Requirements for SQL Server to Store Audit Data
If you plan to generate reports, use alerts and run search queries in Netwrix Auditor, consider that your deployment must include Microsoft SQL Server where audit data will be stored. For report generation, Reporting Services (or Advanced Services) are also required.
Supported SQL Server versions and editions are listed below.
Due to limited database size, Express Edition (with Reporting Services) is recommended only for evaluation, PoC or small environments. For production environment, consider using Standard or Enterprise Edition.
| Version | Edition |
|---|---|
| SQl Server 2022 | - Standard or Enterprise Edition - Express Edition with Reporting Services (for evaluation, PoC and small environments) |
| SQL Server 2019 (on-premises Windows version) cumulative update 10 and above | - Standard or Enterprise Edition - Express Edition with Reporting Services (for evaluation, PoC and small environments) |
| SQL Server 2017 | - Standard or Enterprise Edition - Express Edition with Reporting Services (for evaluation, PoC and small environments) |
| SQL Server 2016 | - Standard or Enterprise Edition - Express Edition with Advanced Services (SP2) (for evaluation, PoC and small environments) |
| SQL Server 2014 | - Standard or Enterprise Edition - Express Edition with Advanced Services (for evaluation, PoC and small environments) |
| SQL Server 2012 | - Standard or Enterprise Edition - Express Edition with Advanced Services (for evaluation, PoC and small environments) |
NOTE: SQL express is only supported for small environments. It might cause performance issues on the medium and large environments.
SQL Server AlwaysOn Availability Group can also be used for hosting Netwrix Auditor audit databases. For that, after specifying audit database settings in Netwrix Auditor, you should manually add created database to a properly configured AlwaysOn Availability Group. These steps must be taken each time a new audit database is created in Netwrix Auditor.
See the Add a database to an Always On availability group with the 'Availability Group Wizard' Microsoft article for details on adding a database to AlwaysOn Availability Group.
You can configure Netwrix Auditor to use an existing SQL Server instance, or deploy a new instance.
If your deployment planning reveals that SQL Server Express Edition will be suitable for your production environment, then you can install, for example, SQL Server 2016 SP2 Express with Advanced Services using the Audit Database Settings wizard or by manually downloading it from Microsoft web site. See the Install Microsoft SQL Server and Reporting Services section for additional information.
SQL Server and Databases
Netwrix Auditor uses SQL Server databases as operational storages that keep audit data for analysis, search and reporting purposes. Supported versions are SQL Server 2012 and later (Reporting Services versions should be 2012 R2 or later).
- You will be prompted to configure the default SQL Server instance when you create the first monitoring plan; also, you can specify it Netwrix Auditor settings.
- You can configure Netwrix Auditor to use an existing instance of SQL Server, or deploy a new instance, as described in the Create a New Monitoring Plan topic.
For evaluation and PoC projects you can deploy Microsoft SQL Server 2016 SP2 Express Edition with Advanced Services (sufficient for report generation).
For production deployment in bigger environments, it is recommended to use Microsoft SQL Server Standard Edition or higher because of the limited database size and other limitations of Express Edition.
Make your choice based on the size of the environment you are going to monitor, the number of users and other factors. This refers, for example, to Netwrix Auditor for Network Devices: if you need to audit successful logons to these devices, consider that large number of activity records will be produced, so plan for SQL Server Standard or Enterprise edition (Express edition will not fit).
Netwrix Auditor supports automated size calculation for all its databases in total, displaying the result, in particular, in the Database Statistics of the Health Status dashboard. This feature, however, is supported only for SQL Server 2012 SP3 and later.
Databases
To store data from the data sources included in the monitoring plan, the Monitoring Plan Wizard
creates an Audit Database. Default database name is Netwrix_Auditor_<monitoring_plan_name>.
It is strongly recommended to target each monitoring plan at a separate database.
Also, several dedicated databases are created automatically on the default SQL Server instance. These databases are intended for storing various data, as listed below.
| Database name | Description |
|---|---|
Netwrix_AlertsDB | Stores alerts. |
Netwrix_Auditor_API | Stores activity records collected using Integration API. |
Netwrix_Auditor_EventLog | Stores internal event records. |
Netwrix_CategoriesDB | Intended for integration with Netwrix Data Classification. This database is always created but is involved in the workflow only if the DDC Provider is enabled. See for more information. |
Netwrix_CommonDB | Stores views to provide cross-database reporting. |
Netwrix_ImportDB | Stores data imported from Long-Term Archive. |
Netwrix_OverviewReportsDB | Stores data required for overview reports. |
Netwrix_Self_Audit | Stores data collected by Netwrix Auditor self-audit (optional, created if the corresponding feature is enabled). |
These databases usually do not appear in the UI; they are only listed in the Database statistics widget of the Health Status dashboard. If you need their settings to be modified via SQL Server Management Studio, please contact your database administrator. For example, you may need to change logging and recovery model (by default, it is set to simple for all these databases, as well as for the Audit databases).
Install Microsoft SQL Server and Reporting Services
Netwrix Auditor uses Microsoft SQL Server database as short-term data storage and utilizes SQL Server Reporting Services engine for report generation. You can either use your existing SQL Server for these purposes, or deploy a new server instance. System requirements for SQL Server are listed in the corresponding section of this guide.
Consider the following:
- Supported versions are 2012 and later.
- NOTE: Please, note that for the Reporting Services, only English operating systems are supported.
- Supported editions are Enterprise, Standard and Express with Advanced Services (it includes Reporting Services).
- If downloading SQL Server Express Edition with Advanced Services from Microsoft site, make sure you download the file whose name contains SQLEXPRADV. Otherwise, Reporting Services will not be deployed, and you will not be able to analyze and report on collected data.
By the way of example, this section provides instructions on how to:
For detailed information on installing other versions/editions, refer to Microsoft website.
Maximum database size provided in SQL Server Express editions may be insufficient for storing data in bigger infrastructures. Thus, when planning for SQL Server, consider maximum database capacity in different editions, considering the size of the audited environment.
SQL Server
When planning for SQL Server that will host Auditor databases, consider the following:
- For PoC, evaluation scenario or small environment SQL Server can run on the same computer where Netwrix Auditor Server will be installed, or on the remote machine accessible by Netwrix Auditor. Remember to check connection settings and access rights.
- In large and extra-large infrastructures SQL Server should be installed on a separate server or cluster. Installation of Netwrix Auditor and SQL Server on the same server is not recommended in such environments.
- If you plan to have Netwrix Auditor and SQL Server running on different machines, establish fast and reliable connection between them (100 Mbps or higher).
- Both standalone servers and SQL Server clusters are supported, as well as AlwaysOn Availability Groups.
- You can configure Netwrix Auditor to use an existing SQL Server instance, or create a new one. As an option, you can install SQL Server 2016 Express Edition, using the Audit Database Settings wizard or manually downloading it from Microsoft web site (see Install Microsoft SQL Server and Reporting Services).
CAUTION: It is not recommended to install Netwrix Auditor databases to a production SQL Server instance. Such instances may have a lot of maintenance plans or scripts running that may affect data uploaded by the product. The product databases are designed for reporting and searching and do not require maintenance or backup. For the long-term data storage, Netwrix Auditor uses Long-Term Archive. See File-Based Repository for Long-Term Archive for additional information.
If you select to set up a new SQL Server instance, the current user account (this should be a member of local Administrators group) will be assigned the sysadmin server role for it.
You will also need to provide a path for storing the SQL Server databases - it is recommended to specify the data drive for that purpose (by default, system drive is used).
-
If you plan to have more than one Netwrix Auditor Servers in your network, make sure to configure them to use different SQL Server instances. The same SQL Server instance cannot be used to store audit data collected by several Netwrix Auditor Servers.
-
Consider that sufficient access rights will be required for the account that will write data to the audit databases hosted on the default SQL Server. This account should be assigned the following roles:
- Database owner (db_owner) database-level role
- dbcreator server-level role
This account can be specified when you configure the Audit Database settings.
Database Sizing
For database sizing, it is recommended to estimate:
- Size of the environment you are going to monitor
- Amount of activity records produced by the audited system
- Retention policy for the audit databases
- Maximum database size supported by different SQL Server versions
To estimate the number of the activity records produced by your data sources, collected and saved by Auditor during the week, you can use the Activity records by date widget of the Health Status dashboard. See the Activity Records Statistics topic for additional information.
Auditor supports automated size calculation for all its databases in total, displaying the result, in particular, in the Database Statistics widget of the Health Status dashboard. To estimate current capacity and daily growth for each database, you can click View details and examine information in the table. See the Database Statistics topic for additional information.
This feature is supported only for SQL Server 2012 SP3 and later.
Remember that database size in SQL Server Express editions may be insufficient. For example, Microsoft SQL Server 2012 SP3 Express Edition has the following limitations which may affect performance:
- Each instance uses only up to 1 GB of RAM
- Each instance uses only up to 4 cores of the first CPU
- Database size cannot exceed 10 GB
Database Settings
Settings of the certain Audit database, including hosting SQL Server, can be specified when you create a monitoring plan and configure data collection for an audited system. Consider the following:
- To store data from the data sources included in the monitoring plan, you can configure the Audit database on the default SQL Server (recommended), or select another server.
- By default, database name will be
Netwrix_Auditor_<monitoring_plan_name>; you can name the database as you need, for example,Active_Directory_Audit_Data.
To avoid syntax errors, for instance, in the PowerShell cmdlets, it is recommended to use the
underscore character (_) instead of space character in the database names.
If not yet existing on the specified SQL server instance, the database will be created there. For this operation to succeed, ensure that Netwrix Auditor service account has sufficient rights on that SQL Server.
Settings of other Auditor databases cannot be modified.
Example
As a database administrator, you can have SQL Server cluster of 2 servers, and 2 Oracle servers. If so, you can create 2 monitoring plans:
- First monitoring plan for collecting data from SQL Servers, targeted at
Netwrix_Auditor_SQL_Monitoringdatabase. - Second monitoring plan for collecting data from Oracle servers, targeted at
Netwrix_Auditor_Oracle_Monitoringdatabase.
Database Retention
Consider that retention is a global setting, that is, it applies to all Audit databases you configure for your monitoring plans.
Follow the steps to change database retention after the product deployment.
Step 1 – In the Auditor main screen, select Settings > Audit Database.
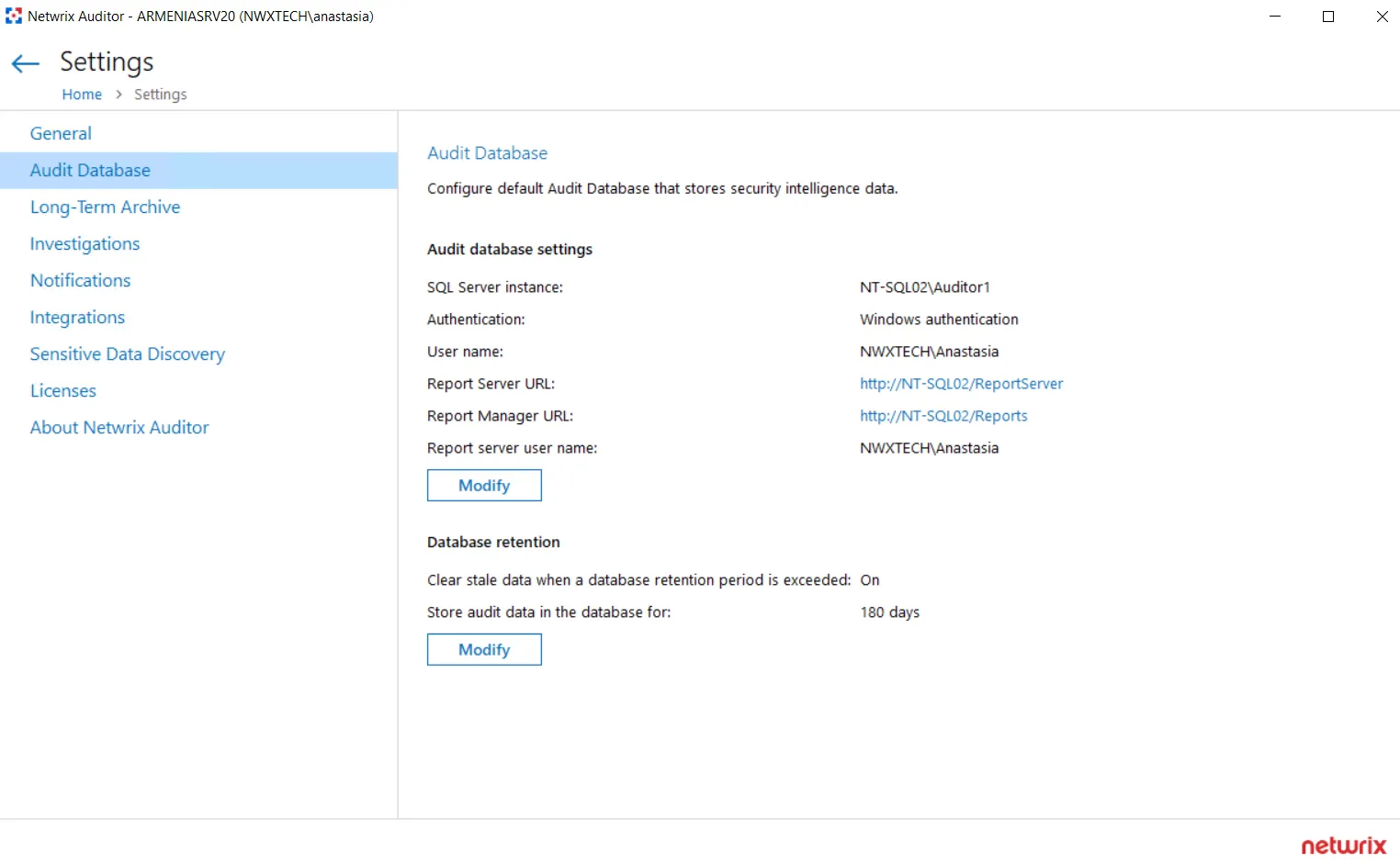
Step 2 – In the dialog displayed, make sure the Clear stale data when a database retention period is exceeded: is set to ON, then click Modify to specify the required retention period (in days).
This setting also applies to the Netwrix_Auditor_API database.
Configure Audit Database Account
This is the account that Auditor uses to write the collected audit data to the audit databases. Starting with version 9.96, you can use Group Managed Service Account (gMSA) for that purpose.
Remember, gMSA cannot be used to access SSRS. Use a standard account for that. See the SQL Server Reporting Services topic for additional information.
This account must be granted the Database owner (db_owner) role and the dbcreator server
role on the SQL Server instance hosting your audit databases.
Follow the steps to assign the dbcreator and db_owner roles.
Step 3 – On the computer where SQL Server instance with the Audit Database resides, navigate to Start > All Programs > Microsoft SQL Server > SQL Server Management Studio.
Step 4 – Connect to the server.
Step 5 – In the left pane, expand the Security node. Right-click the Logins node and select New Login from the pop-up menu.
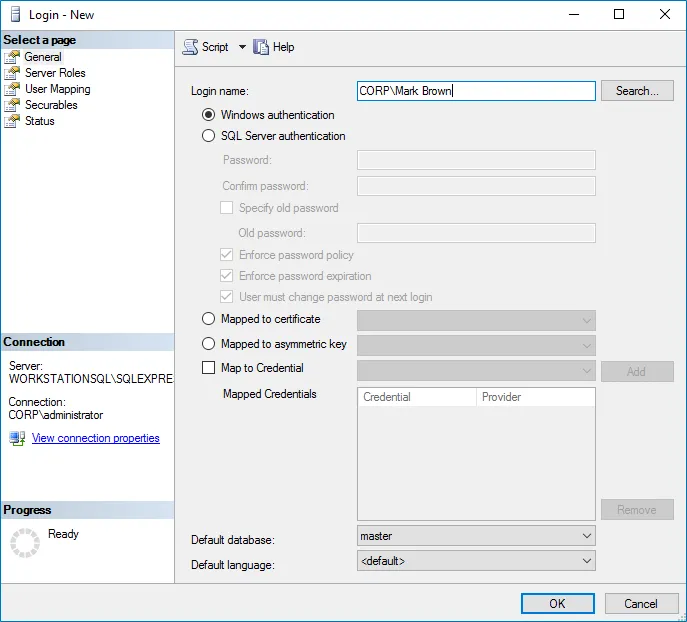
Step 6 – Click Search next to Login Name and specify the user that you want to assign
the db_owner role to.
Step 7 – Select Server roles on the left and assign the dbcreator role to the new login.
Step 8 – Select the User Mapping tab. Select all databases used by Auditor to store audit
data in the upper pane and check db_owner in the lower pane.
NOTE: This step is only required when changing the existing Audit Database Account to a new one.
Step 9 – If the account that you want to assign the db_owner role to has been already
added to SQL Server Logins, expand the Security > Logins node, right-click the account,
select Properties from the pop-up menu, and edit its roles.
If you need to migrate the Audit Database, see the How to Migrate Netwrix Auditor Databases to Another SQL Server Instance knowledge base article.
SQL Server Reporting Services
Netwrix Auditor utilizes SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) engine for report generation.
If you want to generate reports and run search queries against data collected by Netwrix Auditor, you should configure SQL Server Reporting Services (2012 R2 and above required).
Consider the following:
- SQL Server and SQL Server Reporting Services can be deployed on the separate machines only in commercial edition. SQL Server Express Edition with Advanced Services does not support such deployment scenario.
NOTE: It is recommended to use HTTPS instead of HTTP. HTTPS connection should also be configured for Reporting Service.
If you plan, however, not to use Netwrix Auditor built-in intelligence (search, alerts or reports) but only to receive e-mail notifications on audit data collection results, you may not need to configure SSRS or audit database settings.
Configure SSRS Account
An account used to upload data to the SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) Server must be granted the Content Manager role on the SSRS Home folder.
NOTE: gMSA cannot be used to access SSRS. Use a standard account for that purpose.
Follow the steps to assign the Content Manager role.
Step 1 – Navigate to your Report Manager URL.
Step 2 – On the Home page, navigate to Folder Settings and click New Role Assignment (the path can slightly vary depending on your SQL Server version).
Step 3 – Specify an account in the following format: domain\user. The account must belong to the same domain where Netwrix Auditor is installed, or to a trusted domain.
Step 4 – Select Content Manager.
Grant Additional Permissions on Report Server
To be able to generate a report, any user assigned the Global administrator, Global reviewer, or Reviewer role must be granted the Browser role on the Report Server. Netwrix Auditor grants this role automatically when adding a user. If for some reason the product was unable to grant the role, do it manually.
Follow the steps to assign the Browser role to a user.
Step 1 – Open the Report Manager URL in your web browser.
Step 2 – Depending on the user's delegated scope, select the entire Home folder or drill-down to specific data sources or event reports.
Step 3 – Navigate to Manage Folder (the path can slightly vary depending on your SQL Server version) and select Add group or user.
Step 4 – Specify an account in the following format: domain\user. The account must belong to the same domain where Netwrix Auditor Server is installed, or to a trusted domain.
Step 5 – Select Browser.
As a rule, Auditor can use Reporting Services with the default settings. However, to ensure that Reporting Services is properly configured, perform the following procedure:
You must be logged in as a member of the local Administrators group on the computer where SQL Server 2016 Express is installed.
Follow the steps to verify Reporting Services installation.
Step 6 – Navigate to Start >__All Apps > SQL Server__Reporting Services Configuration Manager.
Step 7 – In the Reporting Services Configuration Connection dialog, make sure that your local report server instance (for example, SQLExpress) is selected, and click Connect.
Step 8 – In the Reporting Services Configuration Manager left pane, select Web Service URL. Make sure that:
- Virtual Directory is set to ReportServer
<YourSqlServerInstanceName>_ (e.g., _ReportServer_SQLEXPRESS_ for SQLEXPRESS instance) - TCP Port is set to 80
Step 9 – In the Reporting Services Configuration Manager left pane, select Database. Make sure that the SQL Server Name and Database Name fields contain correct values. If necessary, click Change Database and complete the Report Server Database Configuration wizard.
Step 10 – In the Reporting Services Configuration Manager left pane, select Report Manager URL. Make sure Virtual Directory is set correctly, and that the URL is valid.