Agentless CIS Windows Server & Desktop Compliance Reports
Removing the requirement for agents to be present on target devices has several advantages when it comes to administration, especially in a Managed Service Environment (MSP) where access to and control of target devices may be limited.
This reduction in administration comes at the cost of reduced functionality and potentially a requirement for higher levels of privileges on the target machine.
The Hub does not communicate directly to target devices, so an agent is still required, but this agent can reside on the same device that the Hub is hosted on. This agent (the master proxy) will remotely communicate with devices and relay the data back to the hub. For this reason, with Netwrix Change Tracker, the term proxied device is preferred to agentless device.
Functionality and Scope
Currently, the only functionality for proxied Windows devices is the execution of the following Center for Internet Security (CIS) compliance reports:
- CIS Microsoft Windows Server 2022, 2019
- CIS Microsoft Windows Desktop 11, 10
These CIS compliance reports perform all their checks via remote registry queries or security settings.
Requirements and Permissions
The credential used run the agent service on the master proxy device and the credential used to connect to the proxied Windows devices require domain admin privileges.
Remote Registry Service
The master proxy and target Windows devices require the remote registry service to be running and have remote administration enabled. This can be enabled on each device or on mass with the use of a Group Policy Object.
NOTE: The remote registry service requires port 445 to be open on the target device.
Proxied Windows Device and CIS Windows Server
These sections demonstrate the creation of a proxied Windows device and the execution of a CIS Windows Server report against it. This requires the existence of a device group named RemoteTest, but the steps to create it are out of scope for this guide.
Windows Logon Credentials
Currently Windows logon credentials are added in SSH/Telnet Credentials section of the Credentials Administration page.
Step 1 – Click the Add Shell Credential (SSH/Telnet/Windows) button to open the credential creation form.
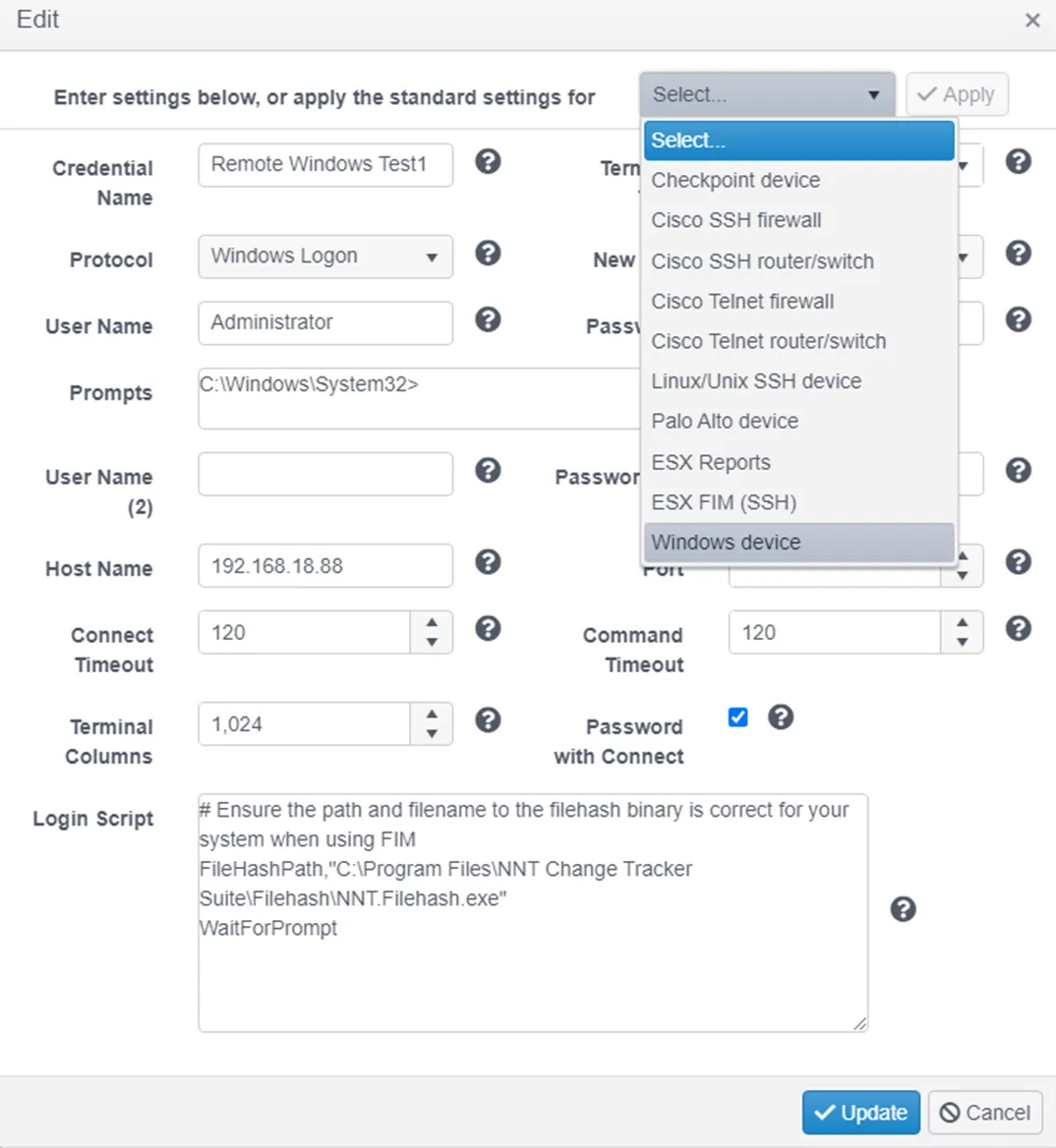
Step 2 – Name the credential. Remote Windows Test1 has been used in this example.
Step 3 – Select Windows device from the top dropdown menu to populate the settings with defaults for proxied devices.
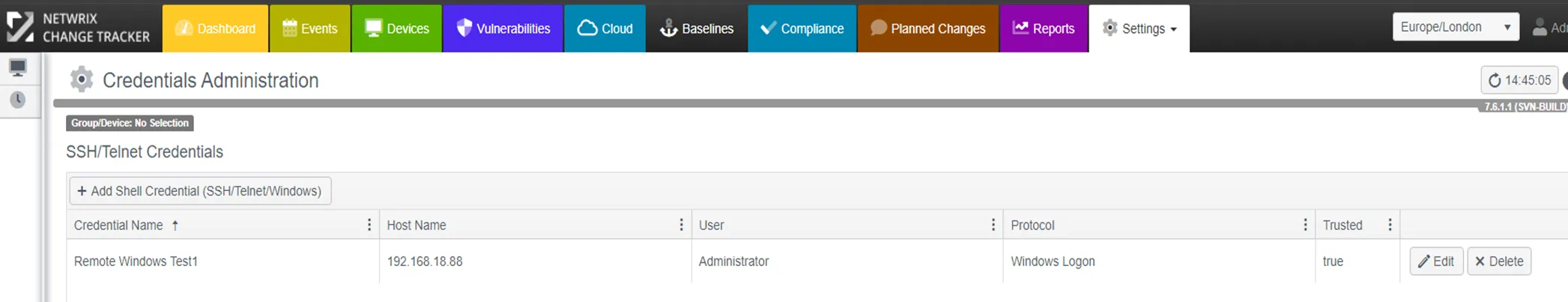
The credential will now be listed in the grid.
Configure the Proxied Windows Device
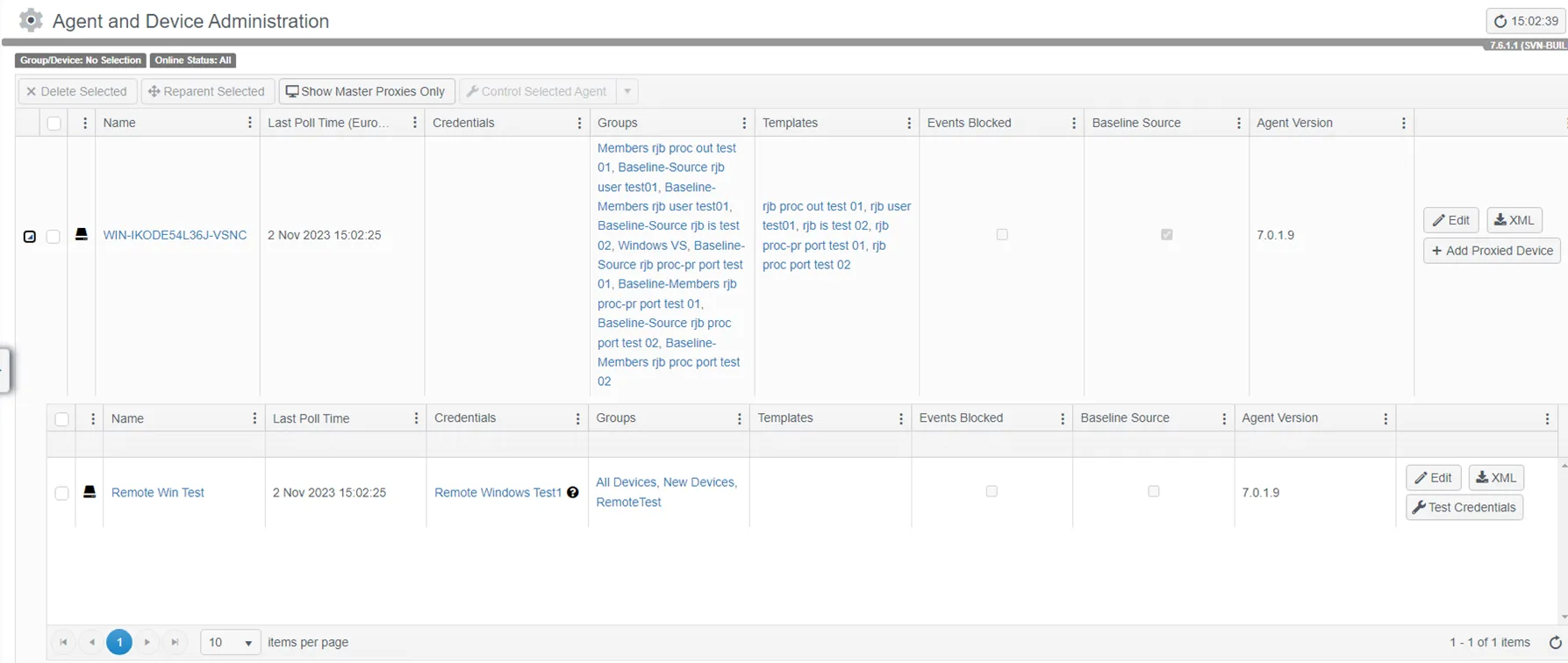
On the Agent and Device Administration page click the “Add Proxied Device” button on the device that will act as the master proxy. The agent on this master proxy device will make the remote calls to the proxied devices.
Step 1 – Name the proxied device.
Step 2 – Enter the host name or IP address of the proxied device.
Step 3 – Select Windows as the device type.
Step 4 – Select the credential created in the previous step.
Step 5 – Add the RemoteTest group to the group list.
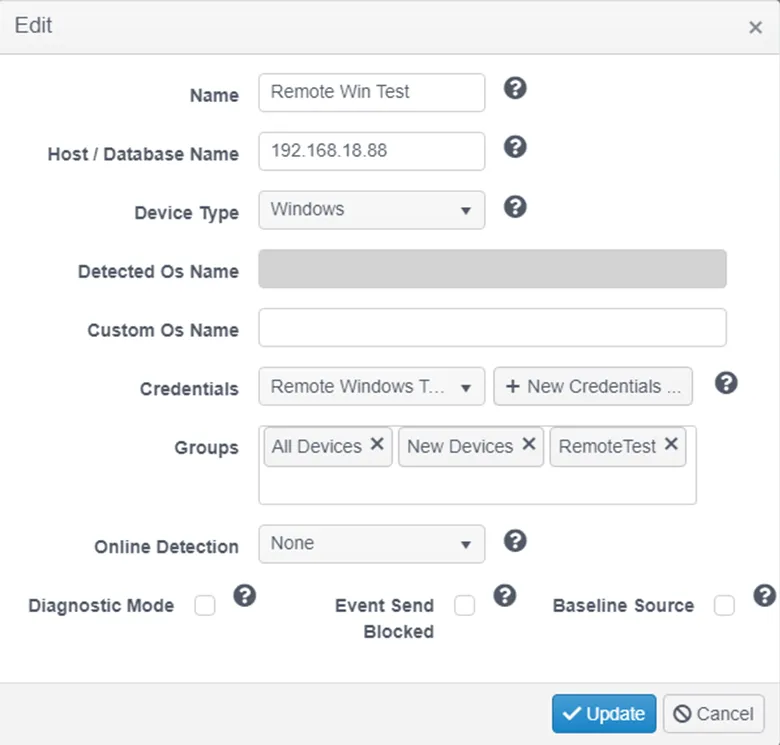
The proxied Windows device will now be present in the detail grid of the master proxy device.
Windows Compliance Reports
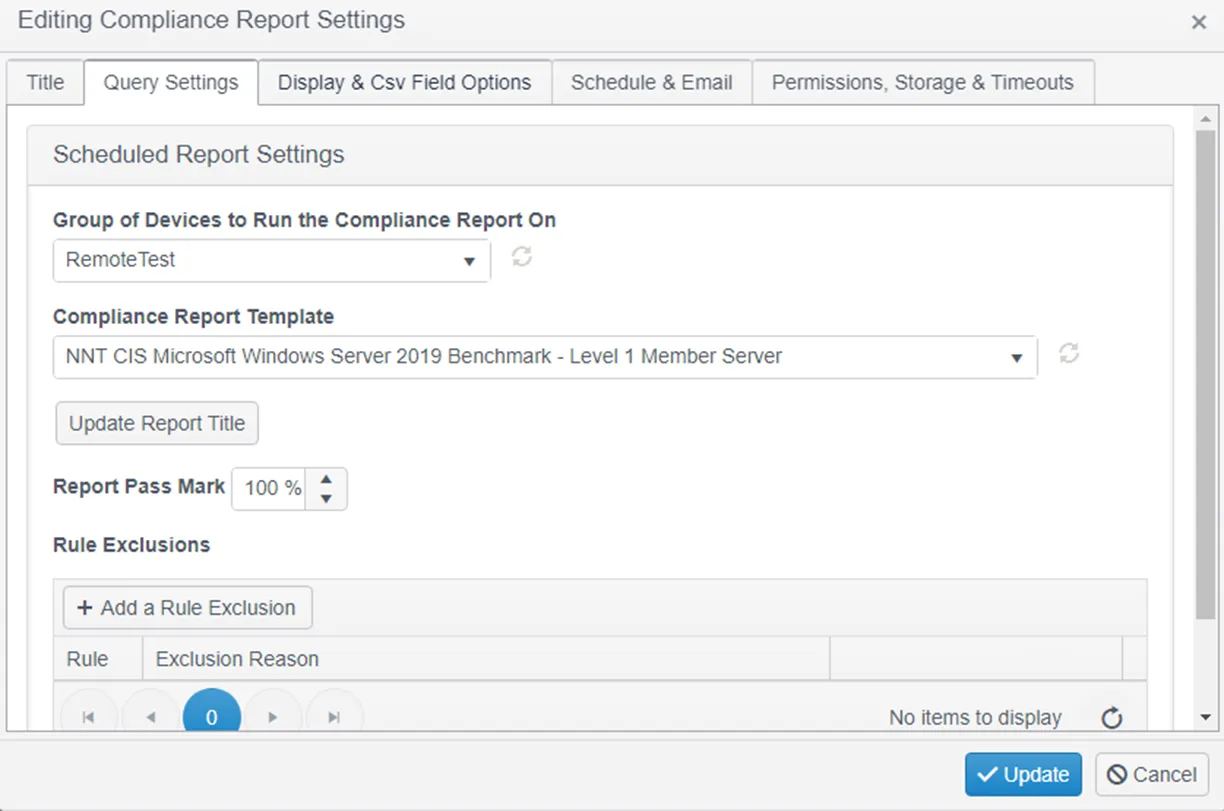
The steps to create or configure a compliance report is out of scope for this guide, but the desired report must be configured to run against the RemoteTest group to ensure the proxied device, created in the previous step, is included in the report.
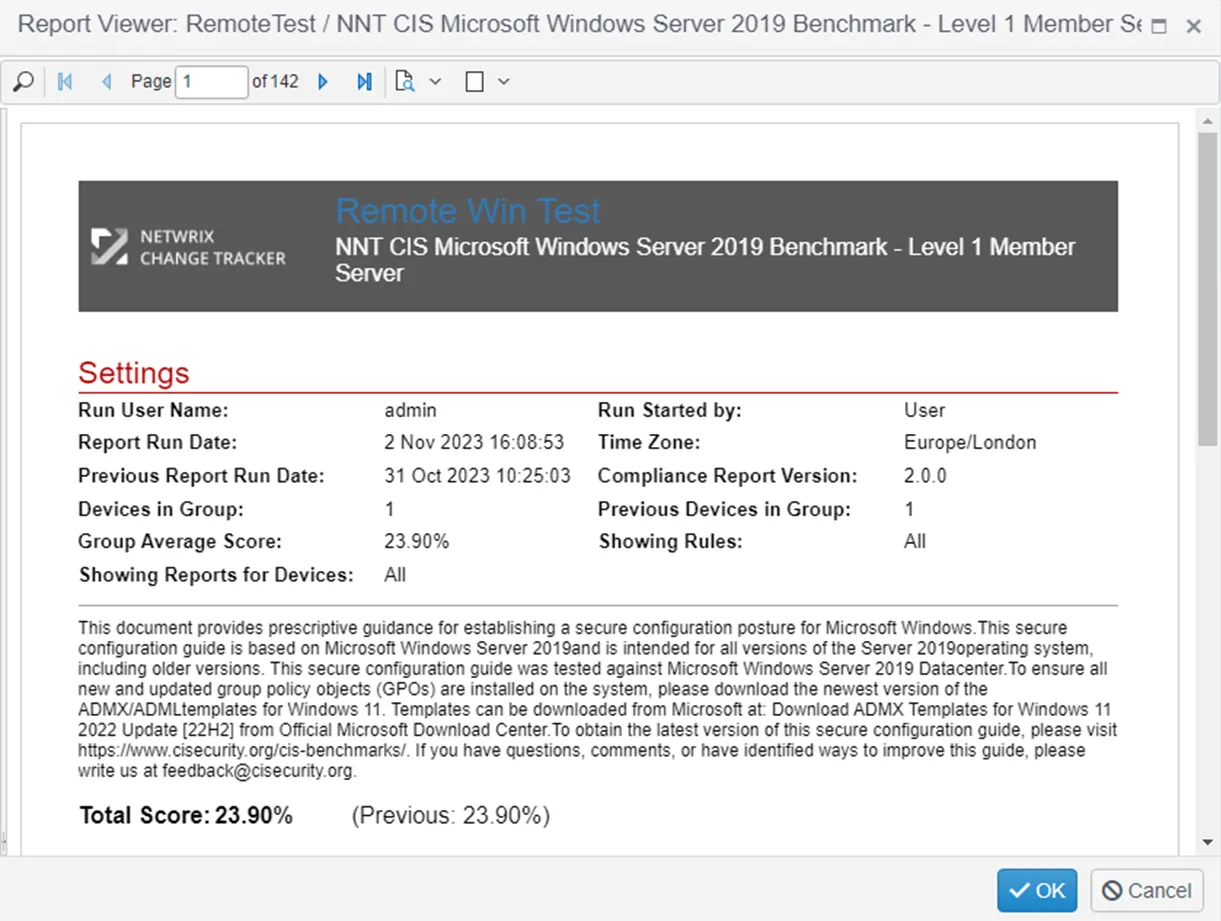
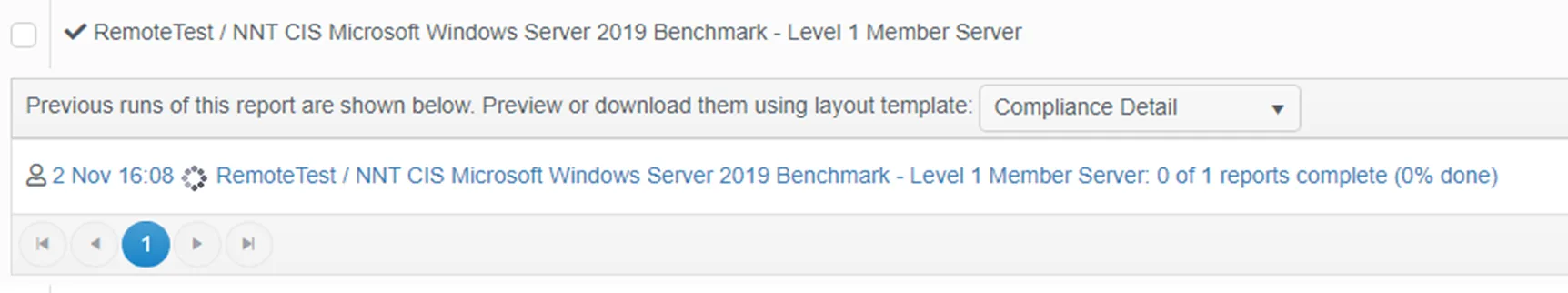
Execute the compliance report in the standard way.
Completed compliance report:
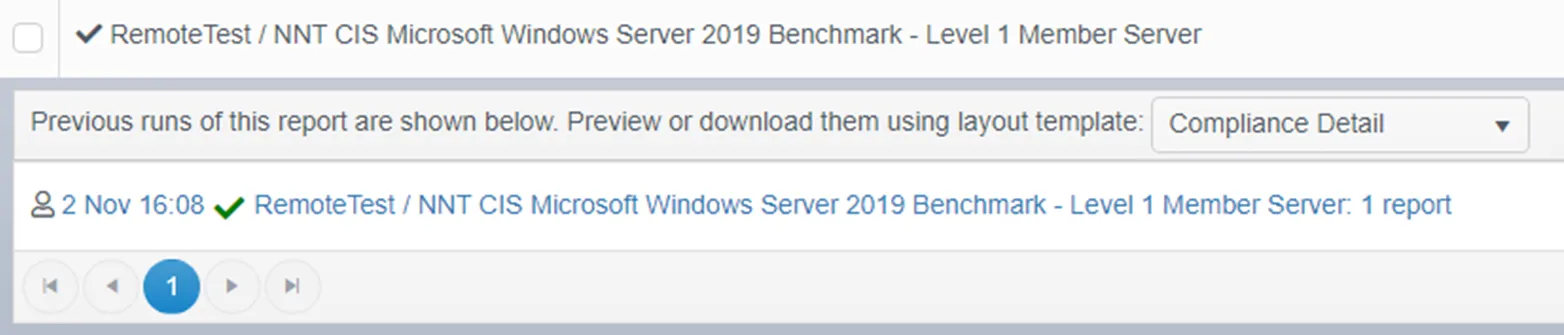
The Windows compliance report will look the just the same as a report executed on Windows devices with agents. The details of the report will contain all passed and failed checks for the proxied Windows device.