created for an identity store when:
-
A server is added for permission analysis on the Entitlement page in an Active Directory identity store. See the Manage File Servers for additional information on adding a server.
Or
-
A SharePoint site is added for permission analysis on the Entitlement page in a Microsoft Entra ID identity store. See the Manage SharePoint Sites topic for additional information on adding a SharePoint site.
By default, the schedule runs weekly to compute permissions on shared files and folders residing on the specified servers (for Active Directory), and the document libraries present in the specified sites (for SharePoint). It then replicates these permissions to Elasticsearch, enabling users to view, manage and update these permissions in the GroupID portal.
On the very first run of the Entitlement schedule, it computes all permissions from scratch and performs a complete replication. On each next run, it will create a parallel index for that specific server/SharePoint site index with the suffix _replication which computes all permissions from scratch. In the meantime, user can perform actions on GroupID Entitlement. The actions performed during this parallel replication are committed directly at the provider and stored in the database. These changes are then immediately committed to elastic after the replication is complete.
The scope schedule changes are replicated after the new index is done replicating permissions from the server/SharePoint. When this parallel index gets completely replicated, it becomes the new primary index for this server/SharePoint site and the _replication index is deleted from indices.
The GroupID Entitlement schedule runs in the context of the following accounts:
- For file servers, the schedule runs in the context of the service account defined for the identity store. In case you specify a different account for a file server, the schedule runs in the context of the changed account. See the Connect to a File Server Using a Different Account topic.
- For a SharePoint site, the schedule runs in the context of the account you specified to connect to the SharePoint admin site. In case you specify a different account for a site, the schedule runs in the context of the changed account. See the Connect to a Site Using a Different Account topic.
You cannot create or delete a GroupID Entitlement schedule; only edit the existing schedule.
What do you want to do?
Update the GroupID Entitlement Schedule
Follow the steps to update the GroupID Entitlement schedule.
Step 1 – In Admin Center, click Identity Stores in the left pane.
Step 2 – On the Identity Stores page, click the ellipsis button for an identity store and select Edit.
Step 3 – Click Schedules under Settings in the left pane.
Step 4 – On the Schedules page, click the plus sign next to GroupID Entitlement. Then click the ellipsis button for the schedule and select Edit.
Step 5 – On the Edit Schedule page, the Schedule Name and Name Preview boxes display the
name of the schedule as read-only. The name format is
Entitlement<the name of the machine the schedule is created on>_.
Step 6 – In the Scheduler Service Name drop-down list, select a Scheduler service that would be responsible for triggering this schedule. The number of services displayed in the list depend on the number of Elasticsearch clusters in the environment, as each cluster has its own Scheduler service. See the Scheduler Service topic.
Step 7 – The Triggers area displays the default triggering frequency for the schedule.
- To change a trigger, click Edit for it.
- To add a new trigger, click Add Trigger.
Step 8 – Follow step 11 in the Create a Group Usage Service Schedule topic to manage triggers.
Step 9 – After making the changes, click Update Schedule.
Step 10 – On the Schedules page, click Save.
For general schedule info, see the
View the Schedules in an Identity Store
topic.
See Also
Entitlement Scope Schedule
An Entitlement Scope schedule is automatically created for an identity store when:
-
A server is added for permission analysis on the Entitlement page in an Active Directory identity store. See the Manage File Servers for additional information on adding a server.
Or
-
A SharePoint site is added for permission analysis on the Entitlement page in a Microsoft Entra ID identity store. See the Manage SharePoint Sites topic for additional information on adding a SharePoint site.
Using the GroupID portal, users can update the permissions on files and folders residing on file servers (for Active Directory) and the document libraries in SharePoint sites (for Microsoft Entra ID). These changes to permissions are instantly committed to the respective file server or site; however, they are displayed in the GroupID portal after the Entitlement Scope schedule runs.
By default, the schedule runs daily to replicate the permissions from file servers or sites to Elasticsearch. Permissions are replicated for the target folder, site, or document library and its sub-trees, till the nth level. Changes made to permissions outside of GroupID are beyond the scope of this schedule.
Permissions replicated by the Entitlement Scope schedule are also replicated by the GroupID Entitlement Schedule, as the latter replicates permissions from scratch. However, the default triggering frequency for the GroupID Entitlement schedule (i.e., weekly) necessitates a separate Entitlement Scope schedule.
The Entitlement Scope schedule runs in the context of the following accounts:
- For file servers, the schedule runs in the context of the service account defined for the identity store. In case you specify a different account for a file server, the schedule runs in the context of the changed account. See the Connect to a File Server Using a Different Account topic.
- For a SharePoint site, the schedule runs in the context of the account you specified to connect to the SharePoint admin site. In case you specify a different account for a site, the schedule runs in the context of the changed account. See the Connect to a Site Using a Different Account topic.
You cannot create or delete an Entitlement Scope schedule; only edit the existing schedule.
What do you want to do?
Update the Entitlement Scope Schedule
Follow the steps to update the Entitlement Scope schedule.
Step 1 – In Admin Center, click Identity Stores in the left pane.
Step 2 – On the Identity Stores page, click the ellipsis button for an identity store and select Edit.
Step 3 – Click Schedules under Settings in the left pane.
Step 4 – On the Schedules page, click the plus sign next to Entitlement Scope. Then click the ellipsis button for the schedule and select Edit.
Step 5 – On the Edit Schedule page, the Schedule Name and Name Preview boxes display the name of the
schedule as read-only. The name format is
Entitlement<the name of the machine the schedule is created on>Scope.
Step 6 – In the Scheduler Service Name drop-down list, select a Scheduler service that would be responsible for triggering this schedule. The number of services displayed in the list depend on the number of Elasticsearch clusters in the environment, as each cluster has its own Scheduler service. See the Scheduler Service topic.
Step 7 – The Triggers area displays the default triggering frequency for the schedule.
- To change a trigger, click Edit for it.
- To add a new trigger, click Add Trigger.
Step 8 – Follow step 11 in the Create a Group Usage Service Schedule topic to manage triggers.
Step 9 – After making the changes, click Update Schedule.
Step 10 – On the Schedules page, click Save.
For general schedule info, see the
View the Schedules in an Identity Store topic.
See Also
Entitlement Temporary Permissions Schedule
An Entitlement Temporary Permissions schedule is automatically created for an identity store when:
-
A server is added for permission analysis on the Entitlement page in an Active Directory identity store. See the Manage File Servers for additional information on adding a server.
Or
-
A SharePoint site is added for permission analysis on the Entitlement page in a Microsoft Entra ID identity store. See the Manage SharePoint Sites topic for additional information on adding a SharePoint site.
The Entitlement Temporary Permissions schedule updates the temporary permissions granted to objects on shared files and folders residing on file servers (for Active Directory), and the document libraries in SharePoint sites (for Microsoft Entra ID). This is how it works:
- Administrators and other users can set a start and end date to grant certain permission(s) temporarily to an object on shared resources, such as file shares and document libraries in a SharePoint site.
- They can also set a start and end date to revoke certain permission(s) temporarily for an object on shared resources, such as file shares and document libraries in a SharePoint site.
- The Entitlement Temporary Permissions schedule temporarily grants and revokes permissions for an object on the specified dates.
Let’s assume that the Entitlement Temporary Permissions schedule is scheduled to run once a week, say Mondays. If temporary permissions are to be granted to an object on file server share for three days - Wednesday till Friday, it will not happen. This is because the Entitlement Temporary Permissions schedule did not run on the specific days for temporary permissions update. Make sure that the schedule is set to run at a frequency that meets your temporary permission requirements.
The Entitlement Temporary Permissions schedule runs in the context of the following accounts:
- For file servers, the schedule runs in the context of the service account defined for the identity store. In case you specify a different account for a file server, the schedule runs in the context of the changed account. See the Connect to a File Server Using a Different Account topic.
- For a SharePoint site, the schedule runs in the context of the account you specified to connect to the SharePoint admin site. In case you specify a different account for a site, the schedule runs in the context of the changed account. See the Connect to a Site Using a Different Account topic.
You cannot create or delete an Entitlement Temporary Permissions schedule; only edit the existing schedule.
What do you want to do?
- Follow the steps to udpate the Entitlement Temporary Permissions schedule
Update the Entitlement Temporary Permissions Schedule
Follow the steps to udpate the Entitlement Temporary Permissions schedule.
Step 1 – In Admin Center, click Identity Stores in the left pane.
Step 2 – On the Identity Stores page, click the ellipsis button for an identity store and select Edit.
Step 3 – Click Schedules under Settings in the left pane.
Step 4 – On the Schedules page, click the plus sign next to Entitlement Temporary Permissions. Then click the ellipsis button for the schedule and select Edit.
Step 5 – On the Edit Schedule page, the Schedule Name and Name Preview boxes display the name of the
schedule as read-only. The name format is
Entitlement<the name of the machine the schedule is created on>_ TemporaryPermission_.
Step 6 – In the Scheduler Service Name drop-down list, select a Scheduler service that would be responsible for triggering this schedule. The number of services displayed in the list depend on the number of Elasticsearch clusters in the environment, as each cluster has its own Scheduler service. See the Scheduler Service topic.
Step 7 – The Triggers area displays the default triggering frequency for the schedule.
- To change a trigger, click Edit for it.
- To add a new trigger, click Add Trigger.
Step 8 – Follow step 11 in the Create a Group Usage Service Schedule topic to manage triggers.
Step 9 – After making the changes, click Update Schedule.
Step 10 – On the Schedules page, click Save.
For general schedule info, see the
View the Schedules in an Identity Store topic.
See Also
Group Usage Service Schedule
A Group Usage Service schedule monitors expansion events and timestamps affected groups of the Microsoft Exchange Server(s) for an identity store.
An expansion event occurs when an Exchange Server expands a distribution list for sending messages. The event is recorded in the Exchange Server's message tracking log, which the Group Usage Service schedule reads, parsing for the timestamp that indicates when the distribution list was last used.
The timestamp is then used by the Group Life Cycle Schedule to extend or reduce the life of mail-enabled distribution groups based on their usage. See the Enable Group Usage Lifecycle topic.
While creating a Group Usage Service schedule, you have to specify a job triggering criterion, the containers the job will process, and the messaging servers for reading expansion logs.
What do you want to do?
Create a Group Usage Service Schedule
-
In Admin Center, click Identity Stores in the left pane.
-
On the Identity Stores page, click the ellipsis button for an identity store and select Edit.
-
Click Schedules under Settings in the left pane.
-
On the Schedules page, click Add Schedule and select Group Usage Service Job.
The Create Schedule page is displayed. -
In the Schedule Name box, enter a name for the schedule.
-
The Name Preview box displays the schedule name prefixed with _GUS__; the schedule is displayed with this name in email notifications.
-
Select a GroupID portal URL in the Portal URL drop-down list to include it in notifications generated for the schedule. Users are redirected to this portal to perform any necessary action.
-
In the Scheduler Service Name drop-down list, select a Scheduler service that would be responsible for triggering this schedule. The number of services displayed in the list depend on the number of Elasticsearch clusters in the environment, as each cluster has its own Scheduler service. See the Scheduler Service topic.
-
You can specify containers as targets for the schedule. The schedule will process all groups in those containers and sub-containers.
- Select the Include all containers check box to run the schedule on all the containers in
the identity store.
Or - Click Add Container to add one or more containers as targets. The Add Container(s) dialog box shows the domain name and the OUs in the identity store. Select the check boxes for the required containers and click Add; the selected containers are displayed in the Target(s) area. To exclude a sub-container, clear the check box for it on the Add Container(s) dialog box.
- To remove a container in the Target(s) area, click Remove for it.
To remove all target objects, click Remove All.
- Select the Include all containers check box to run the schedule on all the containers in
the identity store.
-
You can also specify one or more messaging servers. The job reads expansion logs from these servers.
-
Click Add Server in the Messaging Server area. The Add Messaging Servers dialog box displays the messaging servers in the identity store.
-
Select the check boxes for the messaging servers that the Group Usage Service schedule should process.
Or
Select the Server Name check box if you want this job to read the expansion logs of all messaging servers in the identity store.
-
Click Add. The messaging server(s) are displayed in the Messaging Server area.
-
-
Click Add Triggers in the Triggers area to specify a triggering criterion for the schedule, that, when met, starts the execution of the schedule.
-
In the Begin the Task drop-down list on the New Trigger dialog box, select a trigger to start the schedule.
- On a schedule: To start a schedule at a specific time of day or starting it multiple times on a daily, weekly, or monthly schedule.
- At startup: To start the schedule every time the GroupIDSchedulerService starts. This is a GroupID service created in native IIS.
-
On selecting an option, the dialog box displays relevant settings for the trigger.
The Triggers dialog box is the same as available in Windows Task Scheduler. Visit the Triggers page for help. -
After specifying the settings, click Add. The trigger is displayed in the Triggers area.
A schedule can have one or more triggers, allowing the schedule to be started in many ways. With multiple triggers, the schedule will start when any of the triggers occur.
To enable or disable a trigger - Click Edit for a trigger in the Triggers area and use the toggle button at the top of the Update Trigger dialog box to enable or disable the trigger.
To remove a trigger - Click Remove for a trigger to remove it. -
-
Click Add Authentication in the Authentication area to specify an account for running the schedule in the identity store.
The Authentication dialog box displays your accounts in the respective identity store that you have used for signing in. Select an account to authenticate with it or click Login with a different user to provide the credentials of another account to run the schedule in the identity store.NOTE: Make sure this account falls under a high priority security role that has elevated permissions in the identity store (for example, Administrator).
NOTE: If you are creating this schedule in a Microsoft Entra ID identity store, you can only specify the logged-in user's account. See the Schedules for Microsoft Entra ID Identity Store section of the Schedules topic for additional information.
-
On the Create Schedule page, click Create Schedule.
-
On the Schedules page, click Save.
The schedule is displayed under Group Usage Service. See the View the Schedules in an Identity Store topic for more info.
See Also
Manage Schedules
GroupID enables you to run, modify, disable, and delete the schedules defined for an identity store.
What do you want to do?
- View the Schedules in an Identity Store
- Enable/Disable a Schedule
- Update Triggers for a Schedule
- Update Targets for a Schedule
- Update Notification Settings for a Schedule
- Run a Schedule Instantly
- Terminate a Running Schedule
- Delete a Schedule
View the Schedules in an Identity Store
-
In Admin Center, click Identity Stores in the left pane.
-
On the Identity Stores page, click the ellipsis button for an identity store and select Edit.
-
Click Schedules under Settings in the left pane.
-
On the Schedules page, click the plus sign next to a job name to view the schedules defined for it.
The following is displayed for a schedule:Label Description Enable Shows whether a schedule is enabled or disabled. Use the toggle button next to a schedule to disable an enabled schedule and vice versa. GroupID does not execute a disabled schedule. Job Name The name of a schedule. Target(s) The group(s) and container(s) that a schedule processes. Last Run The date and time a schedule last ran. Next Run The next date and time a schedule will run. Actions Click the ellipsis button for a schedule in the Actions column and select an option: - Edit: to update the schedule's settings, such as targets, triggers, and notifications. - Delete: to delete a schedule. - Run: to manually run a schedule instantly. - Terminate: to manually terminate a running schedule instantly. This option is available for schedules that are currently running.
Search a Schedule
GroupID enables you to search for a schedule by different attributes, such as job name, job target, last run time, the kind of notifications set for a job and the user name used for authentication in a job.
To apply a filter:
-
On the Schedules page, expand the Schedule Filters area by clicking the plus sign.
-
In the Select a Filter box, select an attribute to filter schedules.
-
In the Select an Operator drop-down list, select an operator to apply to the selected attribute. This drop-down displays the operators on the basis of the selected attribute. Available operators are:
(missing or bad snippet)
-
In the Select a Value box, specify a value for the attribute. The selected attribute and operator determine the kind of value that can be entered in this box. For some operators, such as Present and Not Present, this field is not available. These operators check if a value for the attribute is present or not.
To add more filters - On adding a filter, the next row is displayed, so you can add another filter.
To remove a filter row - To remove a filter row, click Remove for it.
To remove the filter - To remove all the filter rows, click Clear. -
To apply the filter, click Apply. With multiple filters, schedules that satisfy all the filters are displayed.
Enable/Disable a Schedule
- In Admin Center, click Identity Stores in the left pane.
- On the Identity Stores page, click the ellipsis button for an identity store and select Edit.
- Click Schedules under Settings in the left pane.
- On the Schedules page, click the plus sign for a job to view the schedules defined for it.
- Use the Enable toggle button for a schedule to enable or disable it.
A disabled schedule is not executed in the identity store. - Click Save.
Update Triggers for a Schedule
A trigger is a criterion that, when met, starts the execution of a schedule.
To update triggers for a schedule:
-
In Admin Center, click Identity Stores in the left pane.
-
On the Identity Stores page, click the ellipsis button for an identity store and select Edit.
-
Click Schedules under Settings in the left pane.
-
On the Schedules page, click the plus sign for a job to view the schedules defined for it.
-
Click the ellipsis button for a schedule and select Edit.
-
On the Edit Schedule page, the Triggers area displays the trigger(s) set for the schedule.
- To update a trigger, click Edit for it.
- To add a new trigger, click Add Trigger.
- To remove a trigger, click Remove for it.
Follow step 11 in the Group Usage Service Schedule topic to manage triggers.
-
Click Update Schedule.
-
Click Save on the Schedules page.
Update Targets for a Schedule
Targets in a schedule are the objects processed by that schedule.
To update the targets:
-
In Admin Center, click Identity Stores in the left pane.
-
On the Identity Stores page, click the ellipsis button for an identity store and select Edit.
-
Click Schedules under Settings in the left pane.
-
On the Schedules page, click the plus sign for a job to view the schedules defined for it.
-
Click the ellipsis button for a schedule and select Edit.
-
On the Edit Schedule page, the Target(s) area displays the target objects for the schedule.
Target types differ for different schedule types. For example, you can set containers as targets for a Group Lifecycle schedule; and jobs and job collections for a Synchronize schedule. Other schedules, such as a User Lifecycle schedule, may not require a target, as they execute certain functions for an identity store.- To add a target object to a schedule, refer to the instructions for the respective schedule.
- To remove a target object, click Remove for it.
- To remove all target objects, click Remove All.
-
Click Update Schedule.
-
Click Save on the Schedules page.
Update Notification Settings for a Schedule
- In Admin Center, click Identity Stores in the left pane.
- On the Identity Stores page, click the ellipsis button for an identity store and select Edit.
- Click Schedules under Settings in the left pane.
- On the Schedules page, click the plus sign for a job to view the schedules defined for it.
- Click the ellipsis button for a schedule and select Edit.
- On the Edit Schedule page, click the Notifications button to update notification settings
for the schedule.
Notification settings differ for different schedule types. For example, a Smart Group Update schedule has a different set of notification options from a Group Lifecycle schedule. Other schedules, such as the GroupID Entitlement and Workflow Acceleration schedules, do not have notification settings.
To manage the notification settings for a schedule, refer to the instructions for the respective schedule. - Click Update Schedule.
- Click Save on the Schedules page.
Run a Schedule Instantly
- In Admin Center, click Identity Stores in the left pane.
- On the Identity Stores page, click the ellipsis button for an identity store and select Edit.
- Click Schedules under Settings in the left pane.
- On the Schedules page, click the plus sign for a job to view the schedules defined for it.
- Click the ellipsis button for a schedule and select Run to execute it instantly.
Terminate a Running Schedule
You can terminate a schedule that is currently running in an identity store. On termination, objects that have already been processed by the schedule will not be reverted while the remaining stay unprocessed.
To terminate a running schedule:
- In Admin Center, click Identity Stores in the left pane.
- On the Identity Stores page, click the ellipsis button for an identity store and select Edit.
- Click Schedules under Settings in the left pane.
- On the Schedules page, click the plus sign for a job to view the schedules defined for it.
- Click the ellipsis button for a currently running schedule and select Terminate to stop it instantly.
Delete a Schedule
- In Admin Center, click Identity Stores in the left pane.
- On the Identity Stores page, click the ellipsis button for an identity store and select Edit.
- Click Schedules under Settings in the left pane.
- On the Schedules page, click the plus sign for a job to view the schedules defined for it.
- Click the ellipsis button for a schedule and select Delete.
The Delete option is not available for system-defined schedules. - On the Delete Schedule dialog box, click Delete.
- Click Save on the Schedules page.
See Also
Orphan Group Update Schedule
An orphan group is one without a primary owner.
An Orphan Group Update schedule is responsible for assigning a primary owner to orphan groups. For this, the orphan group must have at least one additional owner, since the schedule promotes a group’s additional owner as its primary owner.
When an Orphan Group Update schedule runs, it promotes the first additional owner in the additional owners’ list (be it a user, contact, or security group) as the primary owner and a notification is sent to the promoted owner. Note the following:
- A temporary additional owner is not promoted as the primary owner. When such an owner is the first in the list, the schedule skips it and moves to the next additional owner in the list.
- When a security group is promoted as the primary owner, a notification is sent to all group members.
- When a mail-enabled user is promoted as the primary owner, the schedule also adds him or her as the group’s Exchange additional owner.
- When a user is promoted as the primary owner of more than one group, a single notification is sent to him or her, containing details of the groups added to his or her ownership.
The promotion of an additional owner to primary owner may violate the Group Owners policy for the minimum number of additional owners required. A notification is sent to the promoted owner to add an additional owner to comply with the policy. See the Group Owners Policy topic.
With history tracking enabled, history is logged at the group level and at the promoted owner’s level. See the Configure History Tracking topic.
What do you want to do?
Create an Orphan Group Update Schedule
- In Admin Center, click Identity Stores in the left pane.
- On the Identity Stores page, click the ellipsis button for an identity store and select Edit.
- Click Schedules under Settings in the left pane.
- On the Schedules page, click Add Schedule and select Orphan Group Update Job. The Create Schedule page is displayed.
- In the Schedule Name box, enter a name for the schedule.
- The Name Preview box displays the schedule name prefixed with _OrphanGroupUpdater__; the schedule is displayed with this name in email notifications.
- Select a GroupID portal URL in the Portal URL drop-down list to include it in notifications generated by the schedule. Users are redirected to this portal to perform any necessary action.
- In the Scheduler Service Name drop-down list, select a Scheduler service that would be responsible for triggering this schedule. The number of services displayed in the list depend on the number of Elasticsearch clusters in the environment, as each cluster has its own Scheduler service. See the Scheduler Service topic.
- You can specify containers as targets for the schedule. The schedule will process all groups in these containers and their sub-containers. To specific containers as target, follow step 9 in the Create a Group Usage Service Schedule topic.
- Click Add Triggers in the Triggers area to specify a triggering criterion for the schedule, that, when met, starts the execution of the schedule. Follow step 11 in the Create a Group Usage Service Schedule topic to add triggers.
- Click Add Authentication in the Authentication area to specify an account for running the schedule in the identity store. See step 12 in the Create a Group Usage Service Schedule topic for details.
- On the Create Schedule page, click Create Schedule.
- On the Schedules page, click Save.
The schedule is displayed under Orphan Group Update. See the View the Schedules in an Identity Store topic for more info.
See Also
Schedules
The scheduling feature in GroupID enables you to perform several operations by creating scheduled jobs for an identity store. These schedules auto run at the specified day, time, and frequency.
Schedules for Active Directory, Google Workspae, and Generic LDAP Identity Stores
You can define the following schedules for an identity store:
- A Group Usage Service Schedule monitors group usage and time stamps groups with the date and time they were last used.
- A Group Life Cycle Schedule expires and deletes groups according to their expiry policy. It executes the Group Lifecycle policy for the identity store.
- A History Retention Schedule archives identity store history data in GroupID.
- A GroupID Entitlement Schedule replicates object permissions on file servers and SharePoint sites for an Active Directory and Microsoft Entra ID identity store respectively.
- An Entitlement Scope Schedule replicates changes made to object permissions on file servers and SharePoint sites using GroupID.
- An Entitlement Temporary Permissions Schedule updates the temporary permissions for objects on file servers and SharePoint sites.
- A Managed By Life Cycle Schedule manages the temporary additional owners for groups and temporary additional managers for users.
- A Membership Life Cycle Schedule updates the temporary membership of groups.
- An Orphan Group Update Schedule sets the primary owner for an orphan group.
- A Reports Schedulecan automatically generate reports that you link with the schedule.
- A Schema Replication Schedule replicates the schema of an identity provider to the GroupID database.
- A Smart Group Update Scheduleupdates Smart Groups and Dynasties.
- A Synchronize Schedule can execute Synchronize jobs and job groups at a set frequency.
- A User Life Cycle Schedule disables users who do not validate their profiles within a given period, based on the settings defined for user profile validation.
- A Workflow Acceleration Schedule forwards workflow requests to approvers and auto approves requests according to workflow approver acceleration rules.
NOTE: Role members with the Manage Scheduling permission in an identity store can create and manage scheduled jobs. See the Modify Role Permissions topic.
Schedules are saved in the GroupID database. The GroupIDSchedulerService, created in the GroupIDSite11 site in native IIS is responsible for initiating schedule runs.
Schedules for Microsoft Entra ID Identity Store
The following schedules are automatically created when their associated configurations are done in an identity store.
- Entitlement (GroupID Entitlement Schedule, Entitlement Scope Schedule, Entitlement Temporary Permissions Schedule)
- User Life Cycle Schedule
- History Retention Schedule
- Workflow Acceleration Schedule
In a Microsoft Entra ID identity provider, the Entra ID user must be logged into the Admin Center while making configurations of these schedules. The schedules are then run in the context of the logged in user. The following dialog box displays the username of the logged-in user when you configure a schedule:
Use the Login with a different user option to provide the credentials of another account to run the schedule in the identity store is not available for a Microsoft Entra ID identity store.
NOTE: The existing schedules will continue to work. The SAML provider authentication does not apply on them.
See Also
Reports Schedule
GroupID can generate reports for an identity store on a scheduled basis.
You can create a Reports schedule and add reports to it. When the schedule runs, all added reports are auto generated. The Reports schedule also sends email notifications to the designated recipients.
What do you want to do?
Create a Reports Schedule
-
In Admin Center, click Identity Stores in the left pane.
-
On the Identity Stores page, click the ellipsis button for an identity store and select Edit.
-
Click Schedules under Settings in the left pane.
-
On the Schedules page, click Add Schedule and select Reports Job. The Create Schedule page is displayed.
-
In the Schedule Name box, enter a name for the schedule.
-
The Name Preview box displays the schedule name prefixed with _ReportPortal__; the schedule is displayed with this name in email notifications.
-
In the Scheduler Service Name drop-down list, select a Scheduler service that would be responsible for triggering this schedule. The number of services displayed in the list depend on the number of Elasticsearch clusters in the environment, as each cluster has its own Scheduler service. See the Scheduler Service topic.
-
To add reports to the schedule, click Add Report(s) in the Reports area. The Add Reports to Schedule dialog box is displayed.
NOTE: You can only add reports that have been generated in the GroupID portal, since the schedule uses the settings provided there to generate the report. Moreover, you cannot change the settings here, such as the container and filter settings.
-
In the Object Category drop-down list, select a report category. Available categories are: All Categories, Users, Groups, Contacts and Computers. In the GroupID portal, reports are classified under these categories.
-
The Reports drop-down list shows all reports in the selected category. On selecting a report, one of the following happens:
- The report is displayed in the grid on the dialog box. This is because it has previously been added, and you do not need to add it again. If the report has been generated multiple times in the GroupID portal, all instances are displayed, since each instance has its own title, container, and filter settings.
- If the report is not displayed in the grid, you have to add it using the Add button. (The Add button gets enabled if this report has been generated in the GroupID portal.)
Notice that when you select a category, a report may get listed in the grid. This is because the first report in the category is auto selected in the Reports drop-down list. If that report has previously been added, it is displayed in the grid.
-
The report is listed in the grid on the dialog box with the following info:
- Report Title - the name given to the report by the user while generating it.
- Report Name - the name of the report in GroupID.
- Container - the container the report will fetch results from. This container was specified by the user while generating the report.
- Filter - the criteria applied to get the results.
You can add as many reports as required.
-
Select the check box for a report and click Add. The selected reports are displayed in the Reports area on the Create Schedule page. When this Reports schedule runs, it auto generates all added reports.
To remove a report , click Remove for it.
-
-
Click Add Triggers in the Triggers area to specify a triggering criterion for the schedule, that, when met, starts the execution of the schedule. Follow step 11 in the Create a Group Usage Service Schedule topic to add triggers.
-
Click Add Authentication in the Authentication area to specify an account for running the schedule in the identity store. Follow step 12 in the Create a Group Usage Service Schedule topic for details.
-
To set up notifications for the schedule, click Notifications.
- On the Notifications dialog box, enter the email address of recipient(s) to whom you want to send the reports generated by the schedule. Use a semicolon to separate multiple addresses.
- Click Save.
-
On the Create Schedule page, click Create Schedule.
-
On the Schedules page, click Save.
The schedule is displayed under Reports. See the View the Schedules in an Identity Store topic for details.
See Also
Schema Replication Schedule
An Identity store is built on an identity provider, that could be Active Directory, Microsoft Entra ID, Google Workspace, or Generic LDAP. The Schema Replication schedule replicates the schema of these identity providers to the GroupID database.
Unlike other schedules that exist separately for each identity store, GroupID has only one Schema Replication schedule that serves all identity stores. While the schedule is displayed separately for each identity store, it does not represent separate schedules. So when you run the Schema Replication schedule for an identity store, it replicates the schema for all identity stores in GroupID. And if you terminate it, the process is terminated for all identity stores. Moreover, the schedule runs every time it is triggered from any of the identity stores, be it manually or according to its triggers.
When the Schema Replication schedule runs for the first time, it replicates schema from scratch. In all subsequent runs, it replicates any changes made to the schema. Of this replicated schema, you can choose the object attributes you actually want to use in an identity store. See the Specify Object Attributes to Replicate topic for details.
NOTE: For Microsoft Entra ID, schema is replicated from the schema file for Graph API v 3.26.0.
The Schema Replication schedule runs in the context of the super admin account in the GroupID provider. You cannot create or delete a Schema Replication schedule; only update the existing one.
What do you want to do?
Update the Schema Replication Schedule
-
In Admin Center, click Identity Stores in the left pane.
-
On the Identity Stores page, click the ellipsis button for an identity store and select Edit.
-
Click Schedules under Settings in the left pane.
-
On the Schedules page, click the plus sign next to Schema Replication. Then click the ellipsis button for the schedule and select Edit.
-
On the Edit Schedule page, the Schedule Name and Name Preview boxes display the name of the schedule as read-only.
-
In the Scheduler Service Name drop-down list, select a Scheduler service that would be responsible for triggering this schedule. The number of services displayed in the list depend on the number of Elasticsearch clusters in the environment, as each cluster has its own Scheduler service. See the Scheduler Service topic.
CAUTION: In case of multiple Scheduler services, you must bind the same service with the Schema Replication schedules in all the identity stores.
-
The Triggers area displays the default triggering frequency for the schedule.
- To change it, click Edit for it.
- To add a new trigger, click Add Trigger.
Follow step 11 in the Create a Group Usage Service Schedule topic to manage triggers.
-
Click Update Schedule.
-
On the Schedules page, click Save.
For general schedule info, see the View the Schedules in an Identity Store topic.
See Also
Smart Group Update Schedule
You can create a Smart Group Update schedule and bind it to Smart Groups and Dynasties in an identity store. When the schedule runs, it updates the following:
- Group membership - Each Smart Group and Dynasty has a user-defined query specified for it. When a Smart Group Update schedule runs, it updates the membership of target groups with records fetched by the query.
- Certain attribute values for nested Smart Groups and Dynasty children.
A Smart Group or Dynasty that is not linked with a Smart Group Update schedule will not be auto updated.
You can configure notifications for a schedule that are sent to designated recipients in response to an event, such as when the schedule successfully updates all target groups or fails to update any target group.
What do you want to do?
Create a Smart Group Update Schedule
-
In Admin Center, click Identity Stores in the left pane.
-
On the Identity Stores page, click the ellipsis button for an identity store and select Edit.
-
Click Schedules under Settings in the left pane.
-
On the Schedules page, click Add Schedule and select Smart Group Update Job. The Create Schedule page is displayed.
-
In the Schedule Name box, enter a name for the schedule.
-
The Name Preview box displays the schedule name prefixed with _SmartGroup__; the schedule is displayed with this name in email notifications.
-
Select a GroupID portal URL in the Portal URL drop-down list to include it in notifications generated for the schedule. Users are redirected to this portal to perform any necessary action.
-
In the Scheduler Service Name drop-down list, select a Scheduler service that would be responsible for triggering this schedule. The number of services displayed in the list depend on the number of Elasticsearch clusters in the environment, as each cluster has its own Scheduler service. See the Scheduler Service topic.
-
You can specify containers and groups as targets for the schedule. or a container, the schedule processes all groups in it and its sub-containers. In the case of groups, the schedule processes the added groups only (i.e., it does not process nested groups).
-
To specific containers as target, follow step 9 in the Create a Group Usage Service Schedule topic. The schedule will process all Smart Groups and Dynasties in the containers and their sub-containers listed in the Target(s) area.
-
To add Smart Groups and Dynasties as targets, click Add Group. On the Add Object(s) dialog box, specify a container to search for the desired groups; then perform a search to locate and select the groups.
- Click the down arrow in the Search Container box and select a container to limit the search scope to it.
- Select the Include Sub-Containers check box to include the sub-containers within the selected container to search for the group(s).
- Enter a search string in the search box; group names starting with the string are
displayed as you type. Click Add for a group to select it.
You can also perform an advanced search to locate a group. Click Advanced in the search box and use the search fields to enter a search string. On clicking Search, groups matching the string are displayed. Select the group you want to add as target. - After selecting one or more groups, click Add the groups are displayed in the Target(s) area.
-
To remove a container or group in the Target(s) area, click Remove for it.
To remove all target objects, click Remove All.
-
-
Click Add Triggers in the Triggers area to specify a triggering criterion for the schedule, that, when met, starts the execution of the schedule. Follow step 11 in the Create a Group Usage Service Schedule topic to add triggers.
-
Click Add Authentication in the Authentication area to specify an account for running the schedule in the identity store. Follow step 12 in the Create a Group Usage Service Schedule topic for details.
-
To enable notifications for the schedule, click Notifications. On the Notifications dialog box, specify an event for triggering notifications for the schedule and add recipients.
-
Use the toggle button at the top to enable notifications for the schedule.
-
In the Send Notification to the following email IDs box, enter the email addresses of notification recipients, using a semicolon to separate multiple addresses. These recipients will get a report on the event you select for Send Notification.
NOTE: If the email ID of a target group’s additional owner is specified in this box, the additional owner will receive notifications even if the Do not Notify check box is selected for it in the respective group’s properties.
-
Select the Send Report to group owner(s) check box to send a report to each unique group owner of the groups processed by the schedule. A Dynasty owner receives a notification for its groups and direct child Dynasties.
Group owners include the primary owner, additional owner(s), and Exchange additional owner(s).NOTE: An additional owner of a target group will not receive notifications when the Do not Notify check box is selected for it in the respective group’s properties, even with the Send Report to group owner(s) check box selected.
-
In the Send Notification area, select one of the following options:
- Always - Always send notifications, whether the schedule succeeds or fails to update the groups.
- Only when job succeeds - Send notifications when the schedule successfully updates all the groups. Even when one group fails to be updated, notifications are not sent.
- Only when job fails - Send notifications when the schedule fails to update groups, even when all except one group is not updated.
- Only when membership changes - Send notifications when any changes are made to group membership as a result of the schedule run.
-
Click Save.
NOTE: When a Smart Group Update schedule is bound to a single OU that contains all expired Smart Groups/Dynasties, notifications will not be sent, even if the Always option is selected. Expired Smart Groups and Dynasties are not evaluated for the update process. However, even if one group in the OU is not expired, notifications will be sent for all objects with failed status for expired objects.
-
-
On the Create Schedule page, click Create Schedule.
-
On the Schedules page, click Save.
The schedule is displayed under Smart Group Update. See the View the Schedules in an Identity Store topic for more info.
See Also
Synchronize Schedule
The GroupID scheduling function enables you to set any Synchronize job or job collection to run automatically. Create a Synchronize schedule and add Synchronize jobs and job collections as targets. When the schedule runs, the target jobs and job collections are executed.
What do you want to do?
Create a Synchronize Schedule
-
In Admin Center, click Identity Stores in the left pane.
-
On the Identity Stores page, click the ellipsis button for an identity store and select Edit.
-
Click Schedules under Settings in the left pane.
-
On the Schedules page, click Add Schedule and select Synchronize Job. The Create Schedule page is displayed.
-
In the Schedule Name box, enter a name for the schedule.
-
The Name Preview displays the schedule name prefixed with _SynchronizeJobPortal__; the schedule is displayed with this name in email notifications.
-
In the Scheduler Service Name drop-down list, select a Scheduler service that would be responsible for triggering this schedule. The number of services displayed in the list depend on the number of Elasticsearch clusters in the environment, as each cluster has its own Scheduler service. See the Scheduler Service topic.
-
Add a Synchronize job or a job collection or both to this schedule.
- Click Add Jobs to add a Synchronize job to this schedule. The Select Jobs to Add dialog box displays Synchronize jobs. Select one or more jobs and click Add.
- Click Add Job Collection to add a Synchronize job collection to this schedule. The Select Job Collections to Add dialog box displays job collections from Synchronize. Select one or more job collections from the list and click Add.
The selected job(s) and job collection(s) are listed in the Target(s) area. They will be executed when the schedule runs.
To remove a job or job collection in the **Target(s)**area, click Remove for it.
To remove all target objects, click Remove All. -
Click Add Triggers in the Triggers area to specify a triggering criterion for the schedule, that, when met, starts the execution of the schedule. Follow step 11 in the Create a Group Usage Service Schedule topic to add triggers.
-
Click Add Authentication in the Authentication area to specify an account for running the schedule in the identity store. Follow step 12 in the Create a Group Usage Service Schedule topic for details.
-
On the Create Schedule page, click Create Schedule.
-
On the Schedules page, click Save.
The schedule is displayed under Synchronize. See the View the Schedules in an Identity Store topic for more info.
See Also
Workflow Acceleration Schedule
A Workflow Acceleration schedule facilitates the workflow approver acceleration process for workflow requests. This schedule is auto created when approver acceleration is enabled for the identity store. See the Workflow Approver Acceleration topic.
By default, the schedule runs daily to accelerate workflow requests to approvers, according to workflow acceleration settings for an identity store and some predefined rules for approver acceleration. It also generates notifications to inform approvers about pending workflow requests.
You cannot create or delete a Workflow Acceleration schedule; only update the existing one.
What do you want to do?
Update the Workflow Acceleration Schedule
-
In Admin Center, click Identity Stores in the left pane.
-
On the Identity Stores page, click the ellipsis button for an identity store and select Edit.
-
Click Schedules under Settings in the left pane.
-
On the Schedules page, click the plus sign next to Workflow Acceleration. Then click the ellipsis button for the schedule and select Edit.
-
On the Edit Schedule page, the Schedule Name and Name Preview boxes display the name of the schedule as read-only. The schedule is displayed with the name displayed for Name Preview in email notifications
-
In the Scheduler Service Name drop-down list, select a Scheduler service that would be responsible for triggering this schedule. The number of services displayed in the list depend on the number of Elasticsearch clusters in the environment, as each cluster has its own Scheduler service. See the Scheduler Service topic.
-
The Triggers area displays the default triggering frequency for the schedule.
- To change it, click Edit for it.
- To add a new trigger, click Add Trigger.
Follow step 11 in the Create a Group Usage Service Schedule topic to manage triggers.
-
The Authentication area displays an account for running the schedule in the identity store. To change it, click Add Authentication. Follow step 12 in the Create a Group Usage Service Schedule topic for details.
-
Click Update Schedule.
-
On the Schedules page, click Save.
For general schedule info, see the View the Schedules in an Identity Store topic.
See Also