Database
This section describes how to specify configuration settings for the Database source. You can specify which tables / views / queries will be crawled, or set up table configuration. Also, you can use Write Configuration options to configure tagging.
Configure tagging
Tagging allows you to write classification taxonomy attributes back to the source database.
Each registered taxonomy can be mapped to a property in the database table’s metadata. The program will update a specific column per taxonomy within the source repository with the associated classifications for a record. You can specify how the classifications should be mapped to the table:
- Which table should be updated
- Which column should be updated
- How to filter the table to ensure that at most only one row will be updated (each update statement is verified prior to execution in order to ensure that only one row will be updated).
These settings are configured in the Write Configuration window for the selected entity (table or query).
To configure tagging, do the following:
- In the Sources window, select the required source by clicking on the triple cog icon.
- Select the entity that you wish to configure tagging for (table or query) and click Edit.
- Select Write Configuration on the left.
Configure tagging options listed below:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Table Name | Specify the name of the table to be updated (in most cases this will be the same as the table being crawled). |
| Column Name | Specify the name of the column to be updated (text/varchar column). |
| Update Filter | Update filters are the method used to restrict the update at the target destination. If multiple filters are configured then they all must be true. NOTE: Update Filter shouldbe specified as: Column Name (PrimaryKeyName)=@PrimaryKeyName For example, if a column named ID is the primary key in the table, the Update Filter will be: ID=@ID The specified values will result in a query in the following format: UPDATE TABLENAME SET COLUMNNAME=@Classifications WHERE FILTERS |
Other Database Configuration settings
You can also specify the following settings:
- Source Configuration
- Primary Key Query
- Content Query
- Table Configuration
Source Configuration
The Source Configuration screen allows you to define which tables / views / queries will be crawled. The following options are available:
- Add Source—Add a new SQL database connection
- Edit Connection—Amend the connection details of the currently selected source
- Add Query—Add a custom method for crawling content (custom SELECT statements), Templates are provided for Hummingbird, Worksite and Documentum.
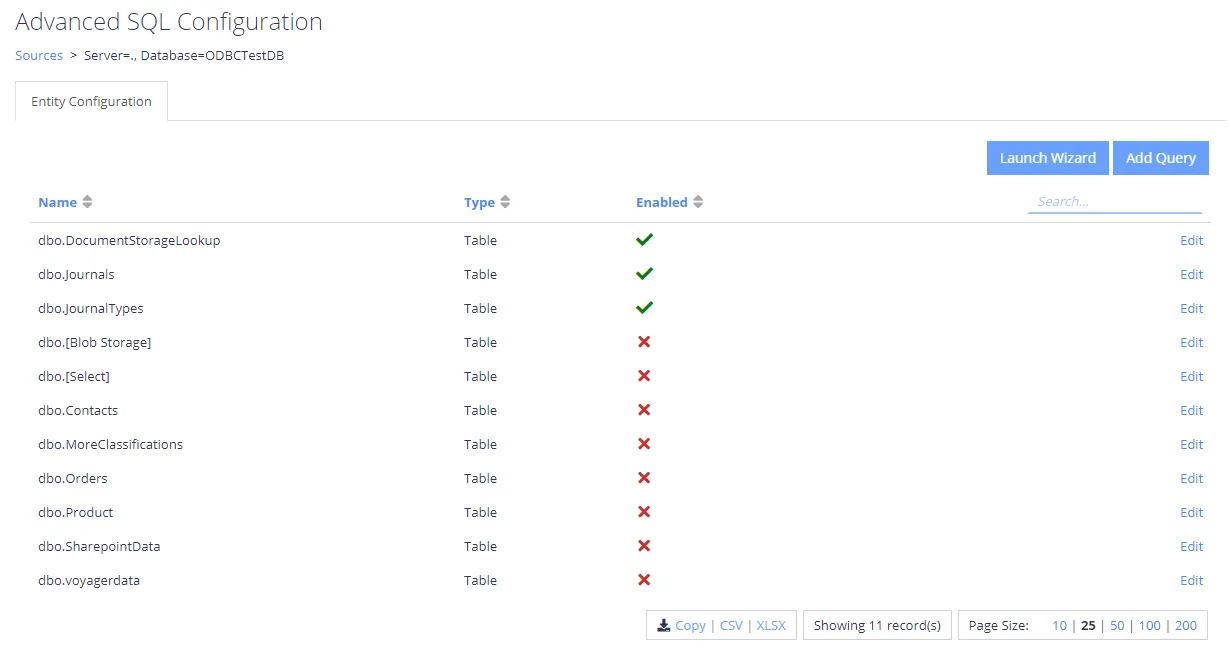
You can access the Source Configuration screen by selecting the multi-cog (Advanced Configuration)
icon from the sources
grid:.
Selecting Edit for one of the tables / queries on the list will redirect you to the entity level configuration, which identifies how content will be mapped into the core index.
Selecting the Add Query option will present a popup allowing you to select a unique name for the query, as well as the queries to be used for crawling:
Primary Key Query
The primary key query should return a set of values that uniquely identify each row to be crawled, in the event that JOINs are used you should JOIN from the largest dataset to the smallest, to ensure that each row is unique.
Example: SELECT PageID FROM Pages
NOTE: Stored procedures are currently not supported.
Content Query
The content query must return all fields to be indexed/classified on, as well as the fields included in the primary key query.
Example: SELECT * FROM Pages
NOTE: Stored procedures are currently not supported
Adding the query will take you to the custom query configuration. Here you can update the primary key query and the content query, all other configuration options are described in the Table Configuration section:
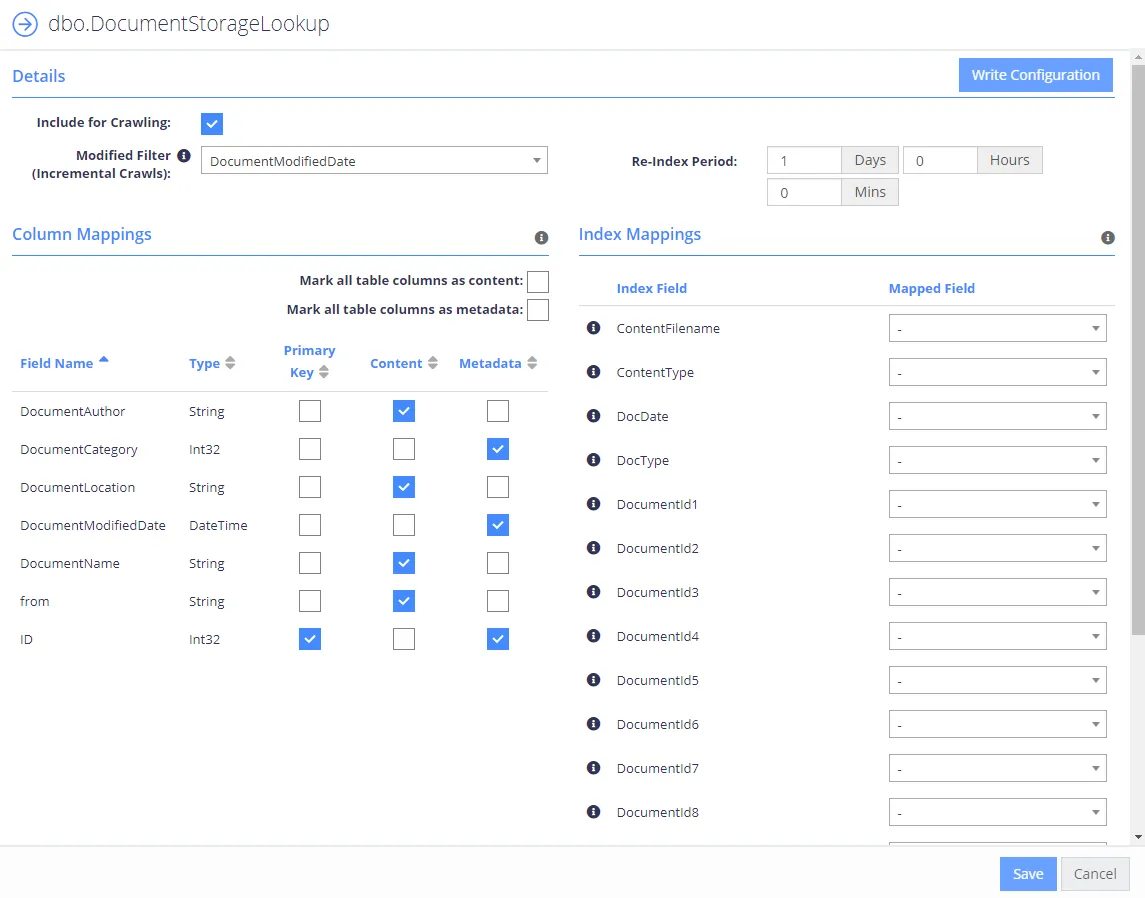
Table Configuration
The table configuration allows you to choose how each specific entity will be crawled:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Include for Crawling | When checked the table/entity will be enabled in the collection schema. |
| Upload Content | When checked the Content fields will be uploaded into the SQL database. Uploaded content can be retrieved after collection by passing the PageId for the record to the QS API call "GetDownload". |
| PK - Primary Key | Please select the fields which uniquely identify the row to be crawled, in the event that multiple rows are returned by the Primary Key, the query will be aborted. Custom queries will not require the primary key to be defined, this will be set automatically from the primary key query. |
| Content | Identifies the fields that will be crawled as searchable text in the core search index. Multiple fields can be mapped to Content, each will be appended with a line break. It is also possible to configure a single binary field type that contains a document, the collection process will load the binary and attempt to convert and extract text from the document. When this functionality is used we recommend setting the ContentFilename or ContentType index mapping to aid the process of text extraction. |
| Metadata | Identifies the fields that will be mapped as metadata values. |
| Index Mappings | Index mappings identifies mappings between the entities fields and the internal core database. Each row also contains an information icon identifying its purpose within the crawling process. |
| Modified Filter (Incremental Crawls) | This should be set to a field that defines when a row has changed (the modified date for the row). When set the collection process will automatically filter the re-indexing process to rows that have a modified date that is larger than the last crawl time. |
| Re-Index Period | This value is the number of days/hours/minutes that will pass between Re-Indexing. The Re-Indexing process involves querying the table(s) to find new and changed records. |