Audit Database
If you want to generate reports and run interactive search queries, you should configure Auditor to store collected data to the SQL Server database (Audit Database). By default, each monitoring plan will use a dedicated database to store data. So, there are two types of database settings:
-
Global settings that apply to all Audit Databases:
- Default SQL Server instance hosting all databases
- SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) settings
- Retention settings
Usually, initial global settings are configured when you create a first monitoring plan. They become the defaults and appear on the Settings > Audit Database tab. If you have not specified the default settings before, click Configure.
-
Specific settings for each dedicated database. You can configure specific database storage settings for each monitoring plan individually. For that, use the Monitoring Plan wizard or navigate to the settings. (Global settings appear as default values there, and you can modify them if needed.) See the Fine-Tune Your Plan and Edit Settings topic for additional information.
Follow the steps to review and update global Audit Database settings:
Step 1 – Navigate to Settings > Audit Database.
Step 2 – Click Modify to edit the settings.
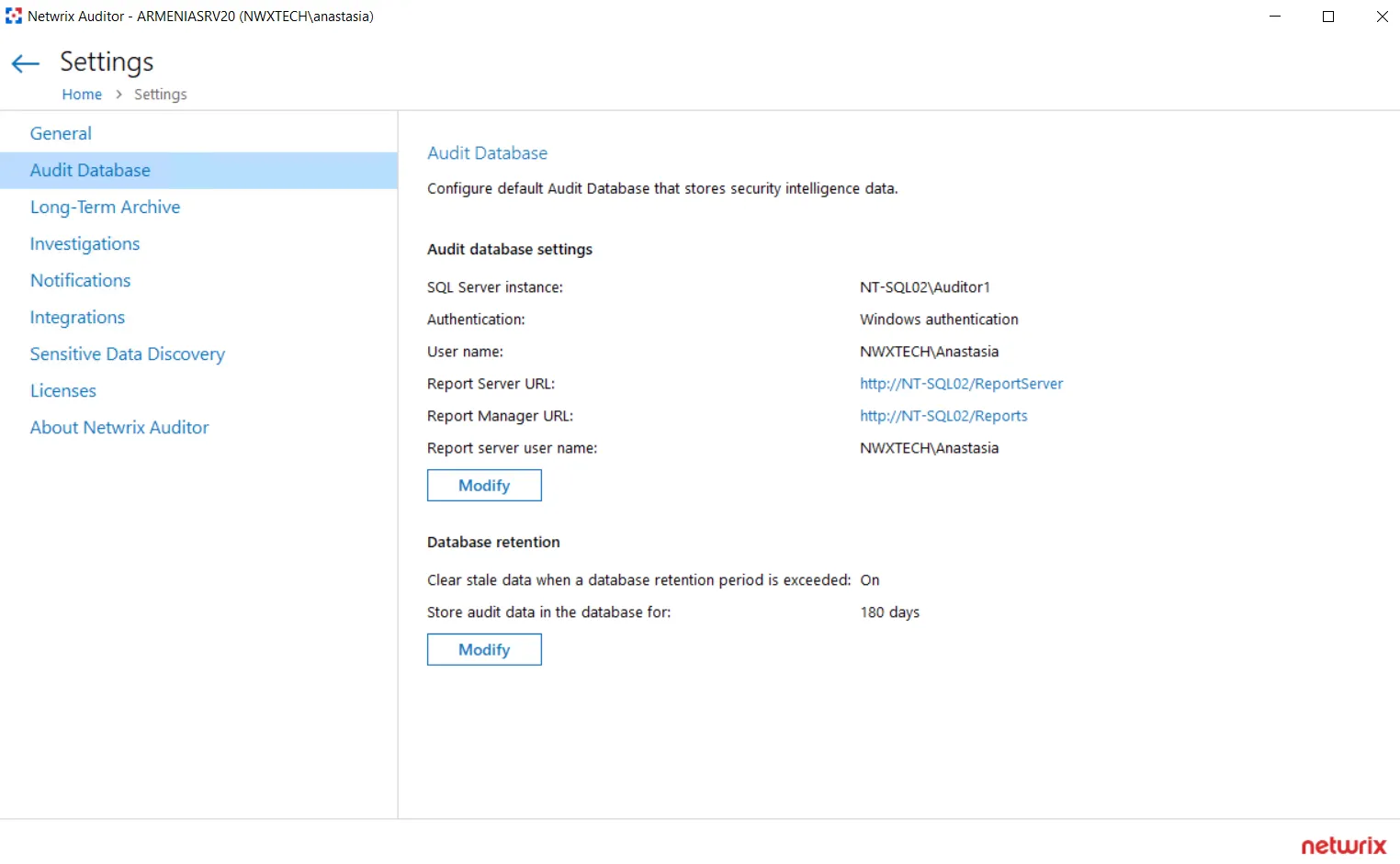
Step 3 – Specify the following database storage settings:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Default SQL Server settings | Specify SQL Server instance name and connection settings. |
| Database retention | Configure retention if you want audit data to be deleted automatically from your Audit Database after a certain period of time. These settings cannot be modified for a certain plan. |
| SQL Server Reporting Services settings | Define the Report Server URL and account used to upload data to Report Server. These settings cannot be modified for a certain plan. |
Configure Default SQL Server Settings
On the Settings > Audit Database tab, review settings and click Modify under the Default SQL Server settings section.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| SQL Server instance | Specify the name of the SQL Server instance to store audit data. If you have more than one Auditor Server running in your network, make sure to configure them to use different SQL Server instances. The same SQL Server instance cannot be used to store audit data collected by several Auditor Servers. |
| Authentication | Select the authentication type you want to use to connect to the SQL Server instance: - Windows authentication - SQL Server authentication |
| User name | Specify the account to be used to connect to the SQL Server instance. This account must be granted the database owner (db_owner) role and the dbcreator server role. |
| Password | Enter a password. |
NOTE: If you want to use Group Managed Service Account (gMSA) to access the SQL Server instance hosting the database, consider that in this case Netwrix Auditor will not be able to generate SSRS-based reports (due to the following Microsoft article: Configure the Unattended Execution Account (Report Server Configuration Manager).
Configure Database Retention
On the Settings > Audit Database tab, review settings and click Modify under the Database retention section.
These settings are global, that is, they will be applied to all audit databases.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Clear stale data when a database retention period is exceeded | Use this option if you want audit data to be deleted automatically from the corresponding database after a certain period of time. |
| Store audit data in database for | Specify the retention period for storing audit data in the database. Default retention period is 180 days. When the retention period is over, data will be deleted automatically. |
Configure SSRS Settings
On the Settings > Audit Database tab, review settings and click Modify under the SQL Server Reporting Services settings section.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Report Server URL | Specify the Report Server URL. Make sure that the resource is reachable. |
| Report Manager URL | Specify the Report Manager URL. Make sure that the resource is reachable. |
| User name | Specify the account to connect to SSRS. Use the following format: domain\username or hostname\username Workgroup format (.\username) is not supported. Use hostname\username instead. Make sure this account is granted the Content Manager role on the Report Server. See the SQL Server Reporting Services topic for additional information. |
| Password | Enter a password. |